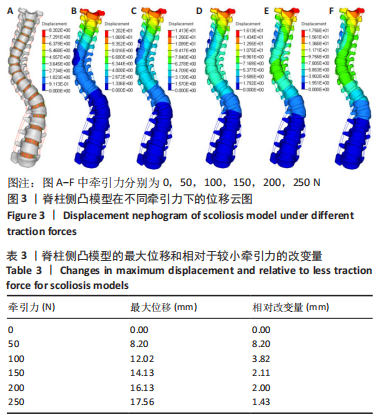
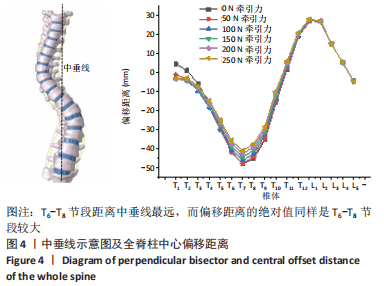
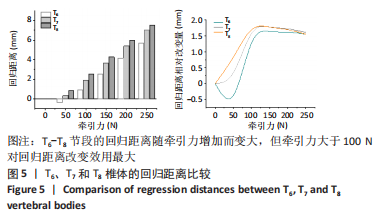
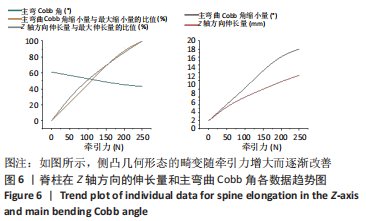
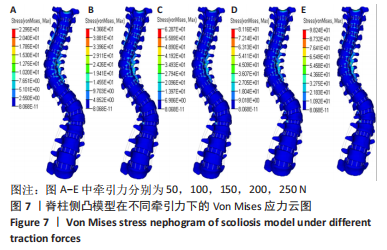
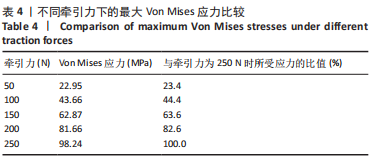
[1] 刘小丹. 脊柱的简化模型及其在侧弯矫正中的应用[D].上海:上海交通大学,2009.
[2] QIAO J, XIAO L, XU L, et al. Skull-femoral traction after posterior release for correction of adult severe scoliosis: efficacy and complications. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):277.
[3] MEHRPOUR S, SORBI R, REZAEI R, et al. Posterior-only surgery with preoperative skeletal traction for management of severe scoliosis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(4):457-463.
[4] NEAL KM, SIEGALL E. Strategies for Surgical Management of Large, Stiff Spinal Deformities in Children. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25(4):e70-e78.
[5] O’DONNELL J, GARCIA S, ALI S, et al. Indications and Efficacy of Halo-Gravity Traction in Pediatric Spinal Deformity: A Critical Analysis Review. JBJS Rev. 2023; 11(3). doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.22.00204.
[6] REED LA, MIHAS A, BUTLER R, et al. Halo Gravity Traction for the Correction of Spinal Deformities in the Pediatric Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2022;164:e636-e648.
[7] 吴春云.Halo重力牵引联合康复干预对Ⅰ型神经纤维瘤病伴重度脊柱侧凸患者肺功能的影响[J].中国医刊,2020,55(11):1192-1195.
[8] 程俊杰,马原,田慧中.一期头盆环牵引二期后路截骨矫正重度脊柱后凸侧后凸的临床效果评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(10):949-951.
[9] MEFTAH K, SEDIRA L, AYADI A. A six-node prismatic solid finite element for geometric nonlinear problems in elasticity. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation. 2021;182;143-164.
[10] ZHAO X, FAN W, WANG ZH, et al. An explicit finite element approach for simulations of transient meshing contact of gear pairs and the resulting wear. Wear. 2023;523:204802.
[11] WANG HZ, YANG P, XIE Q, et al. Crystal plasticity finite element study on the formation of Goss-oriented deformation inhomogeneous regions in electrical steels. Int J Mater Form. 2023. doi: 10.1007/s12289-023-01754-3
[12] NGUYEN AD, NGUYEN VT, KIM YS. Finite element analysis on dynamic behavior of sheet pile quay wall dredged and improved seaside subsoil using cement deep mixing. Int J Geo Eng. 2023;14(1):185.
[13] 周晨,邢文华.3D打印技术与有限元分析在脊柱侧凸矫形中的应用优势[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(12):1898-1903.
[14] 赵龙,王剑,韩正才,等.椎体成形术后残余后凸畸形的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(22):2082-2086.
[15] 邓健全,陈进军,梁洪生,等.仿真分析不同步态下腰椎受力的生物力学变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(28):4541-4545.
[16] 颜文涛,赵改平,方新果,等.人体腰椎L_(4~5)节段有限元建模及分析[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2014,31(3):612-618.
[17] TOTORIBE K, CHOSA E, TAJIMA N. A biomechanical study of lumbar fusion based on a three-dimensional nonlinear finite element method. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004;17(2):147-153.
[18] GUAN T, ZHANG Y, ANWAR A, et al. Determination of Three-Dimensional Corrective Force in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis and Biomechanical Finite Element Analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:963.
[19] CAO F, FU R, WANG W. Comparison of biomechanical performance of single-level triangular and quadrilateral profile anterior cervical plates. PLoS One. 2021; 16(4):e0250270.
[20] 欧华.重度僵硬脊柱侧弯三维有限元模型的建立及PVCR术生物力学分析[D].昆明: 昆明医科大学,2018.
[21] 昌怀,刘志军,晏峻峰,等.Lenke 1AN型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸不同置棒顺序矫形的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(19):1780-1784.
[22] 朱海明,丁亮,张东,等.胸腰椎爆裂性骨折短节段伤椎固定三维有限元模型构建及生物力学比较研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(10):917-920.
[23] 辛大奇,胡侦明,汉迪,等.Lenke3型成人特发性脊柱侧凸有限元模型的参数修正及有效性验证[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(31):4975-4982.
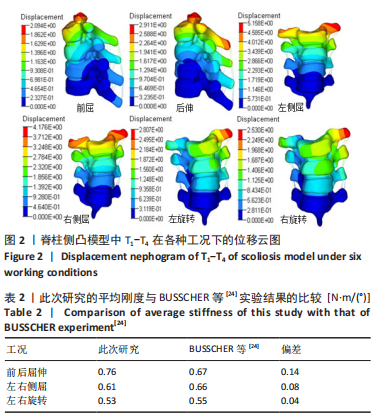
[24] BUSSCHER I, VAN DIEËN JH, KINGMA I, et al. Biomechanical characteristics of different regions of the human spine: an in vitro study on multilevel spinal segments. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(26):2858-2864.
[25] HWANG CJ, KIM DG, LEE CS, et al. Preoperative Halo Traction for Severe Scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(18):E1158-E1165.
[26] 温建清,列平,黄春明,等.头盆环牵引治疗重度僵硬性脊柱侧凸病人的护理[J].护理学杂志,2004,19(20):17-18.
[27] MARKETOS SG, SKIADAS P. Hippocrates. The father of spine surgery. Spine. 1999;24(13):1381-1387.
[28] XU E, GAO R, JIANG H, et al. Combined Halo Gravity Traction and Dual Growing Rod Technique for the Treatment of Early Onset Dystrophic Scoliosis in Neurofibromatosis Type 1. World Neurosurg. 2019:e173-e180.
[29] 王东贵,张承旻,张强,等.新型Halo-重力牵引装置的设计及其初步临床应用[J].局解手术学杂志,2019,28(10):829-833.
[30] KARIMI MT, EBRAHIMI MH, MOHAMMADI A, et al. Evaluation of the influences of various force magnitudes and configurations on scoliotic curve correction using finite element analysis. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2017;40(1):231-236.
[31] PASHA S, AUBIN CE, LABELLE H, et al. The biomechanical effects of spinal fusion on the sacral loading in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2015;30(9):981-987. |