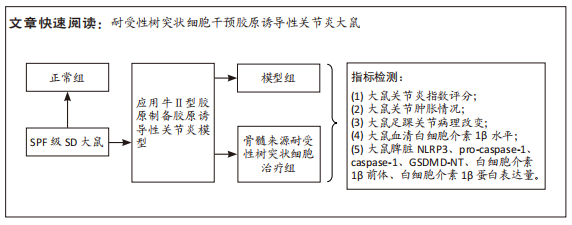
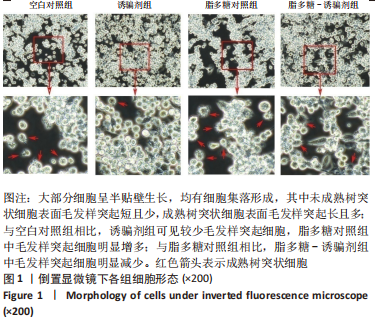
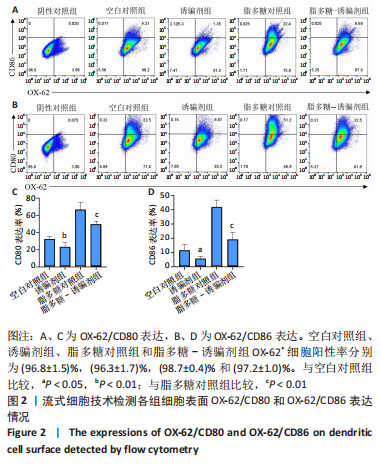
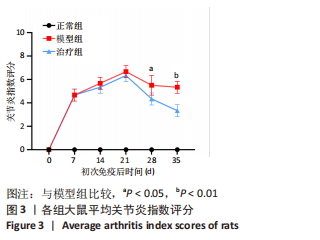
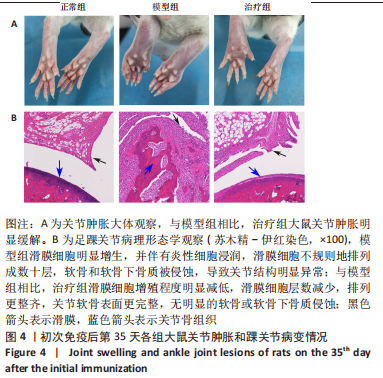
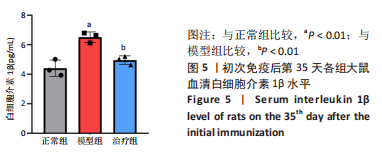
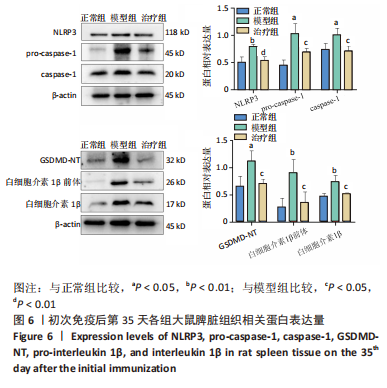
[1] ZHAI Z, YANG F, XU W, et al. Attenuation of rheumatoid arthritis through the inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-induced caspase 3/gasdermin e-mediated pyroptosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022;74(3):427-440.
[2] OTON T, CARMONA L. The epidemiology of established rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2019;33(5):101477.
[3] WANG W, ZHOU H, LIU L. Side effects of methotrexate therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. Eur J Med Chem. 2018;158:502-516.
[4] MOSANYA CH, ISAACS JD. Tolerising cellular therapies: What is their promise for autoimmune disease? Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(3):297-310.
[5] JOHNSON DJ, OHASHI PS. Molecular programming of steady-state dendritic cells: Impact on autoimmunity and tumor immune surveillance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013;1284:46-51.
[6] ORNING P, LIEN E, FITZGERALD KA. Gasdermins and their role in immunity and inflammation. J Exp Med. 2019;216(11):2453-2465.
[7] CHOULAKI C, PAPADAKI G, REPA A, et al. Enhanced activity of NLRP3 inflammasome in peripheral blood cells of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:257.
[8] XIA S, ZHANG Z, MAGUPALLI VG, et al. Gasdermin D pore structure reveals preferential release of mature interleukin-1. Nature. 2021;593(7860):607-611.
[9] DING J, WANG K, LIU W, et al. Pore-forming activity and structural autoinhibition of the gasdermin family. Nature. 2016;535(7610):111-116.
[10] FINK SL, COOKSON BT. Caspase-1-dependent pore formation during pyroptosis leads to osmotic lysis of infected host macrophages. Cell Microbiol. 2006;8(11): 1812-1825.
[11] XU L, WANG H, YU QQ, et al. The monomer derivative of paeoniflorin inhibits macrophage pyroptosis via regulating TLR4/ NLRP3/ GSDMD signaling pathway in adjuvant arthritis rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;101(Pt A):108169.
[12] TIAN Y, SHI P, ZHOU Y, et al. Dir-labeled tolerogenic dendritic cells for targeted imaging in collagen- induced arthritis rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;91: 107273.
[13] 马贵兰,谭艳,田娅玲,等.耐受性树突状细胞通过降低Th1细胞和Th17细胞比例减轻CIA大鼠的关节炎症和病变[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2021, 37(3):193-198.
[14] 谭艳,田娅玲,宁丽常,等.胶原蛋白诱导性关节炎(CIA)大鼠耐受性树突状细胞制备技术的优化[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2019,35(12):1076-1081.
[15] SPARKS JA. Rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170(1):ITC1-ITC16.
[16] LIN YJ, ANZAGHE M, SCHULKE S. Update on the pathomechanism, diagnosis, and treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis. Cells. 2020;9(4):880.
[17] CHAICHIAN Y, GENOVESE MC, WEISMAN MH. The road to rheumatoid arthritis prevention: Challenges and opportunities. Clin Rheumatol. 2020;39(5):1379-1381.
[18] PUT S, WESTHOVENS R, LAHOUTTE T, et al. Molecular imaging of rheumatoidarthritis: emerging markers, tools, and techniques. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):208.
[19] RODRÍGUEZ-FERNÁNDEZ JL. Antigen presentation by dendritic cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Top Med Chem. 2013;13(6):712-719.
[20] MATSUE H, YANG C, MATSUE K, et al. Contrasting impacts of immunosuppressive agents (rapamycin, FK506, cyclosporin A, and dexamethasone) on bidirectional dendritic cell-T cell interaction during antigen presentation. J Immunol. 2002; 169(7):3555-3564.
[21] HUBO M, TRINSCHEK B, KRYCZANOWSKY F, et al. Costimulatory molecules on immunogenic versus tolerogenic human dendritic cells. Front Immunol. 2013; 4:82.
[22] FLÓREZ-GRAU G, ZUBIZARRETA I, CABEZÓN R, et al. Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells as a Promising Antigen-Specific Therapy in the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica From Preclinical to Clinical Trials. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1169.
[23] SONG HY, KIM WS, HAN JM, et al. Galangin treatment during dendritic cell differentiation confers tolerogenic properties in response to lipopolysaccharide stimulation. J Nutr Biochem. 2021;87:108524.
[24] ONAITIS M, KALADY MF, PRUITT S, et al. Dendritic cell gene therapy. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2002;11:645-660.
[25] LI X, HAN Y, ZHOU Q, et al. Apigenin, a potent suppressor of dendritic cell maturation and migration, protects against collagen-induced arthritis. J Cell Mol Med. 2016;20(1):170-180.
[26] MIYOSHI M, LIU S. Collagen-induced arthritis models. Methods Mol Biol. 2018; 1868:3-7.
[27] BURDETTE BE, ESPARZA AN, ZHU H, et al. Gasdermin D in pyroptosis. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11(9):2768-2782.
[28] LI Z, GUO J, BI L. Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in autoimmune diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;130:110542.
[29] TENSHIN H, TERAMACHI J, ASHTAR M, et al. TGF-β-activated kinase-1 inhibitor IL-z1640-2 reduces joint inflammation and bone destruction in mouse models of rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome, TACE, TNF-α and RANKL expression. Clin Transl Immunology. 2022;11(1):e1371.
[30] KONG R, SUN L, LI H, et al. The role of NLRP3 inflammasome in the pathogenesis of rheumatic disease. Autoimmunity. 2022;55(1):1-7.
[31] YANG P, FENG W, LI C, et al. LPS induces fibroblast-like synoviocytes RSC-364 cells to pyroptosis through NF-κB mediated dual signalling pathway. J Mol Histol. 2021;52(4):661-669.
[32] GUO C, FU R, WANG S, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018;194(2):231-243.
[33] PANDEYA A, LI L, LI Z, et al. Gasdermin D (GSDMD) as a new target for the treatment of infection. Medchemcomm. 2019;10(5):660-667.
[34] EVAVOLD CL, HAFNER-BRATKOVIC I, DEVANT P, et al. Control of gasdermin d oligomerization and pyroptosis by the ragulator-rag-mtorc1 pathway. Cell. 2021; 184(17):4495-4511 e4419.
[35] HUANG Y, XU W, ZHOU R. NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18(9):2114-2127.
[36] 余明芳,陈白露,何欣玲,等.时辰艾灸干预类风湿关节炎模型大鼠核心钟基因Clock、Bmal1表达与细胞焦亡的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(35):5700-5706.
[37] EL-WASEEF D. A highlight on CD4+ T-cells in the spleen in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis and possible therapeutic effect of omega-3. Histological and immunofluorescence study. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;81:106283.
[38] WANG Z, ZHUO F, CHU P, et al. Germacrone alleviates collagen-induced arthritis via regulating Th1/Th2 balance and nf-kappab activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;518(3):560-564.
[39] RANA AK, LI Y, DANG Q, et al. Monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis: Circulating precursors of macrophages and osteoclasts and, their heterogeneity and plasticity role in RA pathogenesis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;65:348-359.
[40] YU P, ZHANG X, LIU N, et al. Pyroptosis: Mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):128.
[41] NEGREI C, BOJINCA V, BALANESCU A, et al. Management of rheumatoid arthritis: Impact and risks of various therapeutic approaches. Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(4): 1177-1183.
[42] ACOSTA-RODRIGUEZ EV, NAPOLITANI G, LANZAVECCHIA A, et al. Interleukins 1beta and 6 but not transforming growth factor-beta are essential for the differentiation of interleukin 17-producing human t helper cells. Nat Immunol. 2007;8(9):942-949.
|