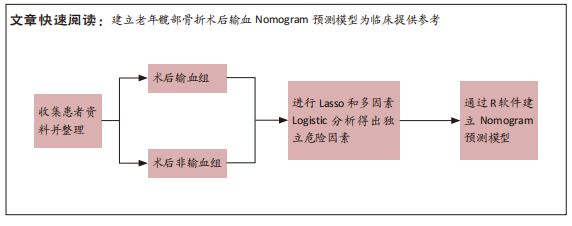
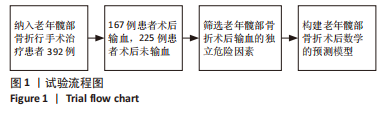
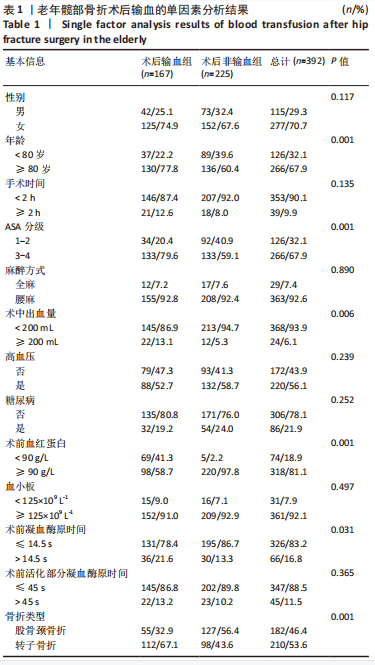
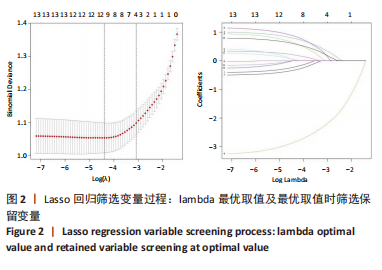
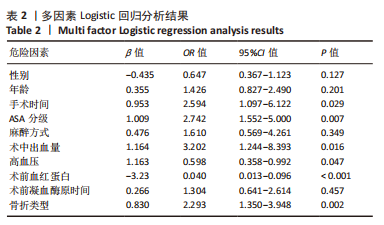
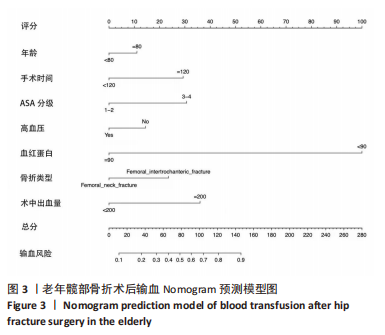
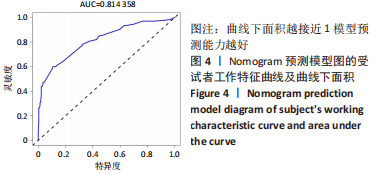
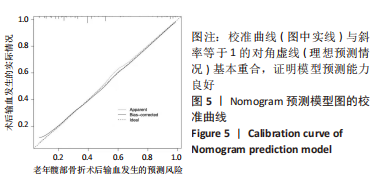
[1] 吴新宝, 杨明辉. 老年髋部骨折诊疗专家共识(2017)[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(11):921-927.
[2] ABRAHAMSEN B, VAN STAA T, ARIELY R, et al. Excess mortality following hip fracture: a systematic epidemiological review. Osteoporos Int. 2009; 20(10):1633-1650.
[3] 张瑞鹏, 尹英超, 李石伦, 等. 髋部骨折指南解读与诊疗现状分析[J]. 河北医科大学学报,2018,39(6):621-622, 627.
[4] ARSHI A, LAI WC, IGLESIAS BC, et al. Blood transfusion rates and predictors following geriatric hip fracture surgery. Hip Int. 2021;31(2):272-279.
[5] GREGERSEN M, BORRIS LC, DAMSGAARD EM. Postoperative blood transfusion strategy in frail, anemic elderly patients with hip fracture: the TRIFE randomized controlled trial. Acta Orthop. 2015;86(3):363-372.
[6] SPAHN DR. Anemia and patient blood management in hip and knee surgery: a systematic review of the literature. Anesthesiology. 2010;113(2):482-495.
[7] SMEETS S, VERBRUGGEN J, POEZE M. Effect of blood transfusion on survival after hip fracture surgery. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018;28(7):1297-1303.
[8] 王默然,王峻,葛艳玲,等. 老年髋部骨折患者围术期输血影响因素的研究[J]. 中国输血杂志,2020,33(7): 668-672.
[9] VIBERG B, GUNDTOFT PH, SCHØNNEMANN J, et al. Introduction of national guidelines for restrictive blood transfusion threshold for hip fracture patients--a consecutive cohort study based on complete follow-up in national databases. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):116.
[10] 周宗科, 翁习生, 孙天胜, 等. 中国骨科手术加速康复——围术期血液管理专家共识[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2017,10(1):1-7.
[11] WANG JQ, CHEN LY, JIANG BJ, et al. Development of a Nomogram for Predicting Blood Transfusion Risk After Hemiarthroplasty for Femoral Neck Fractures in Elderly Patients. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e920255.
[12] DAI CQ, WANG LH, ZHU YQ, et al. Risk factors of perioperative blood transfusion in elderly patients with femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(15):e19726.
[13] DESAI SJ, WOOD KS, MARSH J, et al. Factors affecting transfusion requirement after hip fracture: can we reduce the need for blood? Can J Surg. 2014;57(5):342-348.
[14] 岳睿, 李晓玉, 杨明辉, 等. 老年髋部骨折患者围手术期输血和危险因素[J]. 首都医科大学学报,2021,42(4):629-634.
[15] WANG JQ, CHEN LY, JIANG BJ, et al. Development of a Nomogram for Predicting Blood Transfusion Risk After Hemiarthroplasty for Femoral Neck Fractures in Elderly Patients. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e920255.
[16] SMITH GH, TSANG J, MOLYNEUX SG, et al. The hidden blood loss after hip fracture. Injury. 2011;42(2):133-135.
[17] 吕阳, 刘启宇, 刘军, 等. 中国老年髋部骨折患者术后发生谵妄相关因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(15):2437-2445.
[18] 魏滨, 徐懋, 张利萍, 等. 老年髋部骨折患者术后心血管并发症的危险因素分析[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志,2018,34(3):222-225.
[19] 黄兆松, 张振宇, 张娟, 等. 老年患者髋部骨折全麻与局麻后并发症的比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(9):802-805.
[20] WANG J, ZHAO Y, JIANG B, et al. Development of a Nomogram to Predict Postoperative Transfusion in the Elderly After Intramedullary Nail Fixation of Femoral Intertrochanteric Fractures. Clin Interv Aging. 2021;16:1-7.
[21] SATHIYAKUMAR V, ESTEVEZ-ORDONEZ D, THAKORE RV, et al. American Society of Anesthesiologists Score as a Predictive Tool to Optimize Blood Ordering for Intraoperative Transfusion in Orthopaedic Trauma Cases. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2016;25(2):105-109.
[22] HOU G, ZHOU F, TIAN Y, et al. Predicting the need for blood transfusions in elderly patients with pertrochanteric femoral fractures. Injury. 2014; 45(12):1932-1937.
[23] MORRITT DG, MORRITT AN, KELLEY SP, et al. Blood ordering protocol based on proposed surgical implant in fractured neck of femur patients. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2005;87(6):445-448.
[24] HUANG Z, HUANG C, XIE J, et al. Analysis of a large data set to identify predictors of blood transfusion in primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. Transfusion. 2018;58(8):1855-1862.
[25] 范晓丽,朱雪,马秀凤. 高龄髋部手术患者术后肺部感染高危因素及防控对策[J]. 国际护理学杂志,2022,41(7):1179-1183.
[26] BRUNSKILL SJ, MILLETTE SL, SHOKOOHI A, et al. Red blood cell transfusion for people undergoing hip fracture surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(4):D9699.
[27] KARADEMIR G, BILGIN Y, ERŞEN A, et al. Hip fractures in patients older than 75 years old: Retrospective analysis for prognostic factors. Int J Surg. 2015;24(Pt A):101-104.
[28] GRUSON KI, ACCOUSTI KJ, PARSONS BO, et al. Transfusion after shoulder arthroplasty: an analysis of rates and risk factors. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18(2):225-230.
[29] ZHU C, YIN J, WANG B, et al. Restrictive versus liberal strategy for red blood-cell transfusion in hip fracture patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(32):e16795.
[30] 桂珊珊, 曹亚琴, 闵继康, 等. 全膝/髋关节置换患者短期内非计划性再入院危险因素的Meta分析[J]. 护士进修杂志,2020,35(18):1690-1696.
[31] GUAY J. The effect of neuraxial blocks on surgical blood loss and blood transfusion requirements: a meta-analysis. J Clin Anesth. 2006;18(2):124-128.
[32] MARTINSEN MI, VALLAND H, SOLHEIM LF, et al. A restrictive policy for red blood cell transfusion in older hip fracture patients: experiences from a patient register. BMC Res Notes. 2016;9:75.
[33] HARPER KD, NAVO P, RAMSEY F, et al. “Hidden” Preoperative Blood Loss With Extracapsular Versus Intracapsular Hip Fractures: What Is the Difference? Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2017;8(4):202-207. |