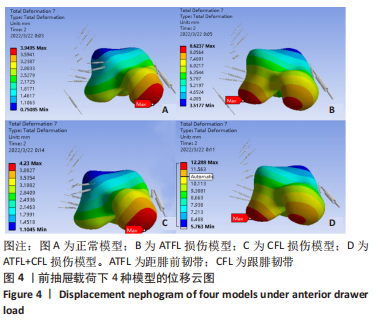
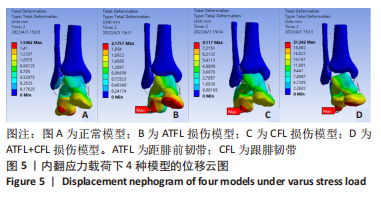
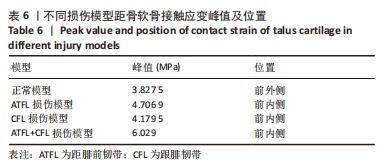
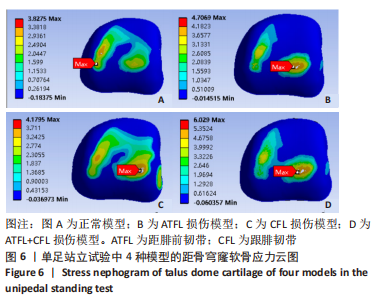
[1] FONG DT, CHAN YY, MOK KM, et al. Understanding acute ankle ligamentous sprain injury in sports. Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol. Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol. 2009;1:14.
[2] DOHERTY C, DELAHUNT E, CAULFIELD B, et al. The incidence and prevalence of ankle sprain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective epidemiological studies. Sports Med. 2014; 44(1):123-140.
[3] 周云烽, 张正政, 江川, 等. 踝关节距腓前韧带和跟腓韧带的解剖学特点[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2021,40(5):364-371.
[4] VAN DEN BEKEROM MP, OOSTRA RJ, GOLANó P, et al. The anatomy in relation to injury of the lateral collateral ligaments of the ankle: a current concepts review. Clin Anat. 2008;21(7):619-626.
[5] BONNEL F, TOULLEC E, MABIT C, et al. Chronic ankle instability: biomechanics and pathomechanics of ligaments injury and associated lesions. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2010;96(4):424-432.
[6] THOMPSON JY, BYRNE C, WILLIAMS MA, et al. Prognostic factors for recovery following acute lateral ankle ligament sprain: a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):421.
[7] SHAKKED R, SHESKIER S. Acute and Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability Diagnosis, Management, and New Concepts. Bull Hosp Jt Dis (2013). 2017;75(1):71-80.
[8] CORREA BELLIDO P, WADHWANI J, GIL MONZO E. Matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation grafting in osteochondral lesions of the talus: Evaluation of cartilage repair using T2 mapping. J Orthop. 2019;16(6):500-503.
[9] AICALE R, MAFFULLI N. Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability: Topical Review. Foot Ankle Int. 2020;41(12):1571-1581.
[10 DAHMEN J, LAMBERS KTA, REILINGH ML, et al. No superior treatment for primary osteochondral defects of the talus. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(7):2142-2157.
[11] VAN DIEPEN PR, DAHMEN J, ALTINK JN, et al. Location Distribution of 2,087 Osteochondral Lesions of the Talus. Cartilage. 2021;13(1_suppl): 1344s-1353s.
[12] 夏煜博, 唐晓霞, 罗文, 等.有限元建模分析牵开成形治疗踝关节骨性关节炎的生物力学响应[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(22): 3469-3475.
[13] BISCHOF JE, SPRITZER CE, CAPUTO AM, et al. In vivo cartilage contact strains in patients with lateral ankle instability. J Biomech. 2010;43(13): 2561-2566.
[14] WANG CW, MUHEREMU A, BAI JP. Use of three-dimensional finite element models of the lateral ankle ligaments to evaluate three surgical techniques. J Int Med Res. 2018;46(2):699-709.
[15] HOEFNAGELS EM, WAITES MD, WING ID, et al. Biomechanical comparison of the interosseous tibiofibular ligament and the anterior tibiofibular ligament. Foot Ankle Int. 2007;28(5):602-604.
[16] PFAEFFLE HJ, TOMAINO MM, GREWAL R, et al. Tensile properties of the interosseous membrane of the human forearm. J Orthop Res. 1996; 14(5):842-845.
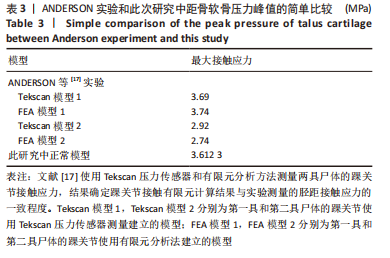
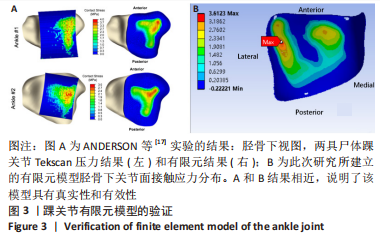
[17] ANDERSON DD, GOLDSWORTHY JK, LI W, et al. Physical validation of a patient-specific contact finite element model of the ankle. J Biomech. 2007;40(8):1662-1669.
[18] 白子兴, 曹旭含, 孙承颐, 等. 步态周期中踝关节有限元模型的构建及生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(9):1362-1366.
[19] NORDIN M, FRANKEL VH.肌肉骨骼系统基础生物力学[M]. 邝适存,郭霞,译.3版. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2008.
[20] OMORI G, KAWAKAMI K, SAKAMOTO M, et al. The effect of an ankle brace on the 3-dimensional kinematics and tibio-talar contact condition for lateral ankle sprains. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2004; 12(5):457-462.
[21] CAPUTO AM, LEE JY, SPRITZER CE, et al. In vivo kinematics of the tibiotalar joint after lateral ankle instability. Am J Sports Med. 2009; 37(11):2241-2248.
[22] BLOM RP, MOL D, VAN RUIJVEN LJ, et al. A Single Axial Impact Load Causes Articular Damage That Is Not Visible with Micro-Computed Tomography: An Ex Vivo Study on Caprine Tibiotalar Joints. Cartilage. 2021;13(2_suppl):1490s-1500s.
[23] LI J, WEI Y, WEI M. Finite Element Analysis of the Effect of Talar Osteochondral Defects of Different Depths on Ankle Joint Stability. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e921823.
|