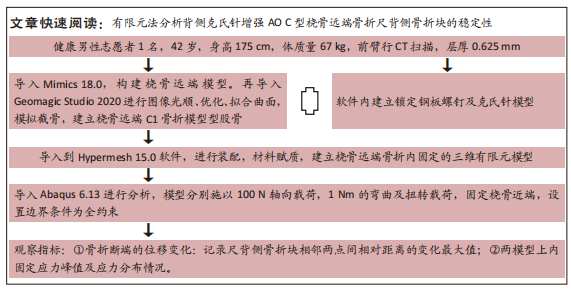
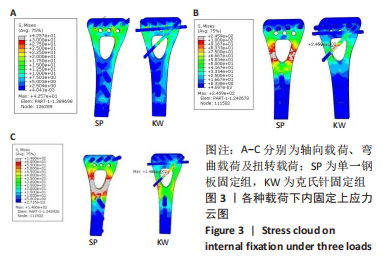
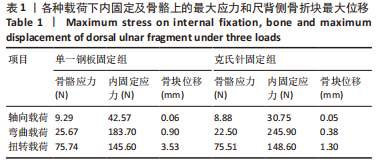
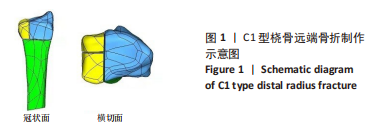
[1] MAUCK BM, SWIGLER CW. Evidence-based review of distal radius fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2018;49(2):211-212.
[2] KWON GD, JANG S, LEE A, et al. Incidence and mortality after distal radius fractures in adults aged 50 years and older in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2016;31(4):630-634.
[3] LAINO DK, TEJWANI N. Indications for operative fixation of distal radius fractures: a review of the evidence. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2012; 70(1):35-40.
[4] LEIXNERING M, ROSENAUER R, PEZZEI C, et al. Indications, surgical approach, reduction, and stabilization techniques of distal radius fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(5):611-621.
[5] 郑上团,吴斗,郝海虎,等.桡骨远端骨折的治疗进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(5):314-320.
[6] 费起礼.桡骨远端骨折的分型和治疗原则[J].中华骨科杂志,2009, 29(2):178-181.
[7] 白求恩公益基金会创伤骨科专业委员会,中国医疗保健国际交流促进会加速康复外科学分会创伤骨科学组.加速康复外科理念下桡骨远端骨折诊疗方案优化的专家共识[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2019,21(2):93-101.
[8] 陆晴友,郝迎新.桡骨远端骨折治疗进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2017, 38(3):154-157,165.
[9] EARP BE, FOSTER B, BLAZAR PE. The use of a single volar locking plate for AO C3-type distal radius fractures. Hand (N Y). 2015;10(4):649-653.
[10] 姜保国,张殿英,傅忠国,等.桡骨远端粉碎性骨折及关节内骨折的手术治疗[J].中华骨科杂志,2002,22(2):80-83.
[11] 魏新锁,杨彪,郭书章,等.不稳定性桡骨远端骨折掌侧或背侧入路内固定的选择[J]. 中华手外科杂志,2021,37(3):199-201.
[12] LEE JI, CHO JH, LEE SJ. The effects of the Frag-Loc(®) compression screw on distal radius fracture with a displaced dorsoulnar fragment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(9):1315-1321.
[13] 杨志全,李海生.两种手术方法治疗桡骨远端粉碎性骨折的临床效果[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(18):1719-1721.
[14] 姚恩洋,田野.微创手术联合单臂外固定架在桡骨远端粉碎性骨折中的临床应用[J].中国医科大学学报,2020,49(5):405-409.
[15] MELONE CP JR. Articular fractures of the distal radius. Orthop Clin North Am. 1984;15(2):217-236.
[16] 吴世桐,宁仁德,方闰,等.掌侧入路内固定治疗桡骨远端粉碎性骨折合并尺背侧骨折块的临床研究[J].创伤外科杂志,2021,23(5): 338-341.
[17] 肖衡,谢世伟,罗明薇.基于DRGs的四川省三甲医院骨科专业住院服务绩效评价[J]. 中国医院, 2021, 25(3):46-47.
[18] 文小焱,石皓,陈媛,等.基于DRGs数据的加权TOPSIS-RSR模型在住院服务质量综合评价上的应用[J].中国病案,2021,22(3):59-62.
[19] YAMAZAKI T, MATSUURA Y, SUZUKI T, et al. Evaluation of fixation after plating of distal radius fractures-a validation study. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2021;24(15):1687-1692.
[20] MATSUURA Y, KUNIYOSHI K, SUZUKI T, et al. Accuracy of specimen-specific nonlinear finite element analysis for evaluation of distal radius strength in cadaver material. J Orthop Sci. 2014;19(6):1012-1018.
[21] 殷浩,周恩昌,潘政军,等.4枚空心钉与3枚空心钉结合支持钢板内固定治疗PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(32):5133-5137.
[22] 钟环, 欧阳汉斌, 魏波,等. 桡骨远端骨折锁定钢板的拓扑优化及有限元分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(23):2189-2194.
[23] 夏长江,袁志峰,方宁.基于尺桡骨三维有限元模型分析桡骨远端骨折的生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(6):893-897.
[24] LIN CL, LIN YH, CHEN AC. Buttressing angle of the double-plating fixation of a distal radius fracture: a finite element study. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2006;744(8):665-673.
[25] KNEŽEVIĆ J, KODVANJ J, ČUKELJ F, et al. A biomechanical comparison of four fixed-angle dorsal plates in a finite element model of dorsally-unstable radius fracture. Injury. 2017,48 Suppl 5:S41-S46.
[26] HARNESS NG, JUPITER JB, ORBAY JL, et al. Loss of fixation of the volar lunate facet fragment in fractures of the distal part of the radius. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(9):1900-1908.
[27] BECK JD, HARNESS NG, SPENCER HT. Volar plate fixation failure for volar shearing distal radius fractures with small lunate facet fragments. J Hand Surg Am. 2014;39(4):670-678.
[28] IKEDA K, OSAMURA N, TADA K. Fixation of an ulnodorsal fragment when treating an intra-articular fracture in the distal radius. Hand Surg. 2014;19(1):139-144.
[29] SPITERI M, NG W, MATTHEWS J, et al. Three year review of dorsal plating for complex Intra-articular fractures of the distal radius.J Hand Surg Asian Pac. 2018;23(2):221-226.
[30] OBATA H, NAITO K, KANEKO A, et al. Clinical outcomes in distal radius fractures accompanied by volar lunate facet fragments: a comparison between dorsal and volar displaced fractures. J Hand Surg Asian Pac. 2020;25(4):417-422.
[31] MIYASHIMA Y, KANESHIRO Y, YANO K, et al. Size and stabilization of the dorsoulnar fragment in AO C3-type distal radius fractures. Injury. 2019;50(11):2004-2008.
[32] ZHANG QL, ZHU XD, LI GD, et al. Treatment of type C3 distal radius fracture resulted from high-energy injuries by volar plate in combination with external fixator. Chin Med J. 2009;122(13):1517-1520.
[33] ABDELGAID SM, ABDELAZEEM ME, ALSHARKAWY W. Fragment-specific fixation of complex distal radial fractures with small intraarticular fragments; volar locked plate augmented with Kirschner wires. Curr Orthop Pract. 2015;26(3):306-313.
[34] PATRICK NC, LEWIS GS, ROUSH EP, et al. Biomechanical stability of volar plate only versus addition of dorsal ulnar pin plate: A dorsal ulnar fragment, c-3-Type, distal radius, cadaver fracture model. J Orthop Trauma. 2020;34(9):e298-e303.
[35] BOYER M. Volar Locking-Plate and Kirschner-Wire Fixation did not differ in terms of functional outcomes after dorsally displaced distal radial fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(10):859.
[36] SHYAMALAN G, THEOKLI C, PEARSE Y, et al. Volar locking plates versus Kirschner wires for distal radial fractures--a cost analysis study. Injury. 2009;40(12):1279-1281.
[37] ZONG SL,KAN SL,SU LX, et al. Meta-analysis for dorsally displaced distal radius fracture fixation: volar locking plate versus percutaneous Kirschner wires. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10(1):1-12.
[38] SCHNEIDERS W, ELENZ J, REHBERG S, et al. Long-term results after Kirschner wire pinning of distal radius fractures. Unfallchirurg. 2012; 115(1):38-46.
[39] EGOL K,WALSH M,TEJWANI N, et al. Bridging external fixation and supplementary Kirschner-wire fixation versus volar locked plating for unstable fractures of the distal radius a randomised prospective trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(9):1214-1221.
[40] SAKAMOTO S,DOI K,HATTORI Y, et al. Comminuted dorsal ulnar fragment in distal radius fractures treated using the integrated compression screw with a mini-plate. J Hand Surg Am. 2022;47(4):394-394. |