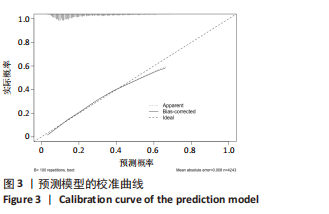
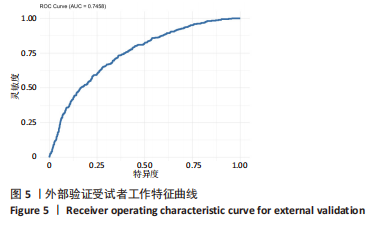
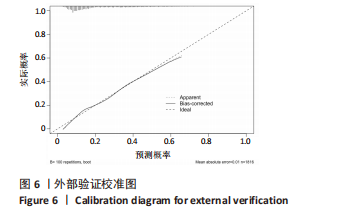
[1] HARTVIGSEN J, HANCOCK MJ, KONGSTED A, et al. Lancet Low Back Pain Series Working Group. What low back pain is and why we need to pay attention. Lancet. 2018;391(10137):2356-2367.
[2] WU A, MARCH L, ZHENG X, et al. Global low back pain prevalence and years lived with disability from 1990 to 2017: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(6):299.
[3] GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789-1858.
[4] BUCHBINDER R, VAN TULDER M, ÖBERG B, et al. Lancet Low Back Pain Series Working Group. Low back pain: a call for action. Lancet. 2018; 391(10137):2384-2388.
[5] LENTZ TA, CORONADO RA, MASTER H. Delivering Value Through Equitable Care for Low Back Pain: A Renewed Call to Action. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2022;52(7):414-418.
[6] PARK SH, YU HY. How useful is the center for epidemiologic studies depression scale in screening for depression in adults? An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2021;302:114037.
[7] 吕燕宇,姜红如,张兵,等. 中国九省(区)农民超重肥胖的变化趋势及人口经济因素的影响[J]. 中国食物与营养,2020,26(1):73-76.
[8] BLAND J MARTIN, ALTMAN DOUGLAS G, 徐晶, 等. Bootstrap重抽样方法[J] . 英国医学杂志中文版,2016,19(3):154-155.
[9] 张砚卓,王倩倩,袁越,等. 中国45岁以上人群腰痛患病率调查:基于中国健康与养老追踪调查数据[J]. 骨科临床与研究杂志,2018, 3(1):38-42.
[10] 吕艳伟,田伟,刘亚军,等. 2010年北京地区18岁及以上人群腰痛患病率研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2013,33(1):60-64.
[11] GROßSCHÄDL F, STOLZ E, MAYERL H, et al. Educational inequality as a predictor of rising back pain prevalence in Austria-sex differences. Eur J Public Health. 2016;26(2):248-253.
[12] ZAJACOVA A, LAWRENCE EM. The Relationship Between Education and Health: Reducing Disparities Through a Contextual Approach. Annu Rev Public Health. 2018;39:273-289.
[13] CALVO LOBO C, VILAR-FERNÁNDEZ JM, LOSA-IGLESIAS ME, et al. Depression Symptoms Among Older Adults With and Without Subacute Low Back Pain. Rehabil Nurs. 2019;44(1):47-51.
[14] TSUJI T, MATSUDAIRA K, SATO H, et al. The impact of depression among chronic low back pain patients in Japan. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1):447.
[15] VIETRI J, OTSUBO T, MONTGOMERY W, et al. The incremental burden of pain in patients with depression: results of a Japanese survey. BMC Psychiatry. 2015;15:104.
[16] DENKINGER MD, LUKAS A, NIKOLAUS T, et al. ActiFE study group. Multisite pain, pain frequency and pain severity are associated with depression in older adults: results from the ActiFE Ulm study. Age Ageing. 2014;43(4):510-514.
[17] SHENG J, LIU S, WANG Y, et al. The Link between Depression and Chronic Pain: Neural Mechanisms in the Brain. Neural Plast. 2017; 2017:9724371.
[18] SONG C, HALBREICH U, HAN C, et al. Imbalance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, and between Th1 and Th2 cytokines in depressed patients: the effect of electroacupuncture or fluoxetine treatment. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2009;42(5):182-188.
[19] 陈苑苑,陈京红,张许来,等.抑郁症伴慢性疼痛炎性机制的研究进展[J]. 神经疾病与精神卫生,2021,21(9):636-641.
[20] BALIKI MN, PETRE B, TORBEY S, et al. Corticostriatal functional connectivity predicts transition to chronic back pain. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15(8):1117-1119.
[21] AMIRI S, BEHNEZHAD S. Sleep disturbances and back pain : Systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychiatr. 2020;34(2):74-84.
[22] FROHNHOFEN H. Pain and sleep: A bidirectional relationship. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2018;51(8):871-874.
[23] KEILANI M, CREVENNA R, DORNER TE. Sleep quality in subjects suffering from chronic pain. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2018;130(1-2): 31-36.
[24] ONEN SH, ALLOUI A, GROSS A, et al. The effects of total sleep deprivation, selective sleep interruption and sleep recovery on pain tolerance thresholds in healthy subjects. J Sleep Res. 2001;10(1):35-42.
[25] KUNDERMANN B, SPERNAL J, HUBER MT, et al. Sleep deprivation affects thermal pain thresholds but not somatosensory thresholds in healthy volunteers. Psychosom Med. 2004;66(6):932-937.
[26] DZIRASA K, RIBEIRO S, COSTA R, et al. Dopaminergic control of sleep-wake states. J Neurosci. 2006;26(41):10577-10589.
[27] FOO H, MASON P. Brainstem modulation of pain during sleep and waking. Sleep Med Rev. 2003;7(2):145-154.
[28] FINAN PH, GOODIN BR, SMITH MT. The association of sleep and pain: an update and a path forward. J Pain. 2013;14(12):1539-1552.
[29] MONTI JM, JANTOS H. The roles of dopamine and serotonin, and of their receptors, in regulating sleep and waking. Prog Brain Res. 2008; 172:625-646.
[30] 黄昀,矫玮,朱晓东,等. 久坐腰痛人群核心肌力状态特征及康复研究[J]. 西安体育学院学报,2020,37(2):218-224.
[31] 黄雷,李军汉. 躯干等速肌力训练与腰腹肌功能锻炼治疗非特异性腰痛的疗效对比研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2015,30(11):1148-1151.
[32] ISHAK NA, ZAHARI Z, JUSTINE M. Kinesiophobia, Pain, Muscle Functions, and Functional Performances among Older Persons with Low Back Pain. Pain Res Treat. 2017;2017:3489617.
[33] SHAHIDA MSN, ZAWIAH MDS, CASE K. The relationship between anthropometry and hand grip strength among elderly Malaysians. Int J Industr Ergon. 2015;50:17-25.
[34] GORDON R, BLOXHAM S. A Systematic Review of the Effects of Exercise and Physical Activity on Non-Specific Chronic Low Back Pain. Healthcare (Basel). 2016;4(2):22.
[35] 刘冉. 有氧运动对延安市中老年人体质健康状况的影响分析[J]. 延安大学学报(自然科学版),2018,37(1):109-112.
[36] RUSSO M, DECKERS K, ELDABE S, et al. Muscle Control and Non-specific Chronic Low Back Pain. Neuromodulation. 2018;21(1):1-9.
[37] 袁伟,梁育磊,杨艳婷,等.慢性非特异性腰痛患者核心肌群锻炼前后腹肌超声测量结果与临床预后的关联性研究[J]. 颈腰痛杂志, 2022,43(3):366-369. |