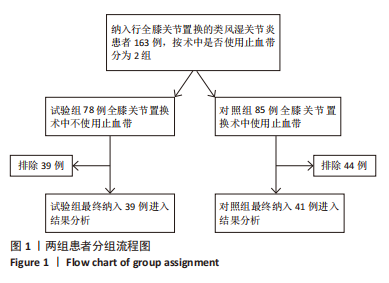
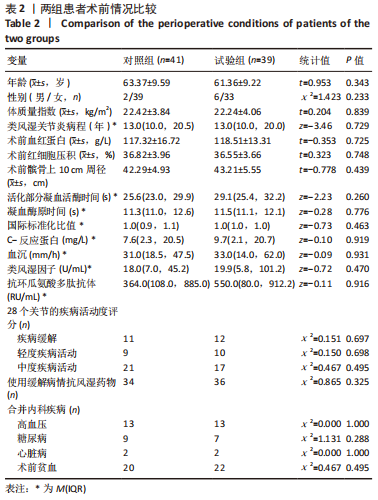
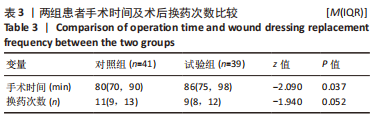
[1] MADERBACHER G, GREIMEL F, SCHAUMBURGER J, et al. The knee joint in rheumatoid arthritis-current orthopaedic surgical treatment options. Z Rheumatol. 2018;7(10):882-888.
[2] LØPPENTHIN K, ESBENSEN BA, ØSTERGAARD M, et al. Morbidity and mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with an age- and sex-matched control population: A nationwide register study. J Comorb. 2019;9:2235042X-19853484X.
[3] YOUNG BL, WATSON SL, PEREZ JL, et al. Trends in Joint Replacement Surgery in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2018;45(2): 158-164.
[4] 刘金磊, 殷力, 张翼, 等. 全膝关节置换中不同体积和剂量氨甲环酸关节腔注射对失血量的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(33): 5303-5310.
[5] 汪萧和, 王志文, 陆鸣, 等. 两种止血带使用方式对150例全膝关节置换术患者失血量和术后康复影响的前瞻性随机对照研究[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020,13(9):736-740.
[6] LEI Y, XIE J, HUANG Q, et al. Is there a role of tranexamic acid in rheumatoid arthritis with total knee arthroplasty? Findings from a multicenter prospective cohort study in China. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(3):489-496.
[7] 王富强, 张晋, 张兆卿. 氨甲环酸对类风湿关节炎患者全膝关节置换术后失血量的影响[J]. 广西医科大学学报,2017,34(5):765-768.
[8] STUNDNER O, DANNINGER T, CHIU YL, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis vs osteoarthritis in patients receiving total knee arthroplasty: perioperative outcomes. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(2):308-313.
[9] CAI DF, FAN QH, ZHONG HH, et al. The effects of tourniquet use on blood loss in primary total knee arthroplasty for patients with osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):348.
[10] SCHNETTLER T, PAPILLON N, REES H. Use of a Tourniquet in Total Knee Arthroplasty Causes a Paradoxical Increase in Total Blood Loss. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(16):1331-1336.
[11] 张子琦, 梁佳林, 左小莉, 等. 气压止血带对人工全膝关节置换术围术期失血量的影响[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(6):681-684.
[12] LEI Y, LIU J, LIANG X, et al. Effectiveness of preemptive antifibrinolysis with tranexamic acid in rheumatoid arthritis patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):465.
[13] GROSS JB. Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology. 1983;58(3):277-280.
[14] NADLER SB, HIDALGO JH, BLOCH T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery. 1962;51(2):224-232.
[15] BRKIC A, ŁOSIŃSKA K, PRIPP AH, et al. Remission or Not Remission, That’s the Question: Shedding Light on Remission and the Impact of Objective and Subjective Measures Reflecting Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatol Ther. 2022;9(6):1531-1547.
[16] HUNTER TM, BOYTSOV NN, ZHANG X, et al. Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in the United States adult population in healthcare claims databases, 2004-2014. Rheumatol Int. 2017;37(9):1551-1557.
[17] 边焱焱, 程开源, 常晓, 等. 2011至2019年中国人工髋膝关节置换手术量的初步统计与分析[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(21):1453-1460.
[18] LEE YH, KO PY, KAO SL, et al. Risk of Total Knee and Hip Arthroplasty in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A 12-Year Retrospective Cohort Study of 65,898 Patients. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(12):3517-3523.
[19] AGLIETTI P, BALDINI A, VENA LM, et al. Effect of tourniquet use on activation of coagulation in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(371):169-177.
[20] PRASAD N, PADMANABHAN V, MULLAJI A. Blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: an analysis of risk factors. Int Orthop. 2007;31(1):39-44.
[21] KING L, RANDLE R, DARE W, et al. Comparison of oral vs. combined topical/intravenous/oral tranexamic acid in the prevention of blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: A randomised clinical trial. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105(6):1073-1077.
[22] LAORUENGTHANA A, RATTANAPRICHAVEJ P, RASAMIMONGKOL S,
et al. Intra-Articular Tranexamic Acid Mitigates Blood Loss and Morphine Use After Total Knee Arthroplasty. A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(5):877-881.
[23] TZATZAIRIS T, DROSOS GI, VOGIATZAKI T, et al. Multiple intravenous tranexamic acid doses in total knee arthroplasty without tourniquet: a randomized controlled study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019;139(6): 859-868.
[24] XU S, MENG FQ, GUO C, et al. Modified Hidden Blood Loss Based on Drainage in Posterior Surgery on Lumbar Stenosis Syndrome with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(8):2263-2270.
[25] 王晶, 徐帅, 刘海鹰. 伴和不伴类风湿性关节炎患者腰椎管狭窄后路减压融合过程中隐性失血的对比[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020, 24(33):5307-5314.
[26] SMOLEN JS, LANDEWÉ R, BIJLSMA J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(6):685-699.
[27] AU K, REED G, CURTIS JR, et al. High disease activity is associated with an increased risk of infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(5):785-791.
[28] SOKKA T, PINCUS T. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, or rheumatoid factor are normal at presentation in 35%-45% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis seen between 1980 and 2004: analyses from Finland and the United States. J Rheumatol. 2009;36(7): 1387-1390.
[29] LIU Y, SI H, ZENG Y, et al. More pain and slower functional recovery when a tourniquet is used during total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(6):1842-1860.
[30] CLARKE MT, LONGSTAFF L, EDWARDS D, et al. Tourniquet-induced wound hypoxia after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83(1):40-44.
[31] VAISHYA R, AGARWAL AK, VIJAY V, et al. Short term outcomes of long duration versus short duration tourniquet in primary total knee arthroplasty: A randomized controlled trial. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2018;9(1):46-50.
[32] JAWHAR A, SKEIREK D, STETZELBERGER V, et al. Influence of the Tourniquet on Pain and Function in Total Knee Arthroplasty: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Z Orthop Unfall. 2020;158(6): 630-640.
[33] 张立创, 高华利, 王竞超, 等. 筋骨并重理筋手法干预全膝关节置换后患者股四头肌功能的加速康复[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(9):1383-1389.
[34] TUNCALI B, BOYA H, KAYHAN Z, et al. Tourniquet pressure settings based on limb occlusion pressure determination or arterial occlusion pressure estimation in total knee arthroplasty? A prospective, randomized, double blind trial. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2018;52(4): 256-260.
|