中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (31): 4939-4944.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1457
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
聚集蛋白代谢通路基因多态性与腰椎间盘突出严重程度的相关性
杨金丰,马三辉
- (定州市人民医院骨科,河北省定州市 073000)
Association between polymorphism of aggregate protein metabolic pathway gene and severity of lumbar disc herniation
Yang Jinfeng, Ma Sanhui
- (Department of Orthopedics, People’s Hospital of Dingzhou, Dingzhou 073000, Hebei Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
基质金属蛋白酶3:基质金属蛋白酶家族蛋白参与细胞外基质在正常生理过程中的破坏,如胚胎发育、生殖、组织重塑,以及在疾病过程中,如关节炎和转移。大多数基质金属蛋白酶是作为非活性的前蛋白分泌的,在细胞外蛋白酶裂解时被激活。该基因编码一种酶,可降解纤维连接蛋白、层粘连蛋白、胶原蛋白Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅸ和Ⅹ,以及软骨蛋白聚糖。这种酶被认为参与了伤口修复、动脉粥样硬化的进展和肿瘤的发生。
蛋白聚糖:是蛋白聚糖家族的成员之一。编码的蛋白是软骨组织中细胞外基质的组成部分,作用是能承受软骨的压缩。该基因的突变可能与骨骼发育不良和脊髓变性有关。目前在该基因中观察到了编码不同蛋白质亚型的多个选择性剪接转录变体。
.jpg)
文题释义:
基质金属蛋白酶3:基质金属蛋白酶家族蛋白参与细胞外基质在正常生理过程中的破坏,如胚胎发育、生殖、组织重塑,以及在疾病过程中,如关节炎和转移。大多数基质金属蛋白酶是作为非活性的前蛋白分泌的,在细胞外蛋白酶裂解时被激活。该基因编码一种酶,可降解纤维连接蛋白、层粘连蛋白、胶原蛋白Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅸ和Ⅹ,以及软骨蛋白聚糖。这种酶被认为参与了伤口修复、动脉粥样硬化的进展和肿瘤的发生。
蛋白聚糖:是蛋白聚糖家族的成员之一。编码的蛋白是软骨组织中细胞外基质的组成部分,作用是能承受软骨的压缩。该基因的突变可能与骨骼发育不良和脊髓变性有关。目前在该基因中观察到了编码不同蛋白质亚型的多个选择性剪接转录变体。
摘要
背景:椎间盘突出是一种复杂的脊柱疾病,与椎间盘退变密切相关,而聚集蛋白聚糖的代谢途径的候选基因可能与腰椎间盘突出的严重程度相关。
目的:评估单核苷酸变异和慢性机械性腰痛患者腰椎间盘突出严重程度的蛋白聚糖的代谢途径的基因的关联。
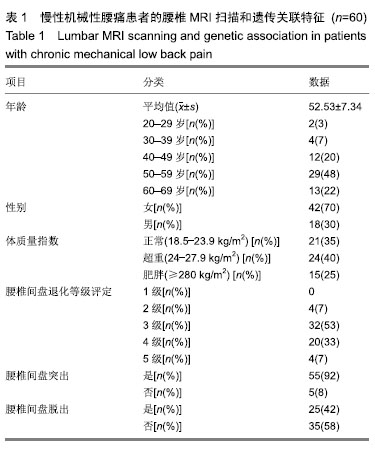
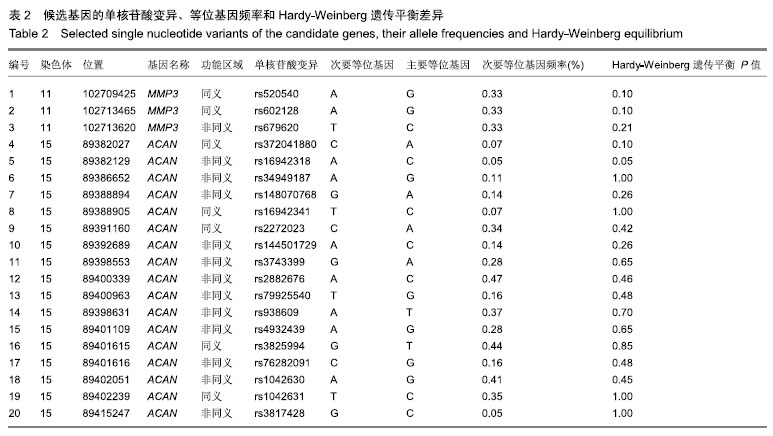
方法:对60例慢性机械性腰痛患者进行了分类描述研究。T2加权正中矢状位腰椎MRI扫描评估椎间盘突出和椎间盘退变的严重程度。对凝集素代谢途径的2个候选基因(蛋白聚糖和基质金属蛋白酶3)的20个外显子单核苷酸变异进行了基因分型。对年龄、性别、体质量指数和椎间盘退变程度进行多元线性回归分析。试验于2015-03-01经定州市人民医院伦理委员会批准(批准号2015002)。
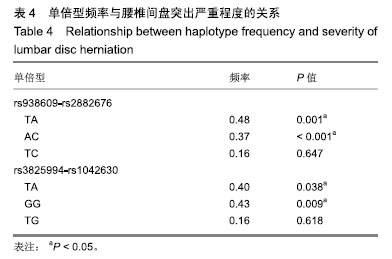
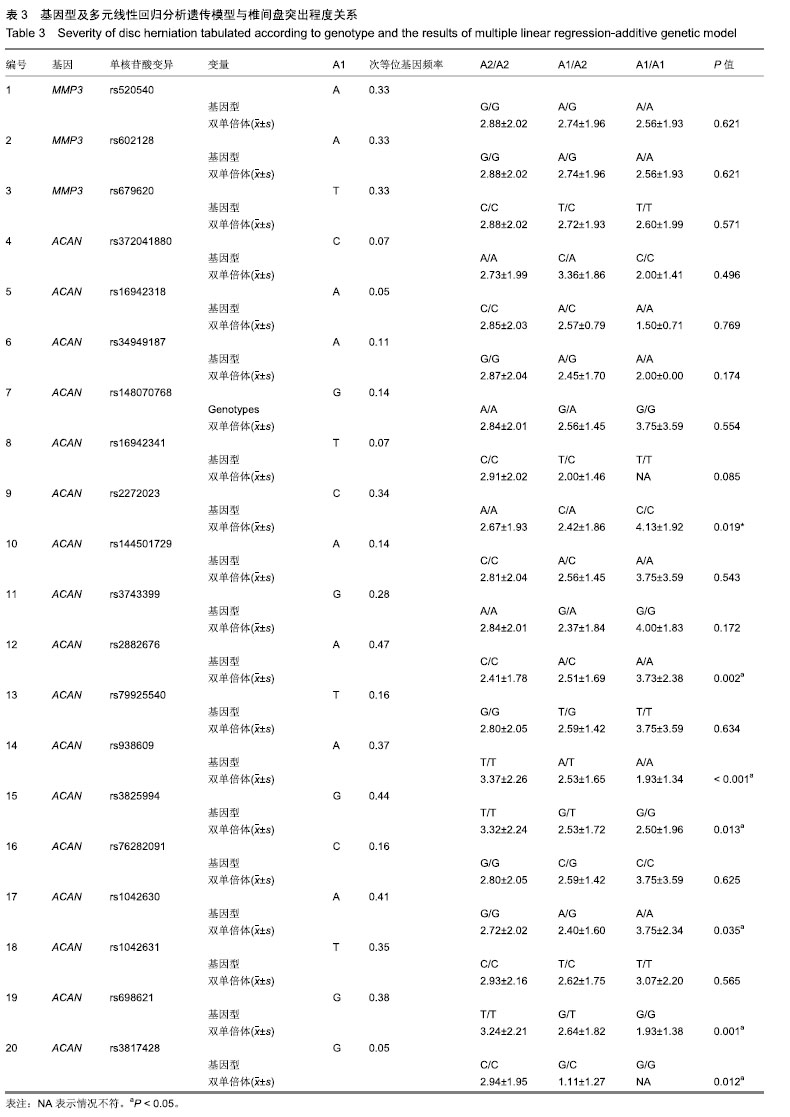
结果与结论:蛋白聚糖的rs2272023、rs938609、rs2882676、rs698621、rs3825994、rs1042630和rs3817428突变体及其单倍型与腰椎间盘突出的严重程度有关。若要确定这些重要的单核苷酸变异在椎间盘突出症的发病机制中的作用,有必要进行功能遗传方面的研究。
背景:椎间盘突出是一种复杂的脊柱疾病,与椎间盘退变密切相关,而聚集蛋白聚糖的代谢途径的候选基因可能与腰椎间盘突出的严重程度相关。
目的:评估单核苷酸变异和慢性机械性腰痛患者腰椎间盘突出严重程度的蛋白聚糖的代谢途径的基因的关联。
方法:对60例慢性机械性腰痛患者进行了分类描述研究。T2加权正中矢状位腰椎MRI扫描评估椎间盘突出和椎间盘退变的严重程度。对凝集素代谢途径的2个候选基因(蛋白聚糖和基质金属蛋白酶3)的20个外显子单核苷酸变异进行了基因分型。对年龄、性别、体质量指数和椎间盘退变程度进行多元线性回归分析。试验于2015-03-01经定州市人民医院伦理委员会批准(批准号2015002)。
结果与结论:蛋白聚糖的rs2272023、rs938609、rs2882676、rs698621、rs3825994、rs1042630和rs3817428突变体及其单倍型与腰椎间盘突出的严重程度有关。若要确定这些重要的单核苷酸变异在椎间盘突出症的发病机制中的作用,有必要进行功能遗传方面的研究。
中图分类号:
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
基质金属蛋白酶3:基质金属蛋白酶家族蛋白参与细胞外基质在正常生理过程中的破坏,如胚胎发育、生殖、组织重塑,以及在疾病过程中,如关节炎和转移。大多数基质金属蛋白酶是作为非活性的前蛋白分泌的,在细胞外蛋白酶裂解时被激活。该基因编码一种酶,可降解纤维连接蛋白、层粘连蛋白、胶原蛋白Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅸ和Ⅹ,以及软骨蛋白聚糖。这种酶被认为参与了伤口修复、动脉粥样硬化的进展和肿瘤的发生。#br#
蛋白聚糖:是蛋白聚糖家族的成员之一。编码的蛋白是软骨组织中细胞外基质的组成部分,作用是能承受软骨的压缩。该基因的突变可能与骨骼发育不良和脊髓变性有关。目前在该基因中观察到了编码不同蛋白质亚型的多个选择性剪接转录变体。
#br#
文题释义:#br#
基质金属蛋白酶3:基质金属蛋白酶家族蛋白参与细胞外基质在正常生理过程中的破坏,如胚胎发育、生殖、组织重塑,以及在疾病过程中,如关节炎和转移。大多数基质金属蛋白酶是作为非活性的前蛋白分泌的,在细胞外蛋白酶裂解时被激活。该基因编码一种酶,可降解纤维连接蛋白、层粘连蛋白、胶原蛋白Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅸ和Ⅹ,以及软骨蛋白聚糖。这种酶被认为参与了伤口修复、动脉粥样硬化的进展和肿瘤的发生。#br#
蛋白聚糖:是蛋白聚糖家族的成员之一。编码的蛋白是软骨组织中细胞外基质的组成部分,作用是能承受软骨的压缩。该基因的突变可能与骨骼发育不良和脊髓变性有关。目前在该基因中观察到了编码不同蛋白质亚型的多个选择性剪接转录变体。