中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (18): 2894-2899.doi: 10.12307/2022.700
• 骨科植入物相关临床实践 Clinical practice of orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
深层肌肉刺激慢性非特异性腰痛患者腰肌表面肌电变化与 步态时空及动力学的参数变化
陈 进1,2,李加斌2,顾铭星2,唐 蓉1,陆建霞1
- 1江苏医药职业学院,江苏省盐城市 224000;2盐城市第一人民医院康复医学科,江苏省盐城市 224000
Effect of deep muscle stimulation on psoas surface electromyography and spatiotemporal and kinetic gait parameters in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain
Chen Jin1, 2, Li Jiabin2, Gu Mingxing2, Tang Rong1, Lu Jianxia1
- 1Jiangsu Vocational College of Medicine, Yancheng 224000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yancheng No. 1 People’s Hospital, Yancheng 224000, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
慢性非特异性腰痛:是临床十分常见的慢性疼痛性疾病,据报道,70%-85%的成年人一生中有腰疼经历,对其工作和生活质量造成严重影响。
深层肌肉刺激疗法:以深层肌肉刺激特定频率的机械振动直接作用于肌筋膜触发点,刺激较强,作用深厚,同时振动波可使肌肉内毛细血管开放,促进局部血液循环,供给痛点肌肉组织足够的营养成分,能促进淋巴回流,有助于水肿吸收,消除神经根水肿,进一步促进局部疼痛物质吸收,短时间内可有效缓解疼痛。
背景:深层肌肉刺激疗法是一种局部振动疗法,可有效缓解因牵拉或劳累所致损伤、乳酸堆积,或筋膜粘连造成的疼痛和功能受限,但其对慢性非特异性腰痛作用的研究报道相对不足。
目的:探讨深层肌肉刺激疗法对慢性非特异性腰痛患者腰肌表面肌电变化、步态时空与动力学参数特征的影响。
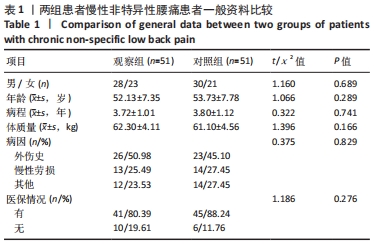
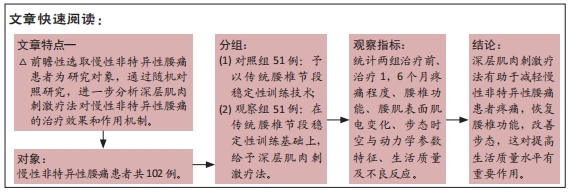
方法:选取2019年2月至2020年6月在盐城市第一人民医院就诊的102例慢性非特异性腰痛患者作为研究对象,采用随机单盲对照试验设计,按随机数字表法分为2组,各51例。对照组予以传统腰椎节段稳定性训练,观察组在传统腰椎节段稳定性训练基础上,给予深层肌肉刺激疗法。统计两组临床疗效、治疗前及治疗1,6个月疼痛程度、腰椎功能、腰肌表面肌电变化、步态时空与动力学参数特征、生活质量及不良反应。
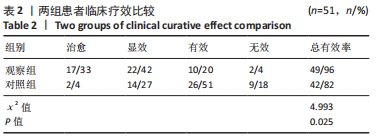
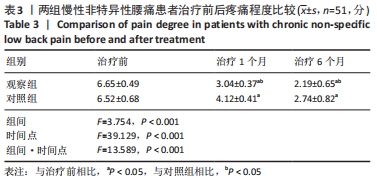
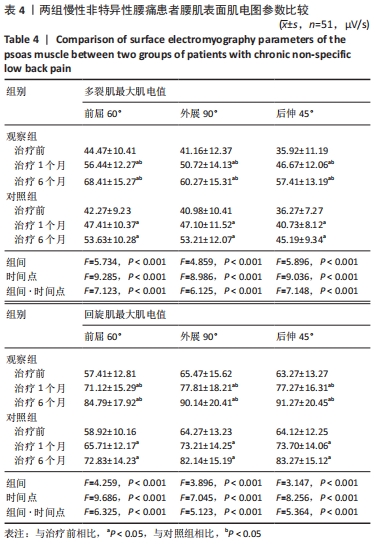
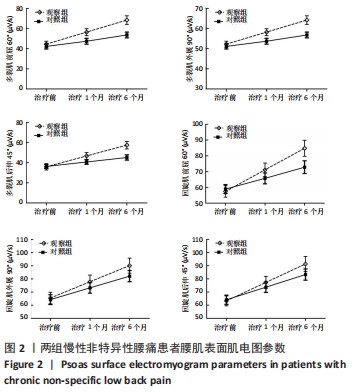
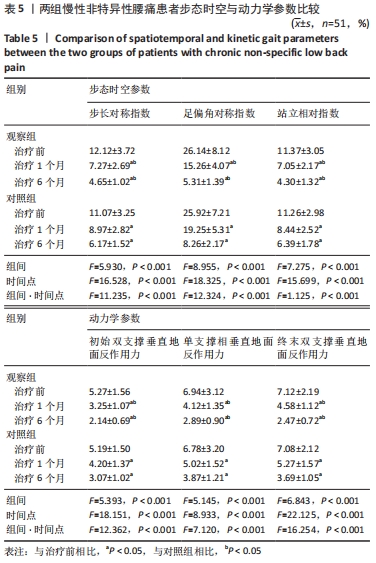
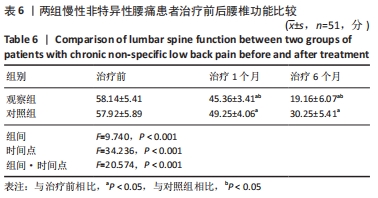
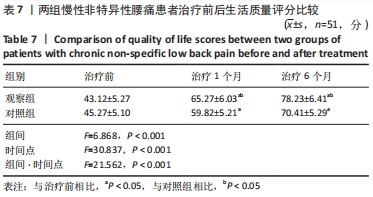
结果与结论:观察组总有效率(96%)高于对照组(82%)(P < 0.05),观察组治疗1,6个月后目测类比评分均低于对照组(P < 0.05),多裂肌、回旋肌前屈60°、外展90°、后伸45°时最大肌电值明显高于对照组(P < 0.05),步长对称指数、足偏角对称指数、站立相对指数、初始双支撑垂直地面反作用力、单支撑相垂直地面反作用力、终末双支撑垂直地面反作用力均低于对照组(P < 0.05),Oswestry功能障碍指数低于对照组(P < 0.05),SF-36评分高于对照组(P < 0.05);观察组和对照组不良反应发生率分别为3.9%(2/51),5.9%(3/51),差异无显著性意义(P﹥0.05)。结果表明,深层肌肉刺激疗法有助于减轻慢性非特异性腰痛患者的疼痛,恢复腰椎功能并改善步态。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4081-2535 (陈进)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: