中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (15): 2395-2403.doi: 10.12307/2023.355
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
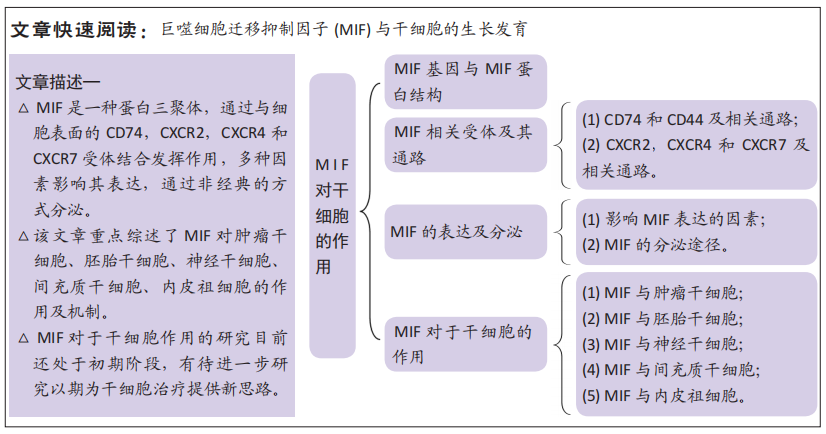
巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对干细胞的作用
郑晓晗1,2,3,魏艳召1,2,3,黄 婷1,2,3,魏绪芳2,孙圣童2,王 埮1,赵振强1
- 1海南医学院第一附属医院神经内科,海南省海口市 570100;2海南医学院,海南省海口市 570100;3海南省热带脑科学研究与转化重点实验室,海南省海口市 570100
-
收稿日期:2022-04-21接受日期:2022-06-27出版日期:2023-05-28发布日期:2022-10-18 -
通讯作者:赵振强,博士,主任医师,海南医学院第一附属医院神经内科,海南省海口市 570100 王埮,博士,主任医师,海南医学院第一附属医院神经内科,海南省海口市 570100 -
作者简介:郑晓晗,女,1995年生,福建省福州市人,汉族,海南医学院在读硕士,主要从事干细胞移植与神经系统疾病的研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(81860238),项目负责人:赵振强;海南省重点研发计划项目(ZDYF2018233),项目负责人:赵振强;海南省自然科学基金项目(821RC694),项目负责人:赵振强;海南省临床医学中心建设项目(琼卫医函[2021]276号);海南省研究生创新科研课题(琼教高[2021]116号),项目负责人:郑晓晗
Role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor for stem cells
Zheng Xiaohan1, 2, 3, Wei Yanzhao1, 2, 3, Huang Ting1, 2, 3, Wei Xufang2, Sun Shengtong2, Wang Tan1, Zhao Zhenqiang1
- 1Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570100, Hainan Province, China; 2Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570100, Hainan Province, China; 3Hainan Provincial Key Laboratory of Tropical Brain Research and Translation, Haikou 570100, Hainan Province, China
-
Received:2022-04-21Accepted:2022-06-27Online:2023-05-28Published:2022-10-18 -
Contact:Zhao Zhenqiang, MD, Chief physician, Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570100, Hainan Province, China Wang Tan, MD, Chief physician, Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570100, Hainan Province, China -
About author:Zheng Xiaohan, Master candidate, Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570100, Hainan Province, China; Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570100, Hainan Province, China; Hainan Provincial Key Laboratory of Tropical Brain Research and Translation, Haikou 570100, Hainan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81860238 (to ZZQ); Hainan Provincial Key Research & Development Program, No. ZDYF2018233 (to ZZQ); Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province, No. 821RC694 (to ZZQ); Hainan Provincial Clinical Medical Center Construction Project, No. [2021]276; Hainan Provincial Postgraduate Innovative Research Project, No. [2021] 116 (to ZXH)
摘要:
文题释义:
巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子:是由多种细胞类型产生的一种多功能细胞因子,影响多种生物过程的调节功能,如增殖、迁移、凋亡和细胞周期进程。
干细胞治疗:是把健康的干细胞移植到患者体内,以修复或替换受损细胞或组织,从而达到治愈的目的。
背景:干细胞是一种可以自我更新并且具有分化潜能的细胞,干细胞治疗是一种很有前景的治疗方法。巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子几乎在所有哺乳动物细胞中都有表达,对许多生理过程至关重要。现有研究证明,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子在多种干细胞上表达并且调节多种干细胞的增殖、分化和迁移。
目的:描述巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的基本特征并着重阐述巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于干细胞的作用及机制。
方法:在PubMed和中国知网数据库中检索近10年文献,英文检索词为“macrophage migration inhibitory factor,cancer stem cell,embryonic stem cell,neural stem cell,mesenchymal stem cell,endothelial progenitor cell,stem cell therapy,tissue engineering”,中文检索词为“巨噬细胞移动抑制因子、肿瘤干细胞、胚胎干细胞、神经干细胞、间充质干细胞、内皮祖细胞、干细胞治疗、组织工程”,经过文题、摘要的筛选,排除相关性差及陈旧和重复的文献,对最终符合标准的85篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子蛋白由3个亚基构成,在细胞表面通过与受体CD74,CD44,CXCR2,CXCR4和CXCR7产生作用。巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子储存在细胞内,通过非经典途径分泌,多种因素能影响其表达以及分泌。②巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子通过不同的信号通路促进肿瘤干细胞的迁移、侵袭、转移、逃逸和致瘤性。③当前研究中,比较明确的是巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子促进小鼠胚胎干细胞的神经分化。④巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子通过多个信号通路促进神经干细胞的增殖和存活。⑤巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子作用于间充质干细胞能够抑制凋亡、促进存活、延缓衰老并增加间充质干细胞的旁分泌作用,除此之外,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子也证明可以通过结合受体CD74抑制间充质干细胞的归巢。⑥多项研究证明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子通过CXCR4受体激活下游信号通路促进内皮细胞的迁移以及血管重建。⑦巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子作用于肿瘤干细胞、胚胎干细胞、神经干细胞、间充质干细胞、内皮祖细胞,对它们的增殖、分化、迁移和凋亡等过程产生影响,但其中部分作用还存在争议,确切机制需要更进一步验证。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0249-2734 (郑晓晗)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
郑晓晗, 魏艳召, 黄 婷, 魏绪芳, 孙圣童, 王 埮, 赵振强. 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对干细胞的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(15): 2395-2403.
Zheng Xiaohan, Wei Yanzhao, Huang Ting, Wei Xufang, Sun Shengtong, Wang Tan, Zhao Zhenqiang. Role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor for stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2395-2403.
2.2 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子相关受体及其通路 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子能与4种细胞表面受体结合,包括CD74,CXCR2,CXCR4 和CXCR7。巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子结合后,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子受体可以组合成4种不同的受体复合物:CD74/CD4,CD74/CXCR2,CD74/CXCR4,CD74/CXCR4/CXCR7[8],激活下游相关信号通路产生作用,见图3。
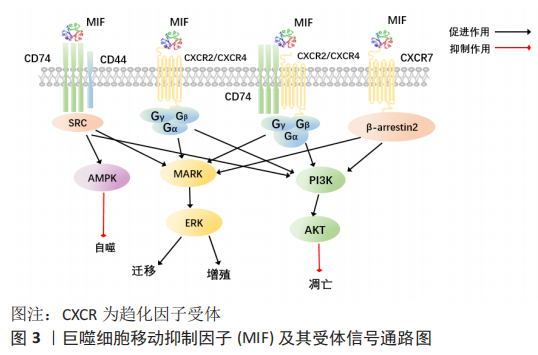
2.2.1 CD74和CD44及相关通路 CD74是主要组织相容性复合体Ⅱ类分子的细胞表面表达形式,其细胞内功能是促进肽片段装载到主要组织相容性复合体Ⅱ类分子中进行抗原呈递[14]。迄今为止,CD74主要的2个功能是作为主要组织相容性复合体Ⅱ分子的伴侣和巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的受体[8]。CD74似乎在所有巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子受体复合物中起着关键作用,如CD74敲除或应用抗CD74抗体能消除巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于CD44,CXCR2,CXCR4或CXCR7产生的作用[8]。虽然CD74对巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子下游信号转导至关重要,但是CD74不能单独诱导信号传导,需要CD44或CXCR受体作为辅助性受体募集信号,介导巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的相关通路[8,15]。CD44确定是巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子信号转导所需的共受体,CD44是一种高度多态性的蛋白质,由选择性剪接产生许多亚型[8,16]。当配体与巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子结合时,CD74招募CD44激活丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)信号通路中的ERK1/2和PI3K-AKT信号、核转录因子κB和AMPK等信号从而调控细胞增殖、细胞凋亡以及细胞迁移[7,14-15]。
2.2.2 CXCR2,CXCR4,CXCR7及相关通路 CXCR2,CXCR4和CXCR7属于CXC趋化因子受体家族。已经证明了巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子与CXCR2,CXCR4和CXCR7的直接结合[8,17]。CXCR的激活是通过其配体与受体的两个不同位点同时结合而触发的。巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子与真正的CXCRs配体,例如CXCL8(用于CXCR2)和SDF-1(用于CXCR4和CXCR7)的序列同源性很低,但包含两种用于CXCR结合和折叠成三级结构后激活必需的序列[8]。CXCR2主要在中性粒细胞和内皮细胞中表达,CXCR4和CXCR7广泛表达于造血细胞系、内皮细胞和神经细胞[8]。巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子直接与CXCR2或CXCR4结合,通过诱导G蛋白偶联受体相关信号传导,导致磷脂酶C活化细胞内钙,激活细胞内信号通路MAPK、PI3K-AKT的活性[18-19]。巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子与CXCR4结合支持动脉粥样硬化性T细胞的募集,但也与癌症转移和内皮祖细胞募集有关[20-21]。CXCR7不与任何类型的G蛋白偶联,而是与β-arrestin2偶联,导致受体与其结合配体的内在化和随后的降解[8,18]。有研究表明,CD74和CXCR2或CXCR4形成复合物,通过G蛋白的Giα亚型激活ERK1/2和AKT途径[17,19]。
通过特异性抗体封闭CD74,消除巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子通过CXCR2或CXCR4产生的影响,这表明CD74与CXCR2或CXCR4形成的物理结构在巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子信号转导过程中具有关键作用[8]。然而,CD74在介导巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子信号中的作用并不是完全不可或缺的,有研究表明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子能单独通过CXCR7激活PI3K-AKT通路,抑制细胞凋亡及促进细胞存活[17];巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子和CXCR7的直接结合刺激B细胞迁移、ERK1/2信号传导和ZAP-70[22]。
2.3 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的表达和分泌
2.3.1 影响巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子蛋白水平的调节因素 现有的研究表明多种因素能提高巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子表达量,包括缺氧、血管紧张素Ⅱ、紫外线、脂多糖和非编码RNA等[7,23-26]。
这些刺激因素通过直接或间接与巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子启动子结合,激活或抑制巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子启动子的活性,达到调控巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的目的。巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子启动子结合位点包括了HRE、AP-1、核转录因子κB、GATA、SP1、CREB和GRE等[27]。缺氧诱导产生的缺氧诱导因子1α与HRE结合可激活巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子启动子活性[8],从而增强巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的表达。巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子基因表达不仅受到启动子结合位点的调控,已知非编码RNA也与巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子表达相关。MicroRNAs(miRNAs)是一种短的非编码RNA,通过促进mRNA降解或抑制靶基因3’-UTR处的翻译来调节基因表达[7,28]。已知miRNA可调节巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的表达,例如,miR-608与巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的3’-UTR直接结合,在转录后水平负调节 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的基因表达[28]。长链非编码RNA(long non-coding RNA,lncRNA)是长度大于200个核苷酸的非编码RNA。与miRNA作用不同,lncRNA通常诱导巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的表达[7] 。
2.3.2 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的分泌途径 可溶性分泌蛋白如激素和细胞因子,通常通过经典内质网和高尔基依赖的分泌途径进行分泌活动[29]。大多数分泌蛋白质编码一段16-30个氨基酸残基的信号序列,该序列引导蛋白质从内质网进一步转移到高尔基体和分泌囊泡[29]。有研究证明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子没有N端信号序列,也没有明显的内质网靶向序列,因此巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子不需要高尔基复合物翻译后修饰,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子是由非经典途径分泌的[30]。与上述研究一致,在内质网或高尔基体中未发现巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子存在[31]。
大多数研究显示,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子在细胞质中[32-33]。在细胞质中,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子储存在囊泡状结构中[34],MERK等[26]用脂多糖刺激人单核细胞,观察到培养上清液中巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子浓度升高,2 h即可检测到,4 h达到平台期,这说明了巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的释放首先来源于预先储存在细胞中的巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子。研究显示高尔基复合体相关蛋白p115与细胞质中的巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子相结合,p115在脂多糖刺激下也部分从高尔基体向质膜重新分布。以上表明p115是调节单核/巨噬细胞分泌巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子 的关键成分。FLIEGER等[30]研究发现由于干扰ABC转运体功能的药物强烈阻断巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子分泌,但对巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子合成和转换没有影响,因此ABC转运体是巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子分泌过程中所需的关键成分。除了上述的分泌方式外,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的分泌也可以通过囊泡与外泌体的方式[35]。
当前巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子分泌的确切机制仍不清楚,期待未来出现更多对于巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子分泌方面的研究,这些研究将对未来的分子研究以及巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子分泌过程的潜在治疗方法具有重要意义。
2.4 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于干细胞的作用 干细胞根据分裂与分化是有序还是失控,可分为正常干细胞和肿瘤干细胞[36]。肿瘤干细胞同时具有干细胞和肿瘤细胞的特征,它不仅能够自我更新和正常分化,还能够异常分化为各类肿瘤细胞,将肿瘤干细胞移植到动物宿主体内时,能够形成肿瘤。正常干细胞依据发育阶段可分类为胚胎干细胞和成体干细胞[36]。胚胎干细胞是一种高度未分化的细胞,可分化为人体的各类细胞、组织甚至器官。成体干细胞是未分化的细胞,发育后可以在整个身体内发现,包括神经干细胞、间充质干细胞和表皮干细胞等[37]。来源于囊胚期的胚胎干细胞具有更强的自我更新能力和分化潜能,而成人组织中的成体干细胞自我更新能力有限,只能分化为组织特异性细胞[38]。上述有关干细胞的分类及来源,见图4。各类干细胞的来源及特点,见表1。
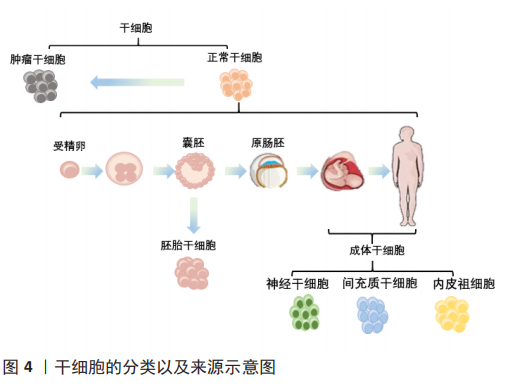
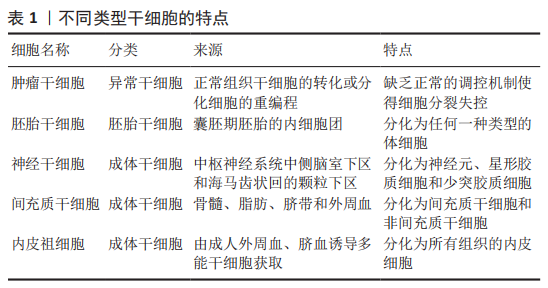
通过检索到的文献,下文将梳理巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于干细胞的研究脉络,表明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对干细胞作用的研究逐渐深入,其应用潜力逐渐彰显[39-44],深入阐述肿瘤干细胞、胚胎干细胞、神经干细胞、间充质干细胞和内皮祖细胞的特点以及巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对它们产生的作用及机制,见表2。
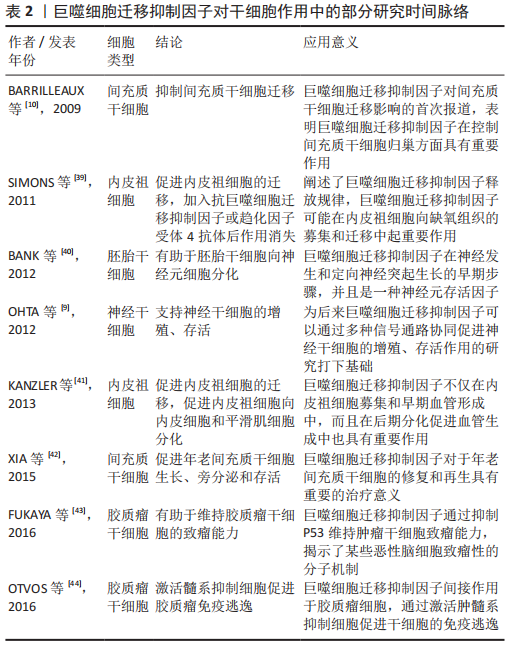
2.4.1 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子与肿瘤干细胞 正常干细胞的增殖受到严格调控,肿瘤干细胞往往缺乏正常的调控机制使得细胞分裂失控[37]。肿瘤干细胞可以来源于正常组织干细胞的转化或分化细胞的重编程[45]。肿瘤干细胞也叫做肿瘤起始细胞,是恶性肿瘤细胞的一个小亚群,固有的自我更新特性和致瘤特性使得它们可以对抗各种形式的抗癌治疗,并向远处组织传播和定植[46-47]。阐明肿瘤干细胞与肿瘤免疫微环境之间的相互作用可能是开启肿瘤治疗新时代的关键[48]。
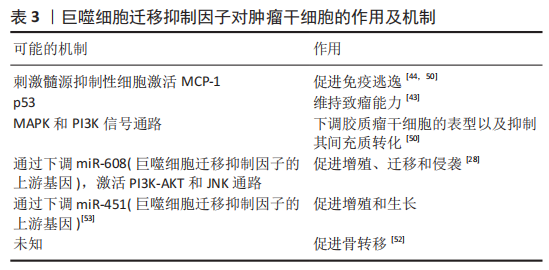
既往已有大量研究表明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子是一种促肿瘤因子,通过上调细胞外调蛋白激酶(extracellular regulated protein kinases,ERK7、蛋白激酶B)和p53等信号通路促进肿瘤细胞的增殖、血管生成和肿瘤侵袭性[49],类似地,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子通过不同的信号通路促进肿瘤干细胞的迁移、侵袭、转移、逃逸和致瘤性[28,43-44,50-53],部分作用及机制见表3。
OTVOS等[44]研究发现胶质瘤干细胞分泌巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子激活髓源抑制性细胞促进人胶质瘤干细胞的免疫逃逸。最初的研究证明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子作用于CXCR2受体,随后ALBAN等[50]证明髓源抑制性细胞的单核细胞亚群表达高水平的巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子受体CD74,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子和CD74之间的相互作用会导致下游信号MCP-1的减少。FUKAYA等[43]发现巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子在人脑肿瘤干细胞中高度表达,其通过直接抑制p53来维持脑肿瘤起始细胞的致瘤能力。SAKAMOTO等[51]研究表明胶质瘤干细胞表达巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子并且巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子有助于维持胶质瘤干细胞的干性。SOHN等[52]研究发现增加巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的表达致使前列腺癌干细胞产生骨转移。WANG等[28]过表达miR-608抑制其直接靶基因巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子激活PI3K-AKT和JNK通路,从而抑制了胶质瘤干细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭,并诱导其凋亡。MAMOORI等[53]发现过表达miR-451能够使结肠癌干细胞的标记物(Sox-2和Oct-4)以及上皮-间质的表达标记物(Snail和Twist)显著下降,MiR-451的过表达下调巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的表达,MiR-451在结肠癌细胞中的过度表达导致细胞增殖减少、凋亡增加:因此认为过表达miR-451通过巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对结肠癌干细胞有抑制作用。总之,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于肿瘤干细胞的发生发展具有促进作用。
上述研究说明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于肿瘤干细胞的促瘤作用并非一成不变,而是多种多样的,包括促进肿瘤细胞的增殖、血管生成和肿瘤侵袭性等,这意味着巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于肿瘤干细胞作用的复杂性。肿瘤干细胞通过多种复杂的分子机制促进肿瘤生长,包括遗传学、表观遗传学、代谢以及各种外在调节因素[47],了解巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于肿瘤干细胞的内在机制有助于肿瘤的治疗。将巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子及其抑制剂运用于临床中将有利于患者的治疗,例如,放射治疗是多形性胶质母细胞瘤最基本的治疗方法之一,与单纯放疗相比,添加巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子抑制剂4-IPP的联合放疗能通过抑制MAPK和PI3K信号通路下调胶质瘤干细胞的表型以及抑制其间充质转化[51]。
2.4.2 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子与胚胎干细胞 胚胎干细胞来源于囊胚期胚胎的内细胞团,能够在培养过程中长时间分裂而不分化,并且可以发育成3个初级胚层的细胞和组织[54]。胚胎干细胞有两个显著的特性,它们可以无限增殖(即具有自我更新的能力),并且可以分化为任何类型的体细胞(即它们是多能性的)。这两个特性使胚胎干细胞成为治疗各种疾病和损伤的细胞疗法的来源。现如今,胚胎干细胞已用于许多疾病和临床前研究[55]。
现有的研究认为巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子能促进小鼠胚胎干细胞的神经分化[40,56-57]。BANK等[40]认为巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子是一种神经元存活因子,促进早期的神经发生和定向神经突起生长。SARKAR等[57]研究表明,维甲酸促进胚胎干细胞的神经分化并诱导早期凋亡,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子在分化第14天时mRNA的表达增加,这表明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子可能在小鼠胚胎干细胞向神经分化过程中发挥重要作用。BANK等[40]添加浓度范围为1 pg/mL-500 ng/mL的外源性小鼠巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子到培养基中,培养48 h后大量小鼠胚胎干细胞出现长神经丝阳性突起,呈现神经元样变化。这种神经元诱导与神经生长因子(NGF)和睫状神经营养因子(CNTF)诱导的神经元表型相似。RAMAMURTHY等[56]证明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子可以促进小鼠胚胎干细胞向神经样细胞以及许旺细胞样细胞分化。巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子不仅在小鼠胚胎干细胞的分化上发挥重要作用,WANG等[58]还发现巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于小鼠胚胎干细胞的增殖具有促进作用。
当前,胚胎干细胞移植面临的3大挑战为致瘤性、免疫原性和异质性。首先,既有研究证明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子促进干细胞的神经分化,那么是否有利于解决异质性等难题还尚待挖掘。再者,人胚胎干细胞与小鼠胚胎干细胞存在差异。当前的研究主要在小鼠胚胎干上进行,还缺乏人胚胎干细胞的研究结果。与其他干细胞相比,胚胎干细胞具有强大的多能性,所以当前的大多数干细胞研究集中在胚胎干细胞上。但是,目前巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于胚胎干细胞的研究还较少,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于胚胎干细胞的主要作用及其机制都还未进行确切地研究。期待研究者在巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于胚胎干细胞的作用及其机制方面有更大的进展。
2.4.3 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子与神经干细胞 神经干细胞是一种成体干细胞,存在于在成人中枢神经系统中侧脑室下区和海马齿状回的颗粒下区[59],能够自我更新并分化为神经元、星形胶质细胞和少突胶质细胞[9]。基于这些特点,神经干细胞在神经系统疾病的再生治疗方面有着巨大的前景,如帕金森病、阿尔茨海默病和脊髓损伤[60]。
OHTA等[9]首次发现人和小鼠的神经干细胞分泌巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子,并且能够促进神经干细胞的增殖和自我更新。小鼠在胚胎第14.5天(E14.5)产生的神经干细胞分泌巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子并且表达巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子受体CD44,CXCR2,CXCR4以及CD74。在此项研究中,CD74是巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子作用于神经干细胞的受体。外源性添加巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子促进神经干细胞的增殖和自我更新,其效果随剂量依赖性上升,未发现细胞分化潜能有显著的改变。巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子能够上调Erk,AKT,AMPK,Stat3-pS727,Hes3和EGFR的表达,而EGFR基因表达增加表明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子可以刺激EGF信号通路;Stat3-pS727刺激Hes3,这是Notch信号的下游。该研究证明了巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子能够通过上调ERK,AKT,AMPK,EGF信号通路以及Notch信号通路促进神经干细胞的自我更新以及维持神经干细胞的未分化状态。基于该研究,此后也有研究多次证明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子能够促进神经干细胞的增殖存活以及维持神经干细胞的干性[61-64]。接下来,研究者们进一步探索了巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于神经干细胞的作用机制。OHTA等[62]外源性添加巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子到神经干细胞后Sox6上调,表明Sox6是巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的下游靶点;过度表达sox6使得神经干细胞数量增多,并抑制分化,并伴随Hes1,Bcl-2,Akt 表达升高;过表达Stat3后,神经干细胞中的Sox6、Hes1和Hes3基因表达均增加,免疫共沉淀结果显示,添加巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子后,Stat3与Sox6启动子的结合增加。因此说明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子使神经干细胞中Stat3与Sox6启动子结合,表明Stat3刺激巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子下游的Sox6表达能够支持神经干细胞的存活和自我更新。OHTA等[63]研究表明CHD7在神经干细胞中表达并受到巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的调控,CHD7的表达有助于神经干细胞增殖和维持干性。MEG3、miR-493e5P是巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的上游基因,ZHAO等[64]通过敲除MEG3基因,发现可以降低缺血性脑卒中后小鼠神经干细胞的miR-493e5P表达并增加巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的表达,从而促进小鼠神经干细胞的增殖。然而,ZHANG等[61]发现巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子通过Wnt/β-连环蛋白途径不仅能促进小鼠神经干细胞增殖还能促进神经干细胞的分化。
大部分研究表明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于神经干细胞的作用是促进增殖和存活,对其分化作用没有影响[9,61-64]。ZHANG等[61]认为巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子通过Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号不但能促进增殖还促进神经干细胞的分化。其原因可能为OHTA等的研究使用的小鼠神经干细胞来自胚胎14.5 d的小鼠,ZHANG等[61]使用的出生后小鼠神经干细胞,而且外源性添加的巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子浓度也有差异。因此,Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号参与了从神经干细胞生成完全功能神经元所需的大部分过程,参与早期步骤,如神经前体增殖和神经诱导,以及晚期过程,如中枢神经系统中的神经元分化[61]。上述研究主要表明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于神经干细胞的增殖存活作用是通过多个信号通路共同作用的。然而哪条信号通路是主要的?信号通路之间是否存在相互作用?巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于不同阶段的神经干细胞作用的通路是否不同?这些问题尚未阐明。巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于神经干细胞的研究起始于2012年,至今只有10年的时间,研究时间较短研究数量也少,丰富其研究对于神经系统疾病的治疗具有重大意义。
2.4.4 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子与间充质干细胞 间充质干细胞是中胚层起源的成体干细胞,具有分化为间充质和非间充质细胞的能力[65]。它们存在于许多不同的组织和器官中,如脂肪组织、骨髓、皮肤、输卵管、脐血、肝脏和肺,间充质干细胞定义为骨髓的基质细胞,具有造血干细胞的特性,但不能分化为造血细胞[66]。间充质干细胞已用于临床的干细胞移植治疗,有证据表明间充质干细胞移植到靶组织中能够存活的细胞很少,颠覆以往认知的是它不是主要通过分化机制而是主要通过旁分泌的机制来发挥一系列作用的[67]。
现有的研究表明间充质干细胞分泌巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子作用于间充质干细胞能够抑制凋亡、促进存活、延缓衰老、增加间充质干细胞的旁分泌作[23,42,68-70]。PALUMBO等[70]发现人间充质干细胞在缺氧的条件下能够上调其胞内和胞外的巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子水平,过表达巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子激活AKT通路,从而能延缓细胞衰老。XIA等[23]也发现缺氧或者饥饿状态能够增加大鼠间充质干细胞的分泌,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子通过与CD74相互作用刺激c-Met,导致下游PI3K-AKT-FOXO3a信号传导,降低氧化应激,从而保护间充质干细胞免受缺氧/饥饿诱导的凋亡。XIA等[68]通过添加外源性巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子抑制氧化应激和激活PI3K-Akt信号通路,将间充质干细胞从阿霉素诱导的衰老状态中解救出来,提高了间充质干细胞的增殖率、存活率、旁分泌功能、端粒长度和端粒酶活性。老年大鼠(24个月)间充质干细胞相比于年轻大鼠(6个月)间充质干细胞巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的表达量和分泌量下调。XIA等[42]研究认为外源性添加巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子可通过与CD74相互作用并随后激活AMPK-FOXO3a信号通路,使间充质干细胞从年龄诱导的衰老状态中恢复年轻状态,增强间充质干细胞的生长、旁分泌功能和存活率。ZHANG等[69]则认为人间充质干细胞上的巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子表达与间充质干细胞衰老呈负相关,过表达巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子可以使年老间充质干细胞恢复增殖能力,而这种作用是通过激活自噬来达成的。
间充质干细胞具有迁移能力,其向损伤部位的迁移取决于间充质干细胞表达的大量细胞黏附分子和趋化因子受体,而间充质干细胞定向迁移到损伤部位的特性称作为“归巢”[71]。除了在抗凋亡和抗衰老方面的作用,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子也证明可以通过结合受体CD74抑制人间充质干细胞的迁移[72]。在2009年,BARRILLEAUX等[10]对于巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子作用于人间充质干细胞迁移的首次报告中表明,在85 ng/mL的培养基中发现,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子抑制50%的人间充质干细胞迁移,在更高的浓度水平,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子几乎完全抑制了人间充质干细胞迁移,并且小分子巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子拮抗剂可以对抗这种抑制迁移作用[10,73]。人软骨终板来源的干细胞是一种间充质干细胞,XIONG等[74]研究发现巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子通过CD74抑制人软骨终板来源的干细胞的迁移。LOURENCO等[75]认为肿瘤细胞旁分泌巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子通过CXCR4激活将MAPK通路中的ERK和JNK分支促进人间充质干细胞向肿瘤细胞归巢。
目前,间充质细胞的外泌体研究备受关注。ZHU等[76]研究发现人间充质干细胞工程化的巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子外泌体可通过促进血管生成、抑制细胞凋亡、减少纤维化。在体内外保护心脏功能而发挥心脏保护作用,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子外泌体的生物学活性机制涉及miR-133a-3p及其下游AKT信号通路。CHEN等[77]研究表明经巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子预处理的人间充质干细胞的外泌体通过lncRNA-NEAT1直接转移对心肌细胞具有保护作用,lncRNA-NEAT1通过对miR-1423p的竞争性内源性RNA活性发挥抗凋亡分子的作用。
因此,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于间充质干细胞的作用及机制分成3个部分。第一,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于间充质干细胞具有抗衰老和抗凋亡的作用,这种作用是通过多种信号机制产生的,PI3K-AKT信号通路在多个研究中被证实,可以认为是主要的信号通路。第二,大部分研究显示巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子抑制间充质干细胞的迁移。LOURENCO等[75]认为巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子促进间充质干细胞的归巢。其迁移的作用为何会产生完全相反的作用?是否通过不同的信号通路会产生不一样的结果?其机制较为复杂,还有待更多的探索研究。第三,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子与间充质干细胞的外泌体心脏保护方面的研究已经崭露头角,关于其他疾病的研究还有待挖掘。由于间充质干细胞来源的多样性,还需注意不同来源的间充质干细胞是否在作用与机制方面存在差异。间充质干细胞具有的分化能力、旁分泌作用以及归巢能力,在很多难治性疾病中表现出强大的治疗潜力与良好应用前景。深入了解巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于间充质干细胞的多样作用及其机制有利于发挥其潜在的治疗作用。
2.4.5 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子与内皮祖细胞 内皮祖细胞是一种成体干细胞,具有分化为所有组织内皮细胞的潜能。内皮祖细胞可以由成人外周血和脐血中获得,也可以从诱导的多能干细胞中分化而来[78]。内皮祖细胞是指能够分化为成熟内皮细胞和血管生成(血管网络的新生形成)的细胞群[79]。内皮祖细胞可以分为早期内皮祖细胞和晚期内皮祖细胞。由于内皮祖细胞具有很高的增殖潜能,循环中的内皮祖细胞负责新血管的生成。内皮祖细胞通过以下两种机制发挥其作用:第一,晚期内皮祖细胞主要是在血管网的形成过程中可以直接并入新的血管组织;第二,早期内皮祖细胞主要是释放一些促进血管生成的介质,包括血管内皮生长因子、一氧化氮和基质金属蛋白酶蛋白等,促进内皮修复和内膜新生[80-81]。
现有的研究一致认为巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子通过CXCR4作用于内皮祖细胞,促进内皮祖细胞的迁移从而促进血管重建[39,41]。SIMONS等[39]发现巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子可能在内皮祖细胞向缺氧组织的募集和迁移中起重要作用。多个实验证明10-100 ng/mL的巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子均通过CXCR4受体对内皮祖细胞的迁移有促进作用[20,39,41,81]。KANZLER等[41]证明缺氧诱导小鼠内皮祖细胞上CXCR2受体和CXCR4受体的上调,而不是CD74的上调,并且诱导小鼠内皮祖细胞自分泌巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子;外源性添加50 ng/mL的巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子增强了小鼠内皮祖细胞的迁移活性和黏附能力。除此以外,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子促进内皮祖细胞向内皮细胞和平滑肌细胞分化,确定了巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子不仅在内皮祖细胞募集和早期血管形成过程中,而且内皮祖细胞后期分化在后期血管生成过程中也具有重要作用。鉴于内皮祖细胞对于血管重建和创伤修复的作用,除了基础研究外,在临床中血管疾病、皮瓣移植等方面进行了研究[81-83]。
多项研究表明创伤、炎症及手术等因素使得体内血清的巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子含量上升并促进内皮祖细胞招募迁移。例如,EMONTZPOHL等[82]报道与未接受皮瓣移植手术患者相比,接受带蒂皮瓣移植手术的患者血清巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子浓度增高,并且促进内皮祖细胞迁移,抗巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子抗体可以阻断这种作用。在小鼠视网膜病变中,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子在缺血诱导的视网膜新生血管中具有促血管生成和促炎症特性,这种作用可能是与内皮祖细胞的募集和炎症有关[84]。然而,在具体的疾病中,内皮祖细胞的迁移往往由多种因子参与调节[20]。GRIEB等[20]在对急性创伤与慢性创伤中的巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子研究显示,与对照组相比,急性创伤组血清中的巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子水平显著升高,急性伤口的血清显著增强了内皮祖细胞的定向迁移,特异性抗巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子抗体部分抑制这种迁移作用。这一观察结果可能反映了患者血清的复杂性;急性创伤患者血清中的多种成分可能参与调节内皮祖细胞的迁移和募集。文章再次观察到,抗巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子抗体未能完全抑制内皮祖细胞迁移,这为多种因素和蛋白质对内皮细胞趋化性的贡献提供了进一步的证据。
综上所述,可以看出不同文献中使用不同浓度的外源性巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子均能促进内皮祖细胞的迁移,且此效果是通过CXCR2受体和CXCR4受体而不是巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子经典受体CD74。巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子不仅促进内皮祖细胞的迁移,而且促进内皮祖细胞向内皮细胞和平滑肌细胞分化。确定了巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子不仅在内皮祖细胞募集和早期血管形成过程中,而且内皮祖细胞后期分化在后期血管生成过程中也具有重要作用。除了在基础研究中,在临床研究中也表明巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子作用于内皮祖细胞有利于新生血管的形成。接下来研究者们需要进一步探索用药剂量、作用持续时间以及安全性等关键问题,进一步实现巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于内皮祖细胞作用的临床转化。
| [1] BALISTRERI CR, DE FALCO E, BORDIN A, et al. Stem cell therapy: old challenges and new solutions. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(4):3117-3131. [2] ALESSANDRINI M, PREYNAT-SEAUVE O, DE BRUIN K, et al. Stem cell therapy for neurological disorders. S Afr Med J. 2019;109(8b):70-77. [3] NAIR N, GONGORA E. Stem cell therapy in heart failure: where do we stand today? Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(4):165489. [4] BUJKO K, KUCIA M, RATAJCZAK J, et al. Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs). Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1201:49-77. [5] AL-GHADBAN S, ARTILES M, BUNNELL BA. Adipose stem cells in regenerative medicine: looking forward. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:837464. [6] KWON SG, KWON YW, LEE TW, et al. Recent advances in stem cell therapeutics and tissue engineering strategies. Biomater Res. 2018;22:36. [7] SUMAIYA K, LANGFORD D, NATARAJASEENIVASAN K, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF): a multifaceted cytokine regulated by genetic and physiological strategies. Pharmacol Ther. 2022;233:108024. [8] JANKAUSKAS SS, WONG DWL, BUCALA R, et al. Evolving complexity of MIF signaling. Cell Signal. 2019;57:76-88. [9] OHTA S, MISAWA A, FUKAYA R, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) promotes cell survival and proliferation of neural stem/progenitor cells. J Cell Sci. 2012;125(Pt 13):3210-3220. [10] BARRILLEAUX BL, PHINNEY DG, FISCHER-VALUCK BW, et al. Small-molecule antagonist of macrophage migration inhibitory factor enhances migratory response of mesenchymal stem cells to bronchial epithelial cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(9):2335-2346. [11] BECKER-HERMAN S, ROZENBERG M, HILLEL-KARNIEL C, et al. CD74 is a regulator of hematopoietic stem cell maintenance. PLoS Biol. 2021;19(3):e3001121. [12] KARABOWICZ J, DLUGOSZ E, BASKA P, et al. Nematode orthologs of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) as modulators of the host immune response and potential therapeutic targets. Pathogens. 2022;11(2):258. [13] SUN HW, BERNHAGEN J, BUCALA R, et al. Crystal structure at 2.6-A resolution of human macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996; 93(11):5191-5196. [14] BILSBORROW JB, DOHERTY E, TILSTAM PV, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) as a therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019;23(9):733-744. [15] SU H, NA N, ZHANG X, et al. The biological function and significance of CD74 in immune diseases. Inflamm Res. 2017;66(3):209-216. [16] PONTA H, SHERMAN L, HERRLICH PA. CD44: from adhesion molecules to signalling regulators. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4(1):33-45. [17] CHATTERJEE M, BORST O, WALKER B, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor limits activation-induced apoptosis of platelets via CXCR7-dependent Akt signaling. Circ Res. 2014;115(11):939-949. [18] VAN DER VORST EP, DöRING Y, WEBER C. Chemokines and their receptors in Atherosclerosis. J Mol Med (Berl). 2015;93(9):963-971. [19] DAYAWANSA NH, GAO XM, WHITE DA, et al. Role of MIF in myocardial ischaemia and infarction: insight from recent clinical and experimental findings. Clin Sci (Lond). 2014;127(3):149-161. [20] GRIEB G, SIMONS D, ECKERT L, et al. Levels of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and glucocorticoids in chronic wound patients and their potential interactions with impaired wound endothelial progenitor cell migration. Wound Repair Regen. 2012;20(5):707-714. [21] SINITSKI D, KONTOS C, KRAMMER C, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)-based therapeutic concepts in atherosclerosis and inflammation. Thromb Haemost. 2019;119(4):553-566. [22] ALAMPOUR-RAJABI S, EL BOUNKARI O, ROT A, et al. MIF interacts with CXCR7 to promote receptor internalization, ERK1/2 and ZAP-70 signaling, and lymphocyte chemotaxis. FASEB J. 2015;29(11):4497-4511. [23] XIA W, XIE C, JIANG M, et al. Improved survival of mesenchymal stem cells by macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015;404(1-2):11-24. [24] LIANG JN, ZOU X, FANG XH, et al. The Smad3-miR-29b/miR-29c axis mediates the protective effect of macrophage migration inhibitory factor against cardiac fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865(9):2441-2450. [25] LEE J, LEE J, JUNG E, et al. Ultraviolet A regulates adipogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells via up-regulation of Kruppel-like factor 2. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(42):32647-32656. [26] MERK M, BAUGH J, ZIEROW S, et al. The Golgi-associated protein p115 mediates the secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. J Immunol. 2009;182(11):6896-6906. [27] 黄琳,马元芬,王灵军,等.巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子调节寄生虫与宿主免疫系统相互作用机制的研究进展[J].中国血吸虫病防治杂志,2019,31(4):446-449. [28] WANG Z, XUE Y, WANG P, et al. MiR-608 inhibits the migration and invasion of glioma stem cells by targeting macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Oncol Rep. 2016;35(5):2733-2742. [29] LEE MC, MILLER EA, GOLDBERG J, et al. Bi-directional protein transport between the ER and Golgi. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:87-123. [30] FLIEGER O, ENGLING A, BUCALA R, et al. Regulated secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor is mediated by a non-classical pathway involving an ABC transporter. FEBS Lett. 2003;551(1-3):78-86. [31] EICKHOFF R, JENNEMANN G, HOFFBAUER G, et al. Immunohistochemical detection of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in fetal and adult bovine epididymis: release by the apocrine secretion mode? Cells Tissues Organs. 2006; 182(1):22-31. [32] ROTH S, AGTHE M, EICKHOFF S, et al. Secondary necrotic neutrophils release interleukin-16C and macrophage migration inhibitory factor from stores in the cytosol. Cell death Discov. 2015;1(1):1-9. [33] DUMITRU CA, GHOLAMAN H, TRELLAKIS S, et al. Tumor-derived macrophage migration inhibitory factor modulates the biology of head and neck cancer cells via neutrophil activation. Int J Cancer. 2011;129(4):859-869. [34] NISHINO T, BERNHAGEN J, SHIIKI H, et al. Localization of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) to secretory granules within the corticotrophic and thyrotrophic cells of the pituitary gland. Mol Med. 1995;1(7):781-788. [35] COSTA-SILVA B, AIELLO NM, OCEAN AJ, et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17(6):816-826. [36] TALUKDAR S, DAS SK, EMDAD L, et al. Autophagy and senescence: Insights from normal and cancer stem cells. Adv Cancer Res. 2021;150:147-208. [37] ZAKRZEWSKI W, DOBRZYŃSKI M, SZYMONOWICZ M, et al. Stem cells: past, present, and future. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):68. [38] KOLIOS G, MOODLEY Y.Introduction to stem cells and regenerative medicine. Respiration. 2013;85(1):3-10. [39] SIMONS D, GRIEB G, HRISTOV M, et al. Hypoxia-induced endothelial secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and role in endothelial progenitor cell recruitment. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(3):668-678. [40] BANK LM, BIANCHI LM, EBISU F, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor acts as a neurotrophin in the developing inner ear. Development. 2012;139(24):4666-4674. [41] KANZLER I, TUCHSCHEERER N, STEFFENS G, et al. Differential roles of angiogenic chemokines in endothelial progenitor cell-induced angiogenesis. Basic Res Cardiol. 2013;108(1):310. [42] XIA W, ZHANG F, XIE C, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor confers resistance to senescence through CD74-dependent AMPK-FOXO3a signaling in mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6(1):82. [43] FUKAYA R, OHTA S, YAGUCHI T, et al. MIF maintains the tumorigenic capacity of brain tumor-initiating cells by directly inhibiting p53. Cancer Res. 2016;76(9):2813-2823. [44] OTVOS B, SILVER DJ, MULKEARNS-HUBERT EE, et al. Cancer stem cell-secreted macrophage migration inhibitory factor stimulates myeloid derived suppressor cell function and facilitates glioblastoma immune evasion. Stem Cells. 2016;34(8): 2026-2039. [45] SMITH J, ZYOUD A, ALLEGRUCCI C. A case of identity: HOX genes in normal and cancer stem cells. Cancers. 2019;11(4):512. [46] KUŞOĞLU A, BIRAY AVCı Ç. Cancer stem cells: a brief review of the current status. Gene. 2019;681:80-85. [47] CLARA JA, MONGE C, YANG Y, et al. Targeting signalling pathways and the immune microenvironment of cancer stem cells -a clinical update. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020;17(4):204-232. [48] SIVANDZADE F, CUCULLO L. Regenerative stem cell therapy for neurodegenerative diseases: an overview. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):2153. [49] PENTICUFF JC, WOOLBRIGHT BL, SIELECKI TM, et al. MIF family proteins in genitourinary cancer: tumorigenic roles and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Urol. 2019;16(5):318-328. [50] ALBAN TJ, BAYIK D, OTVOS B, et al. Glioblastoma myeloid-derived suppressor cell subsets express differential macrophage migration inhibitory factor receptor profiles that can be targeted to reduce immune suppression. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1191. [51] SAKAMOTO D, TAKAGI T, FUJITA M, et al. Basic gene expression characteristics of glioma stem cells and human glioblastoma. Anticancer Res. 2019;39(2):597-607. [52] SOHN HM, KIM B, PARK M, et al. Effect of CD133 overexpression on bone metastasis in prostate cancer cell line LNCaP. Oncol Lett. 2019;18(2):1189-1198. [53] MAMOORI A, WAHAB R, VIDER J, et al. The tumour suppressor effects and regulation of cancer stem cells by macrophage migration inhibitory factor targeted miR-451 in colon cancer. Gene. 2019;697:165-174. [54] GAO SW, LIU F. Novel insights into cell cycle regulation of cell fate determination. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2019;20(6):467-475. [55] YAMANAKA S. Pluripotent stem cell-based cell therapy-promise and challenges. Cell Stem Cell. 2020;27(4):523-531. [56] RAMAMURTHY P, WHITE JB, YULL PARK J, et al. Concomitant differentiation of a population of mouse embryonic stem cells into neuron-like cells and schwann cell-like cells in a slow-flow microfluidic device. Dev Dyn. 2017;246(1):7-27. [57] SARKAR SA, SHARMA RP. Expression of selected apoptosis related genes, MIF, IGIF and TNF alpha, during retinoic acid-induced neural differentiation in murine embryonic stem cells. Cell Struct Funct. 2002;27(2):99-107. [58] WANG X, CHEN T, LENG L, et al. MIF produced by bone marrow-derived macrophages contributes to teratoma progression after embryonic stem cell transplantation. Cancer Res. 2012;72(11):2867-2878. [59] FERRARO F, CELSO CL, SCADDEN D. Adult stem cels and their niches. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;695:155-168. [60] LIU D, PAVATHUPARAMBIL ABDUL MANAPH N, AL-HAWWAS M, et al. Coating materials for neural stem/progenitor cell culture and differentiation. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(8):463-474. [61] ZHANG X, CHEN L, WANG Y, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes proliferation and neuronal differentiation of neural stem/precursor cells through Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2013;9(10):1108-1120. [62] OHTA S, MISAWA A, LEFEBVRE V, et al. Sox6 up-regulation by macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes survival and maintenance of mouse neural stem/progenitor cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74315. [63] OHTA S, YAGUCHI T, OKUNO H, et al. CHD7 promotes proliferation of neural stem cells mediated by MIF. Mol Brain. 2016;9(1):96. [64] ZHAO F, XING Y, JIANG P, et al. LncRNA MEG3 inhibits the proliferation of neural stem cells after ischemic stroke via the miR-493-5P/MIF axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;568:186-192. [65] TORALDO DM, TORALDO S, CONTE L. The clinical use of stem cell research in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a critical analysis of current policies. J Clin Med Res. 2018;10(9):671-678. [66] VASANTHAN J, GURUSAMY N, RAJASINGH S, et al. Role of human mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative therapy. Cells. 2020. doi:10.3390/cells10010054. [67] KULUBYA ES, CLARK K, HAO DK, et al. The unique properties of placental mesenchymal stromal cells: a novel source of therapy for congenital and acquired spinal cord injury. Cells. 2021;10(11):2837. [68] XIA W, HOU M. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor rescues mesenchymal stem cells from doxorubicin-induced senescence though the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(2):1127-1137. [69] ZHANG Y, ZHU W, HE H, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor rejuvenates aged human mesenchymal stem cells and improves myocardial repair. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(24):12641-12660. [70] PALUMBO S, TSAI TL, LI WJ. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor regulates AKT signaling in hypoxic culture to modulate senescence of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(8):852-865. [71] LOU SY, DUAN YT, NIE HZ, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: biological characteristics and application in disease therapy. Biochimie. 2021;185:9-21. [72] BARRILLEAUX BL, FISCHER-VALUCK BW, GILLIAM JK, et al. Activation of CD74 inhibits migration of human mesenchymal stem cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2010;46(6):566-572. [73] FISCHER-VALUCK BW, BARRILLEAUX BL, PHINNEY DG, et al. Migratory response of mesenchymal stem cells to macrophage migration inhibitory factor and its antagonist as a function of colony-forming efficiency. Biotechnol Lett. 2010;32(1): 19-27. [74] XIONG CJ, HUANG B, ZHOU Y, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor inhibits the migration of cartilage end plate-derived stem cells by reacting with CD74. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43984. [75] LOURENCO S, TEIXEIRA VH, KALBER T, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor-CXCR4 is the dominant chemotactic axis in human mesenchymal stem cell recruitment to tumors. J Immunol. 2015;194(7):3463-3474. [76] ZHU W, SUN L, ZHAO P, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor facilitates the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes in acute myocardial infarction through upregulating miR-133a-3p. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19(1):61. [77] CHEN H, XIA W, HOU M. LncRNA-NEAT1 from the competing endogenous RNA network promotes cardioprotective efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes induced by macrophage migration inhibitory factor via the miR-142-3p/FOXO1 signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):31. [78] PETERS EB. Endothelial progenitor cells for the vascularization of engineered tissues. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2018;24(1):1-24. [79] PERROTTA F, PERNA A, KOMICI K, et al. The state of art of regenerative therapy in cardiovascular ischemic disease: biology, signaling pathways, and epigenetics of endothelial progenitor cells. Cells. 2020;9(8):1886. [80] KOU F, ZHU C, WAN H, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells as the target for cardiovascular disease prediction, personalized prevention, and treatments: progressing beyond the state-of-the-art. EPMA J. 2020;11(4):629-643. [81] EMONTZPOHL C, SIMONS D, KRAEMER S, et al. Isolation of endothelial progenitor cells from healthy volunteers and their migratory potential influenced by serum samples after cardiac surgery. J Vis Exp. 2017;(120):e55192. [82] EMONTZPOHL C, GOETZENICH A, SIMONS D, et al. Key role of MIF in the migration of endothelial progenitor cells in patients during cardiac surgery. Int J Cardiol. 2015;181:284-287. [83] GRIEB G, PIATKOWSKI A, SIMONS D, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is a potential inducer of endothelial progenitor cell mobilization after flap operation. Surgery. 2012;151(2):268-277.e261. [84] WANG J, LIN J, KAISER U, et al. Absence of macrophage migration inhibitory factor reduces proliferative retinopathy in a mouse model. Acta Diabetol. 2017; 54(4):383-392. [85] HU L, ZHAO B, WANG S. Stem-cell therapy advances in China. Hum Gene Ther. 2018;29(2):188-196. |
| [1] | 孙可欣, 曾今实, 李佳, 蒋海越, 刘霞. 力学刺激提高生物3D打印软骨构建物基质的形成[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | 党 祎, 杜成砚, 姚红林, 袁能华, 曹 金, 熊 山, 张顶梅, 王 信. 激素型骨坏死与氧化应激[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [3] | 徐星星, 文超举, 孟茂花, 王勤英, 陈镜桥, 董 强. 口腔种植中的碳纳米材料[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [4] | 杨怡天, 王 璐, 姚 蔚, 赵 彬. 生物支架与巨噬细胞在骨再生中的相互影响及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1071-1079. |
| [5] | 李 诚, 郑国爽, 蒯贤东, 于炜婷. 海藻酸盐支架修复关节软骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [6] | 史业弘, 王 成, 陈世玖. 小口径人工血管的早期血栓形成与预防[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1110-1116. |
| [7] | 唐昊天, 廖荣东, 田 京. 压电材料修复骨缺损的应用及设计思路[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [8] | 许 言, 李 平, 赖春花, 朱培君, 杨 烁, 徐淑兰. 血管化骨再生中压电生物材料的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1126-1132. |
| [9] | 薛 婷, 张新日, 孔晓梅. 纳米材料多模态显像示踪技术在间充质干细胞治疗尘肺中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1133-1140. |
| [10] | 李欣悦, 李熙恒, 毛天娇, 唐 亮, 李 江. 三维培养人牙周膜干细胞的形态、活性及成骨分化能力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 846-852. |
| [11] | 李启程, 邓 进, 付小洋, 韩 娜. 骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体对成肌细胞缺氧状态的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [12] | 王 敏, 尹秀山, 王盈熹, 张 妍, 赵 龙, 夏书月. 吸入骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体减轻慢性阻塞性肺疾病的炎性损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [13] | 郝柳芳, 段红梅, 王子珏, 郝 飞, 郝 鹏, 赵 文, 高钰丹, 杨朝阳, 李晓光. 转基因小鼠脊髓损伤后室管膜细胞的时空动态变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 883-889. |
| [14] | 李晓寅, 杨晓青, 陈淑莲, 李正超, 王梓琪, 宋 震, 朱达仁, 陈旭义. 胶原/丝素蛋白支架联合神经干细胞治疗创伤性脊髓损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 890-896. |
| [15] | 黄贵江, 季雨伟, 赵 鑫, 杨 艺, 赵玉兰, 王佩锦, 唐 薇, 角建林. 胎盘间充质干细胞不同给药途径治疗骨质疏松性骨折树鼩的疗效和机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 909-914. |
随着人们对于巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的深入认识,已证明其在对不同病原体的耐药性和驱动各种类型的免疫和自身免疫疾病方面发挥了关键作用,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子在多种类型的恶性肿瘤中表达增强,其表达与疾病进展相关[8]。巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子在病理条件下的作用似乎多种多样,既有正面作用也有负面作用,因此,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子是有争议的细胞因子[7]。现有研究证明,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子在多种干细胞上表达并且调节多种干细胞的增殖、分化和迁移,包括神经干细胞、间充质干细胞和造血干细胞
等[9-11]。到目前为止,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对干细胞作用的研究还处于初期阶段,尚未就巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对干细胞产生的作用有非常清晰的认识。
文章首次就巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于干细胞的作用进行综述,概述了巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子基因与巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子蛋白结构、巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子相关受体及其通路、巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的分泌和表达并重点介绍了巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于肿瘤干细胞、胚胎干细胞、神经干细胞、间充质干细胞和内皮祖细胞的作用及机制,有助于填补巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的研究空白,以期为干细胞治疗提供新思路。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2021年10月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 重点检索时间范围为2010年1月至2021年10月,同时纳入少量远期经典文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed和中国知网数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“macrophage migration inhibitory factor,cancer stem cell,embryonic stem cell,neural stem cell,mesenchymal stem cell,endothelial progenitor cell,stem cell therapy,Organizational engineering”,中文检索词为“巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子、肿瘤干细胞、胚胎干细胞、神经干细胞、间充质干细胞、内皮祖细胞、干细胞治疗、组织工程”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究性论文及综述性论文。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 PubMed和中国知网数据库文献检索策略,见图1。
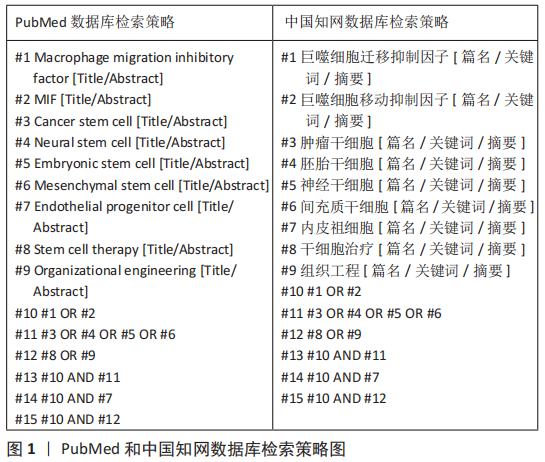
1.1.8 检索文献量 初检文献量253篇。
1.2 入组标准1.2.1 纳入标准 ①巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子与干细胞相关的研究和综述;②具有创新性的文章。
1.2.2 排除标准 重复性、与文章目的相关性低的研究。
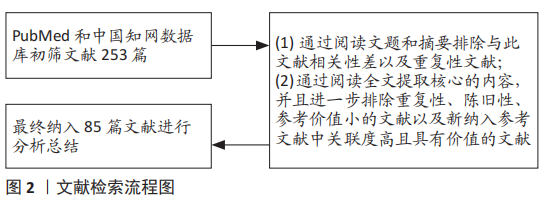
1.3 文献质量评估及数据提取 计算机初检得到253篇文献,经资料收集者互相评估纳入文献的有效性和适用性,通过阅读文题和摘要进行初步筛选;排除中英文文献重复性研究、内容不相关的文献;增加文献阅读中经典的、相关性强的参考文献,最后纳入85篇文献进行综述。文献筛选流程,见图2。
首先,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对干细胞影响的研究大都是在体外的细胞水平进行的,将来如何将这些研究转移至体内并进行实验研究是一个很大的挑战。其次,文章中出现巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对不同细胞产生的完全相反的作用,或者相同的细胞也产生完全不同的效果。例如巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子通过CXCR4促进间充质干细胞以及内皮祖细胞的迁移,而通过CD74抑制间充质干细胞的迁移。是否由于作用于不同的受体产生完全相反的作用,或者是外源性添加的巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子浓度产生的影响等,其具体的原因和复杂的内在机制还有待
研究。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 到目前为止,人们还没有就巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于干细胞产生的作用有非常清晰的认识。文章首次对巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子与干细胞的作用进行综述。该文章综述了巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子基因与巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子蛋白结构、巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子相关受体及其通路、巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的表达和分泌,并重点阐述巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于肿瘤干细胞、胚胎干细胞、神经干细胞、间充质干细胞及内皮祖细胞的作用及机制。
3.3 综述的局限性 除了上述干细胞,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于造血干细胞及心肌干细胞等也有少许研究。由于研究报道太少,不成系统,这里没有具体列出。尽管还存在问题,随着技术的进步和理论水平的提高,相信上述问题在人们的不懈努力之下将会逐步克服。
3.4 综述的重要意义 干细胞疗法是治疗多种疾病和损伤的一种前沿的方法。中国的干细胞研究发展迅速,已经建立了大约100个干细胞库,10种干细胞药物目前正在审批过程中,已经注册了400多个基于干细胞的临床试验[85]。现有研究证明,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子在多种干细胞上表达并且调节多种干细胞的增殖、分化和迁移。总之,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于干细胞的作用目前还处于初期阶段,人们需要利用前期对于巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的认识,对巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子在干细胞产生的影响进行进一步的实验研究,有利于人们完善巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的认识,有利于了解干细胞生长发育过程的机制,为干细胞的治疗提供新思路。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 首先,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于干细胞部分的作用存在一定的争议,确切机制需要进一步更为系统的验证。后期应从分子、蛋白、细胞和动物水平入手,再到临床随机对照试验上进一步验证。其次,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于干细胞的研究起步较晚,缺乏高水平的研究数据及证据。目前巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于干细胞的研究仍处在初期阶段,除了文章中所涉及到的干细胞,其他干细胞的领域鲜有文献报道。还需要更多的高水平研究涉足巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于其他干细胞的作用。最后,根据文章综述结果,巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对于干细胞有一定的应用价值。对于巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子的探索是有价值的,有理由相信巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子终有一日能够应用于干细胞治疗方面。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程

文题释义:#br# 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子:是由多种细胞类型产生的一种多功能细胞因子,影响多种生物过程的调节功能,如增殖、迁移、凋亡和细胞周期进程。#br# 干细胞治疗:是把健康的干细胞移植到患者体内,以修复或替换受损细胞或组织,从而达到治愈的目的。#br# 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
干细胞是一种可以自我更新并且具有分化潜能的细胞。由于上述特性,干细胞可以修复、替换或再生细胞、组织或器官,从而修复任何原因造成的受损功能,包括先天性缺陷、疾病、创伤和衰老[1]。许多干细胞正在研究并应用于治疗神经退行性疾病、血液病、心脏病和其他疾病[2-4]。在过去十年中,基于干细胞的再生医学已经发展到临床试验和治疗应用[5]。因此,干细胞治疗是一种很有前景的治疗方法。尽管如此,干细胞治疗的实验研究以及临床应用还存在一系列的问题。组织工程是将特定类型的细胞或细胞产物传送到受损组织或器官以恢复组织和器官功能[6]。干细胞的研究是组织工程的基础。干细胞关键特征、自我更新和分化特性受到多种信号通路、翻译因子和表观遗传变化等不同机制的严格控制。因此,深入了解干细胞的生长发育机制对于干细胞治疗以及组织工程意义重大。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||