中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (14): 2257-2265.doi: 10.12307/2023.154
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
循环miRNAs作为骨骼肌对运动反应与适应的生物标志物的可能性
周 进,徐 贞
- 江西财经大学体育学院,江西省南昌市 330013
-
收稿日期:2021-07-06接受日期:2021-07-06出版日期:2023-05-18发布日期:2022-09-30 -
通讯作者:周进,博士,副教授,江西财经大学体育学院,江西省南昌市 330013 -
作者简介:周进,女,1979年生,重庆市人,汉族,博士,副教授,主要从事运动人体科学专业方面的教学与科研。
Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers of exercise response and adaptation in the skeletal muscle
Zhou Jin, Xu Zhen
- School of Physical Education, Jiangxi University of Finance and Economics, Nanchang 330013, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-07-06Accepted:2021-07-06Online:2023-05-18Published:2022-09-30 -
Contact:Zhou Jin, School of Physical Education, Jiangxi University of Finance and Economics, Nanchang 330013, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Zhou Jin, PhD, Associate professor, School of Physical Education, Jiangxi University of Finance and Economics, Nanchang 330013, Jiangxi Province, China
摘要:
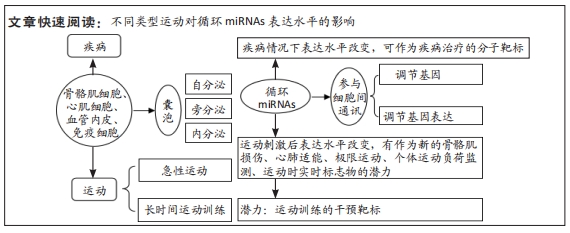
文题释义:
运动:运动通过调节蛋白质平衡和调节卫星细胞的命运来诱导人类骨骼肌质量变化,发挥转录、翻译和翻译后的调节,并诱导表观遗传修饰和控制mRNA的稳定性,这些都有助于蛋白质合成的调节。骨骼肌是一种动态组织,能根据生长、衰老、身体活动、营养和健康状况而肥大或萎缩。运动的类型有多种,主要分为有氧运动、无氧运动,运动也有多种方式,如马拉松、中长跑、高强度间歇训练、抗阻训练等,各种运动方式通过miRNAs以不同的机制调节肌肉质量和机体健康。
循环miRNAs:微小核糖核酸(microRNAs,miRNAs)是一类重要的生命活动调控因子,已证实循环miRNAs是多种疾病新的生物标志物,与疾病的发生发展密切相关。近年来研究发现miRNAs可以通过被微囊泡包裹的形式稳定存在于血液和其他体液中,它们被称为循环miRNAs(ci-miRNAs)。除了病理条件导致的机体变化外,循环miRNAs也参与调节了体育运动导致的反应和适应,从而可能有助于体育运动观察到的有益影响。
背景:运动对机体产生刺激反应和生物学适应,对骨骼肌和心肌中的miRNAs表达水平产生影响。不同运动方式能诱导不同的生物适应,比较而言离心收缩运动相对于向心收缩运动对肌肉刺激更大、生物学效应更积极。miRNAs是短的非编码RNA,通过调节转录后的基因表达来影响生物过程。在大多数体液中有稳定存在的循环miRNAs,对运动类型和强度有高度敏感性和特异性。
目的:综述不同运动类型对循环miRNAs表达水平的影响,分析了循环miRNAs作为骨骼肌对运动反应与适应的生物标志物的可能性,以期为运动训练和运动促进健康过程中的干预提供参考。
方法:检索有关骨骼肌miRNAs、循环miRNAs、运动对miRNAs影响的文献,以“exercise;myomiRNAs;ci-miRNAs;HIIT;biomarker”为关键词,在PubMed、Web of Science等数据库进行检索;以“运动、miRNAs、myomiRNAs、ci-miRNAs、反应、生物标志物”为关键词,在CNKI、万方、维普等数据库进行检索。对检索获得的全部文献阅读、分析、判断,最终纳入符合标准的86篇文献进行归纳总结。
结果与结论:循环miRNAs的表达水平会随着人体运动类型和运动强度的改变而升高或降低,有非常大的潜力成为运动反应和适应的生物标志物。对于各种具体的运动方式产生的循环miRNAs表达水平的具体变化,及其在运动过程中和恢复过程中的生物学意义,还存在很大的研究空间。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1292-7164(周进)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
周 进, 徐 贞. 循环miRNAs作为骨骼肌对运动反应与适应的生物标志物的可能性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(14): 2257-2265.
Zhou Jin, Xu Zhen. Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers of exercise response and adaptation in the skeletal muscle[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(14): 2257-2265.
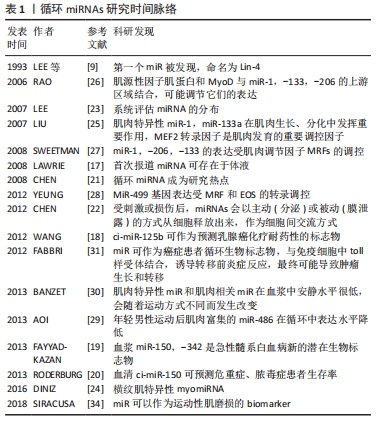
第一个mRNA早在1993年被发现[9],但一直到最近几年这类基因的多样性和广泛性才被揭示。据推测,脊椎动物基因组有多达1 000个不同的miRNAs,调控至少30%以上的基因表达。miRNAs在介导应激反应过程中发挥关键作用,包括细胞对不同环境变化时的不同反应。在某些情况下,miRNAs可以微调靶mRNA的表达,而在其他情况下,它们具有“开关”的功能,miRNAs介导的基因表达控制在肌肉发育和疾病过程中起重要作用,有很大潜力作为疾病治疗的靶点[10];miRNAs 在血管中高表达,是细胞分化、迁移、增殖和凋亡等血管细胞功能的关键调节因子,因此研究者指出可以作为血管疾病的生物标志物和治疗靶点[11];后来,研究者发现miRNAs在运动员对抗阻训练的适应过程中起着非常重要的细胞内调节作用,包括血管增生、炎性反应、线粒体代谢、心肌和骨骼肌收缩、组织细胞肥大等[12]。细胞内miRNAs选择性地被释放到循环中,虽然miRNAs在细胞损伤或者在某些情况下衰老时(如心肌梗死后miR-1的释放)被释放[13],但有证据表明机体受刺激后miRNAs的包装和释放是细胞间交流的一种方式[14]。miRNAs的细胞间转运和受体细胞中基因表达的亚序列功能调控现在是细胞间交流的良好支持机制,涉及各种细胞类型和转运方法[15]。然而,引起miRNAs分泌/包装和受体细胞吸收的确切机制尚不清楚。
2.2 ci-miRNAs
2.2.1 ci-miRNAs 的生理特征 目前已经在人和动物的外周体液中发现miRNAs,包括血清和血浆,其中一些ci-miRNAs已作为多种疾病的生物标记物,用作疾病分子或防治靶标[16]。2008年LAWRIE等[17]首次报道miRNAs可稳定存在于血清、血浆等体液中,称为循环miRNAs(circulating miRNAs),并发现弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤患者血清中miRNAs表达水平改变。随后大量实验证明在多种疾病状态下ci-miRNAs表达谱改变,具有疾病诊断、疗效评价及预后判断等潜在临床价值[18-20]。
2.2.2 ci-miRNAs的来源 ci-miRNAs易获取,不受高温、极端 pH 值、长期储存、反复冻融影响,具有良好稳定性,这些优点使其成为研究热点[21]。在受刺激或损伤后,miRNAs 会以主动(分泌)或被动(膜泄露)的方式从细胞释放出来[22]。许多miRNAs在大多数组织和细胞中普遍表达,但有些是组织特异性(成熟miRNAs 表达比其他组织平均表达高 20倍)或组织富集(成熟 miRNAs 表达高于其他组织,但不到20倍)[23]。其中,miRNAs 的一个子集可以被描述为横纹肌特异性的myomiRs(miR-1,
-133a,-133b,-206,-208a,-208b,-499),或者肌肉富集的(miR-486),它们参与成肌细胞增殖/分化、肌肉再生或纤维类型的分化[24]。myomiRs 的组织特异性是由于其编码基因组定位或肌肉特异性转录因子如成肌分化抗原(MyoD)、肌细胞增强因子2(Mef2)或血清反应因子(Srf)等的转录调控所致[25-28]。因此,几种 myomiRs 既在骨骼肌表达也在心肌表达;但miR-206 和miR-133b 是骨骼肌特异,miR-208a 是心肌特异。和其他任何miRNAs一样,myomiRs 可以被释放到循环中,能在血浆或血清中进行测量。健康人循环中myomiRs 的基础水平很低[29-30],但其在生理、病理状态下表达水平的改变及其生物学作用已有报道。
2.2.3 ci-miRNAs 的生物学意义 细胞外miRNAs对其他细胞有直接生物学作用[2,31]。细胞外小泡是一种纳米大小的小泡,由于其miRNAs的含量被认为是细胞间通讯的强有力媒介,如外小体、微囊泡、高密度脂蛋白和凋亡小体等,是由大多数细胞分泌的,含有多种分子,包括miRNAs。这些小泡被释放到细胞外空间或血液循环,能被邻近细胞带走,它们的内容物被释放到受体细胞胞浆,miRNAs 在那里通过调节基因表达来发挥作用。miRNAs最常通过诱导互补性mRNA的翻译抑制、mRNA降解或脱腺苷而导致靶细胞翻译的下调或抑制。因此,miRNAs 可能以自分泌、旁分泌或内分泌方式参与细胞间通讯。研究循环中细胞外小泡对于理解骨骼肌运动损伤和修复过程中细胞间信息传递有重要意义。
沿内皮细胞的剪切应力增加是导致运动中观察到的ci-miRNAs分泌的一种潜在机制,因为它可能会刺激内皮细胞中特定的miRNAs的分泌。LOVETT等[32]发现普通受试者完成2次连续离心运动(快速伸缩复合练习Plyometric和下坡跑)后,肌酸激酶和肌肉酸痛感明显升高,表明发生了肌肉损伤;同时电子显微镜显示,细胞外小泡大小和数量无明显改变,囊泡内骨骼肌特异性 miR-206 个体差异明显,miR-31 在运动后24 h明显降低,研究者认为小强度至中等强度运动引起的肌肉损伤在运动后24 h内会改变循环细胞外小泡中的 miR-31,但没有改变myomiRs。由于该研究采用的运动方式由 Plyometric 跳跃和下坡跑组成,其中下坡跑含有氧运动成分,难以说明循环中 miR-31 水平改变是由肌肉离心收缩引起,还是有氧运动和离心收缩共同导致。为研究不同的运动方式后ci-miRNAs的改变情况,用单纯 Plyometric 或其他导致肌肉损伤的离心运动方式进行研究是有必要的。随急性和慢性运动而改变的ci-miRNAs被认为通过翻译下调其靶mRNA转录本来调节/减缓训练的有益适应。
关于ci-miRNAs的研究时间脉络,见表1。
2.3 运动对ci-miRNAs 的影响 虽然大多数研究都集中在疾病环境中miRNAs的不同表达水平上,但对其他生理变化的影响也进行了研究,尽管研究相对较少。运动可以引起良好反应,重复训练会对许多生理系统产生有益适应。然而,在急性运动和长期运动训练中miRNAs的研究已经滞后,只是最近研究兴趣高涨。miRNAs 对运动刺激敏感,可以作为有氧能力[33]、运动性肌损伤 (exercise-induced muscle damage,EIMD) 及急慢性肌肉损伤的强有力的生物学标志[34]。目前研究多集中于长期有氧耐力训练对ci-miRNAs的影响,对急性运动后的ci-miRNAs研究较少。
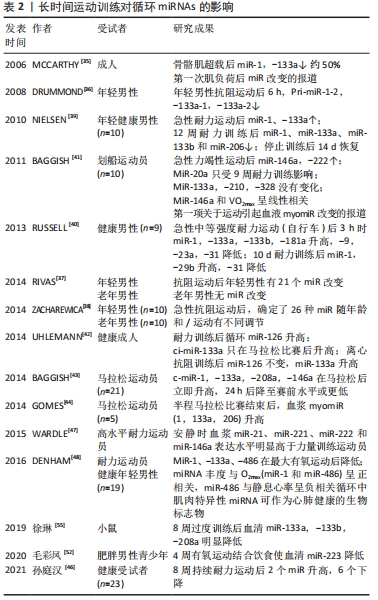
2.3.1 长时运动训练对ci-miRNAs 的影响 miRNAs 参与了基因表达的调控,对运动训练中肌肉的适应有一定作用。在一个功能过载大鼠模型中发现肌肉中pri-mir-1-2、pri-mir-133a-2和pri-mir-206 水平升高[35],这是第一次对肌肉负荷改变后 miRNAs 表达改变的研究报道。类似研究也见于人类,抗阻练习后骨骼肌中 miR-1,miR-133a,miR-133b表达水平降低[36-37],然而在其他研究中没有改变[38]。相反,一次耐力练习(3 h自行车)引起肌肉中miR-1,133a轻度但明显增加,miR-206水平无改变[39-40]。因此,运动能调节肌组织中 myomiRs 表达水平,虽然这些改变的生理意义还不清楚。
肌肉中 myomiRs 水平的改变是否会引起它们在血液中水平的改变?第一项相关研究报道来自于 BAGGISH等[41],研究了急性力竭性运动(短时递增负荷自行车)和 9 周耐力训练(赛艇),检测了与炎症相关或与血管再生相关的miRNAs,只检测了一种 myomiR(miR-133a),结果没有改变。在急性自行车运动(60 min,70%VO2max)后只有miR-486 轻微改变[37],血清miR-133在年轻运动员自行车测试(70%VO2max)过程中和测试结束后4 h 没有改变[29],原因可能是取材时myomiRs已恢复正常水平,亦或是和运动类型有关。长距离跑是一种与ci-miRNAs反应有关的特征性运动,关于马拉松运动的几篇报道结果比较一致,血浆中 miR-1,miR-133a,miR-133b,miR-206,miR-208b和miR-499在马拉松跑结束后即刻或者恢复过程中升高[42-44],在运动后24 h恢复到正常水平,表明了循环myomiRs 改变和运动类型有关。
急性耐力运动[45]、长期耐力训练均被证实可以引起循环中miRNAs表达水平的改变[46],具有强大的潜在生物标志物意义。BAGGISH等[43]将所选ci-miRNAs和反映骨骼肌损伤、心脏应激和坏死及全身炎症的传统蛋白质生物标志物进行了对比,发现ci-miRNAs在马拉松比赛后立即增加,比赛结束24 h后即下降到赛前水平或更低;而传统生物标志物在运动后增加,在运动后24 h再次升高。ci-miRNAs对长时间运动的反应与传统生物标志物不同,表明其释放和清除的特定机制不能完全用广泛细胞损伤来解释;且ci-miRNAs表达模式在时间上不同于传统组织特异性生物标志物,突出了其独特的实时标志物的潜力。NIELSEN等[39]研究发现10 名健康男性急性运动会导致miR-133a和miR-1表达增加,经12周耐力训练后再进行急性运动,miR-133a、miR-1无变化。可见急性运动和耐力性运动对miRNAs 的影响效应不同,也说明耐力训练后miRNAs 表达水平可能会发生相应的适应性改变。半程马拉松被认为是一种剧烈耐力运动项目,对肌细胞会产生明显影响。不断有文献指出miRNAs会从受损细胞或应激细胞漏出,GOMES等[44]对半程马拉松运动员血浆myomiRs(1,133a,206)进行定量分析,发现比赛结束后3种血浆myomiRs均明显升高,表明其在长时间耐力运动后改变比较明显,也体现了其作为肌肉损伤或耐力训练适应的生物标记物的潜在用途。WARDLE等[47]检测了高水平耐力运动员安静状态下血浆miRNAs,结果发现miR-21、miR-221、miR-222和miR-146a表达水平明显高于力量训练运动员。也有研究发现,长期剧烈有氧运动训练的耐力运动员静息全血miR-1、-486和-494含量增加,而健康受试者进行单次最大有氧运动后即刻miR-1、-133a、-486降低,同时还发现miR-1和miR-486丰度与VO2max呈正相关,而miR-486与静息心率呈负相关[48]。因此,全血中肌肉富含的miRNA受到急性和长期有氧运动的调节,可以作为心肺健康的生物标志物。李新[45]对受试者8 km跑后血浆中miR和心肌损伤标志物的急性变化进行检测,发现运动结束后循环miR显著增加,而肌钙蛋白Ⅰ水平极低,肌酸激酶同工酶无明显差异,ci-miR-133a、miR-133b、miR-206水平和心率变异性指标、肌红蛋白之间的相关性表明这些miRNAs可以用于个体运动负荷检测的潜在生物标志物。
细胞通过线粒体自噬可以消除具有功能障碍的线粒体,适应应激环境并维持细胞内内环境稳定。miRNAs可通过调控靶基因的表达而调控线粒体自噬的水平,可有效防治炎症、免疫、肿瘤、神经类等疾病[49]。动物实验发现,大鼠进行4周无负重游泳训练后,循环中外泌体浓度不变,有氧运动组大鼠循环外泌体中miR-342-5p水平明显升高,认为有氧运动时循环外泌体通过传递miR-342-5p减轻心肌缺血/再灌注损伤[50]。闫冬[51]研究发现SD大鼠进行8周跑台运动预处理后脑、血液miR-146a表达升高,也可以减少缺血性脑卒中的肿瘤坏死因子受体相关分子6(TRAF6)、NF-kB(核因子激活的B细胞的k-轻链增强)和肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)的表达,降低对大脑损伤程度,对大脑有一定保护作用。肥胖男性青少年进行4周以有氧运动为主的运动结合饮食干预后,其血清miR-223水平和体内炎症水平降低[52]。
AOI等[29]发现4周中等强度自行车训练(3 d/周)后ci-miRNAs发生类似60 min急性自行车运动后的反应。在训练前,在7个肌肉富集ci-miRNAs中,只有ci-miR-486在运动后即刻降低;训练后,ci-miR-486的安静水平降低,这一变化与血清胰岛素水平呈正相关(r=0.43)[29]。已知miR-486可以靶向同源性磷酸酶–张力蛋白(phosphatase and tensin homolog, PTEN),它是磷脂酰肌醇激酶/蛋白激酶(PI3k/AKT)通路在胰岛素信号传导下游的负调节剂。因此,在急性运动中,ci-miR-486可能被肌肉摄取,在那里它通过抑制PTEN刺激葡萄糖摄取。在持续的耐力运动中,更多的miR-486的肌肉摄取可能会转化为较低的运动能力,因为具有较高有氧能力的个体对脂质利用有更强的依赖性[53]。而且,休息时ci-miR-486的降低可能反映出骨骼肌里具有更高浓度,引起PTEN的降低,并增强胰岛素信号来适应耐力训练。在不活跃、年轻和年龄较大的男性队列研究中,脂肪质量和血糖浓度解释了血清miR-486水平差异的52%(r=0.72)[54],为ci-miR-486可能参与代谢健康的相关途径提供了证据。这些假设一旦得到证实,将非常有意义,值得进一步广泛研究。长时间运动对ci-miRNAs的影响,见表2。
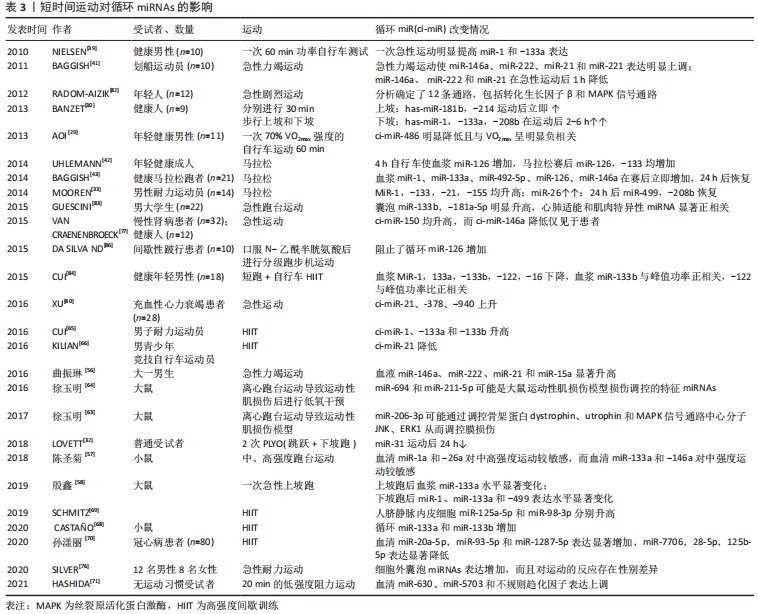
2.3.2 短时运动对ci-miRNAs 的影响 国内文献多见长时间有氧运动对ci-miRNAs影响的研究,对急性运动尤其是肌肉离心收缩运动的研究少见。曲振琳等[56]研究发现,普通大一男生急性力竭运动后血液中miR-146a、miR-222、miR-21和miR-15a显著升高,表明这4种miRs对急性运动会产生显著反应;经8周有氧训练后,血液中miR-146a、miR-222、miR-21、miR-15a和miR-199a表达水平高于训练前,但是与训练前急性力竭运动后水平相当,可能是有氧训练产生适应。BAGGISH 等[41]研究了10名划船运动员安静时和急性力竭运动后ci-miRNAs 的反应,选择与血管生成相关(miR-20a,miR-210,miR-221,miR-222,miR-328)、与炎症有关(miR-21,miR-146a)、与骨骼肌和心肌收缩相关(miR-21,miR-133a)、与缺氧/缺血适应相关(miR-21,miR-146a,miR-210)的miRs;结果发现急性力竭运动使miR-146a、miR-222、miR-21 和 miR-221 表达明显上调;miR-146a、miR-222 和 miR-21 在急性运动后1 h降低;miR-221也有类似下调趋势。这是第一篇关于运动对ci-miRNAs影响的研究,这4种表达水平发生变化的miRNAs在内皮细胞富集,并根据它们在血管生成和/或炎症中的作用而选择;同时,运动后即刻ci-miR-146a表达水平升高的绝对值与最大摄氧量VO2max绝对值显著线性相关(r=0.63),提示其作为心肺适能和极限运动能力生物标记物的潜力。
(1)ci-miRNAs可用于运动性肌损伤研究:运动能引起血清中miRNAs水平发生变化,其变化程度和运动强度有关。陈圣菊等[57]研究小鼠进行中强度、高强度跑台运动后ci-miRNAs 水平变化,血清miR-1a和-26a对中高强度运动较敏感,而血清miR-133a和-146a对中强度运动较敏感;小鼠比目鱼肌中miR-1a和-133a对中强度运动较敏感,而miR-26a和-146a未对运动强度产生敏感反应,认为比目鱼肌可能是血清miRNAs来源之一。NIELSEN等[39]研究发现一次急性运动明显提高miR-1和-133a表达,认为这种适应性变化可能有利于骨骼肌结构和功能的重塑,另一方面可能与组织损伤有关。殷鑫[58]的研究表明,大鼠一次急性上坡跑后(90 min,20 m/min跑台,坡度+15°)血浆miR-133a水平显著变化,下坡跑(90 min,20 m/min跑台,坡度-15°)后miR-1、miR-133a和-499表达水平显著变化,且下坡跑后股四头肌miR-1和-133a水平显著降低,上坡跑后没有变化。
在运动训练实践中为追求训练成绩,运动员不断冲破极限挑战高强度,肌肉损伤极易发生,由于个体差异,经典血液指标肌酸激酶经常达不到满意效果,因此确定新的可靠的生物学标志物显得非常重要,ci-miRNAs具有很大潜力。骨骼肌细胞损伤实验研究显示,miR-181表达上调,可以靶向下调 MyoD和HOX-A11(同源异型复合基因-A11)[57]。随后心脏毒素诱发的损伤、基因敲除及离体实验等研究陆续证实,miR-351[59]、miR-206[60]、miR-26a[61]、miR-133均与肌损伤有关[62]。但关于运动导致肌损伤后ci-miRNAs表达水平改变的研究相对较少。BANZET等[30]研究发现,血浆myomiRs水平改变和运动方式有关,9名健康受试者分别完成30 min跑步机步行运动,一次上坡(向心运动为主),一次下坡(离心运动为主),结果只有离心运动时血浆myomiRs升高,表明发生了肌肉损伤,认为循环myomiRs可以作为运动性肌损伤的生物标志物。在一场马拉松比赛后,循环myomiRs 和血清肌酸激酶水平一致地升高,表明有肌肉损伤[42-43];而长时间自行车运动后ci-miRNAs和肌酸激酶没有升高,可能因为自行车运动几乎不含离心运动成分[42]。值得注意的是,虽然马拉松比赛后心肌损伤或应激指标(肌酸激酶同工酶CK-MB、肌钙蛋白、脑利钠肽前体pro-BNP)水平较高[29,43],但同时也提高了在血清中发现的部分 myomiRs 来源于心肌而不是骨骼肌的可能性。然而,miR-133b 和 miR-206 是只在骨骼肌表达的,而且因为跑步时募集的骨骼肌比心肌多,因此骨骼肌对 ci-miRNAs 的贡献可能是最重要的。虽然主动释放也可能发生,但 myomiRs 从损伤的肌纤维释放可能是主要原因。
miRNAs 还可用于运动性肌损伤的调控机制研究。关于运动性肌损伤发生的机制认为有机械损伤、炎症、代谢紊乱、Ca2+超载等,通常认为第一阶段主要是由机械损伤引起,第二阶段则是由于机械损伤引起的一系列炎症、代谢紊乱等,但机械损伤是如何过渡到代谢损伤的问题一直没能得到很好的解答。徐玉明等[63]用大鼠离心跑台运动构建运动性肌损伤模型,对腓肠肌miRNAs进行筛选并验证了2条运动性肌损伤特征性miRNAs:miR-206-3p和miR-139-3p;且发现miR-206-3p与骨架蛋白dystrophin、utrophin和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)信号通路中心分子c-Jun氨基端激酶(JNK)、细胞外调节蛋白激酶1(extracellular-signalregu-latedkinase,ERK1)中度负相关,认为miR-206-3p可能通过调控骨架蛋白dystrophin、utrophin和MAPK信号通路中心分子 JNK、ERK1从而调控膜损伤。该研究小组的另一篇研究报道对大鼠离心运动导致运动性肌损伤后采用低氧干预,综合分析得出miR-694和miR-211-5p可能是大鼠运动性肌损伤模型损伤调控的特征miRNAs,尤其是 miR-694 在低氧对运动性肌损伤的调控中发挥重要作用[64]。从现有研究来看,由于肌细胞miRNAs表达水平的改变情况和血液miRNAs表达水平的变化存在一定差异性,二者有可能一致、不一致甚或相反,因此欲从体液miRNAs角度来分析运动性肌损伤,需要进一步研究。
(2)不同类型运动后ci-miRNAs表达水平改变:人类研究表明,高强度间歇训练(high-intensity interval training,HIIT)对心血管影响有益,与传统的耐力运动相比通常更有效。对耐力训练男子进行高强度间歇训练和高强度持续运动后的ci-miRNAs进行全面筛查,发现在两种不同的运动后即刻,12种ci-miRNAs表达水平均升高,包括ci-miR-1、-133a和-133b[65];唯一的区别是高强度间歇训练以后ci-miR-1的水平比高强度持续运动后更低,表明与持续性耐力运动相比,间歇性冲刺可能会导致更多或不一样的肌肉损伤。KILIAN等[66]做了类似的对比研究,但受试者是男青少年竞技自行车运动员,研究人员从耳朵毛细血管血中获取ci-miRNAs,高强度持续运动后20-60 min,ci-miR-126升高;运动后30 min时,高强度持续运动组ci-miR-16升高,而高强度间歇训练组ci-miR-21降低,这可能反映了运动适应的特异性,因为这两种miRNAs都是原血管生成蛋白内皮生长因子(VEGF)的正调节剂,并且在内皮细胞中通过维持层状剪切应力上调[67]。
以动物进行高强度间歇训练运动的研究有类似的发现。高强度间歇训练可以改变小鼠循环外泌体的miRNA谱,包括显著增加miR-133a和miR-133b[68]。而且,从训练小鼠血浆中分离的外泌体治疗久坐小鼠可以提高糖耐量、胰岛素敏感性,并降低血浆三酰甘油水平。研究者认为,肌肉释放的循环外泌体携带一种特定的miRNA特征,这种特征通过运动改变,并诱导肝脏的表达变化,从而影响全身代谢谱。
循环miRs在身体活动中受到调节,并可能发挥抗动脉粥样硬化作用。血管内皮是ci-miR的丰富来源,SCHMITZ等[69]研究发现,4周高强度间歇训练后,人脐静脉内皮细胞miR-125a-5p和miR-98-3p分别升高,表明这两种miRs可被内皮细胞快速分泌,可能是高强度间歇训练反应中miR-125a-5p和miR-98-3p升高的来源,这两种miRNAs都能减轻内皮细胞炎症,并可能介导包括高强度间歇训练在内的体育运动的血管保护作用。
冠心病患者进行高强度间歇训练后心功能改善、生活质量改善显著优于常规药物治疗组,且血清miR-20a-5p,miR-93-5p和miR-1287-5p表达显著增加,miR-7706、28-5p、125b-5p表达显著降低,表明高强度间歇训练对冠心病患者的心肺功能及生活质量起到明显改善作用,其机制可能与调控miRNAs差异化表达有关[70]。无运动习惯受试者进行大约20 min的低强度阻力运动后血清miR-630、miR-5703和不规则趋化因子表达上调,表明即使是低强度的运动也可能改变人类的miRs和细胞因子/肌因子的表达来发挥生物学作用[71]。小鼠8周过度训练后血清miR-133a,-133b,-208a明显降低,认为myomiRs可作为监测过度训练的潜在标志物,反映其生理过程[55]。
(3)ci-miRNAs表达水平有性别、年龄、体质量指数差异:一项基于人群的队列研究显示ci-miRNAs与年龄、性别和体质量指数有关,不同性别的miRNAs调节存在激素和遗传差异[72-73]。此外,另一项研究表明,高VO2max和低VO2max组之间的ci-miRNAs
因性别不同而不同[74]。低VO2max的受试者ci-miR-21水平高于高VO2max受试者,但只有男性有此规律[74]。BACKES等[75]是在运动结束30 min后取血,BAGGISH等[41]是在运动后即刻发现显著变化,但所有的ci-miRNAs都在1 h后回到基线。SILVER等[76]研究也发现急性耐力运动后细胞外囊泡miRNAs表达增加,而且对运动的反应存在性别差异。
(4)慢性肾病、心力衰竭者运动后ci-miRNAs的改变:VAN CRAENENBROECK等[77]比较了慢性肾病患者急性运动(进行运动心肺试验时出现最大限制症状时停止运动)后12种ci-miRNAs的反应,并与健康组进行对照,运动后即刻所有受试者ci-miR-150均升高,而ci-miR-146a降低仅见于患者。此外,同一研究小组发现慢性肾病患者ci-miR-146a、-150、-210与VO2max呈负相关,通过颈动脉-股动脉波速测量,在纠正动脉僵硬时,该峰值消失[78]。ci-miR-146a与有氧能力负相关,与之前在年轻健康男性中发现的正相关相反[41]。miR-146a和-150都和慢性肾病患者的动脉僵硬度有关,而且和心血管疾病的发展和疾病的许多机制密切相关[75]。miR-150也参与了生理上的左心室肥厚[79],提高了其在这种有益的适应性训练中的可能作用。进一步的研究需要确定它们作为该人群生物标志物或用于靶治疗的必要性。
相反,心力衰竭者的ci-miR-146a或-150没有任何变化,尽管ci-miR-21、-378、-940都上升了[80],这些循环miRs的改变和VO2max、炎症标志物或肌肉损伤均不相关。心肌富有的miR-940在循环中升高,而其他心肌和骨骼肌富有的miRNAs和肌肉损伤标记物和炎症标记物没有升高,表明miRNAs在运动时从肌肉释放到循环的不同机制。这在BANZET等[30]的报告中得到支持,该研究比较了健康、平时积极运动的年轻人下坡行走和上坡行走的不同反应:受试者完成30 min跑步机行走,坡度25%,穿着负重背心,发现运动后72 h以内有8种肌肉相关的ci-miRNAs发生改变。上坡行走后发生的唯一改变是运动后即刻ci-miRs-181b和-214的升高;另一方面,下坡运动后即刻没有任何改变,虽然运动后ci-miR-1在运动后2 h升高;ci-miRs -1、-133a、-133b与-208b在运动后6 h升高。虽然下坡跑后升高的4种ci-miRNAs被认为是由骨骼肌损伤引起,但miR-181b和miR-214不是肌肉特征性,在很多组织都有分布。比如,它们在肌肉缺氧时上调[81],自行车运动后miR-181b在中性粒细胞和外周血单核细胞中上调[82]。虽然这些ci-miRNAs的细胞来源在这项研究中尚不清楚,但它们似乎不是被动释放,而是积极地主动释放,例如在造成肌肉损伤的下坡运动后的ci-miRNAs释放。
(5)ci-miRNAs表达水平改变的可能机制:GUESCINI等[83]指出,在安静时肌肉会分泌含有miRNAs的细胞外囊泡(extracellular vesicles,EVs)进入循环,后来他们发现健康人在跑步机上以80%VO2max强度跑40 min后,血浆细胞外囊泡中的ci-miR-181a-5p升高,ci-miR-1、-133b、-206和-499也发现来源于肌肉的细胞外囊泡,所有这些miRs的表达水平和VO2max相对值均呈正相关。然而,其他常见的肌肉特征性miRNAs没增加,表明了在运动中骨骼肌选择性地进行miRNAs包裹和释放的机制。这个过程的机制、这些细胞外囊泡包裹的ci-miRNAs的最终靶标和目的、以及它们是否可以解释机体对运动的适应,都需要进一步研究。
在另一项对肌肉富集的ci-miRNAs的研究中,AOI和他的同事[29]让健康男性以70%VO2max强度骑行60 min,在7种ci-miRNAs中,只有ci-miR-486表达水平有改变:运动后即刻降低,运动后3 h回到正常水平;ci-miR-486表达水平改变和VO2max相对值之间呈负相关(r=0.58)。为解释这个现象,作者证实了通过收缩骨骼肌来增加ci-miR-486摄取的可能性,这可能会影响能量代谢。他们没有研究ci-miR-181b或-214,但ci-miR-1、-133a和-133b没有反应,表明它们不是单纯由肌肉收缩而释放,并支持了可能会由于肌肉损伤而导致分泌增多的假设。最近发现,静坐少动的年轻人进行最大强度跑步机测试后全血中ci-miR-486水平降低[48];此外,在更大的受试者样本(包括耐力训练者和不活跃男性)研究中,安静时ci-miR-486水平和VO2max呈正相关,与安静心率呈负相关,这表明它可能在心血管适能中发挥积极作用[48]。ci-miR-1和-133a在最大测试后降低,安静时ci-miR-1水平和VO2max最大值相关 [48]。Nielsen和他同事[39]研究表明,健康有训练经历的男性进行60 min 65%最大输出功率的自行车运动后,8种ci-miRNAs便出现下调,包括miR-146a;运动结束休息1,3 h后,分别有7种和4种不同的ci-miRNAs表达水平升高。在任何时间点都没有不同表达的ci-miRNAs重叠的事实表明,有不同的时间敏感性释放机制。研究者对752个ci-miRNAs进行了初步的全面筛查,并进行了其中188个靶点的验证,这也增加了假阳性的可能性。由于大多数运动和ci-miRNAs的研究只预先检查了一定数量的靶点,因此这些研究的结果不一定与之前的结果不一致,但它们应该在另一个队列中得到验证。CUI等[84]则发现在对7个事先选择的靶标调测中,运动后即刻血清ci-miRNAs表达水平降低;ci-miR-1、-133a、-133b、-122和-16在2次Wingate试验(间隔4 min)后全部降低;而且,ci-miR-133b与第一次Wingate试验的峰值功率呈正相关,而ci-miR-122与第一次冲刺的峰值功率和第二次冲刺的峰值功率比值呈正相关。这些ci-miRNAs在无氧耐力中的作用值得关注。
miR-126是一种内皮细胞富集的miRNA,通过抑制SPRD1和PIK3R2( 磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶)、导致血管内皮生长因子上调,从而诱导血管生成[85]。DA SILVA等[86]评估了间歇性跛行患者进行自身最大强度行走测试后全血中ci-miR-126和其他循环中血管生成因子水平,也评估了抗氧化药物N-乙酰半胱氨酸的治疗效果,结果发现补充N-乙酰半胱氨酸进行运动后1 h的氧化还原平衡状态得到改善;然而,在安慰剂疗程运动后30 min,循环中ci-miR-126、血管内皮生长因子、内皮型一氧化氮合成酶(eNOS)的表达水平升高,但在N-乙酰半胱氨酸补充后的测试中没有变化。此外,miR-126的抗血管生成靶点——PIK32R2 mRNA仅在N-乙酰半胱氨酸疗程内运动后才在循环中升高。这些结果与作者的假设相反,并得出结论:miR-126信号在间歇性跛行患者具有氧化还原敏感性。运动诱导的氧化应激在刺激内皮细胞的血管生成ci-miR-126释放中的作用,目前仍有待阐明;在健康个体是否也是如此,这个结果是否外周动脉疾病的结果,有待确定。
ci-miR-126已被证明在健康的中年个体进行最大自行车测力计测试后即刻增加[42]。而且,UHLEMANN等[42]测试了3个其他运动方式后ci-miR-126和-133的改变,ci-miR-126在70%通气阈值下增加了30 min,并在4 h的运动中保持升高状态;马拉松赛后ci-miR-126和-133均升高,而在抗阻训练中增加离心负荷后,只有ci-miR-133升高,这支持了ci-miR-133作为骨骼肌损伤标记物的可能性。研究者认为,ci-miR-126的增加是有氧运动过程中内皮损伤/裂解的证据,尽管文中没有提供任何证据来支持这一说法。在他们的研究中,ci-miR-126在70%通气阈自行车运动30 min后升高,而以前的研究没有显示内皮损伤的证据(由循环中内皮细胞数量决定),直到以相同强度循环2 h[42]。总之,这些数据并没有指出内皮损伤是ci-miRNAs增加的原因,表明还可能有其他机制。短时间运动对ci-miRNAs的影响,见表3。
| [1] 刘雯,沙银中,李亚东,等.循环 microRNA 在常见肿瘤中的应用研究进展[J].国际检验医学杂志,2018,39(16):1950-1954. [2] 田迎.血清及体液中微小核糖核酸的检测、表达及临床意义分析[D].南京:南京师范大学,2009. [3] KELLY BN, HAVERSTICK DM, LEE JK, et al. Circulating microRNA as a biomarker of human growth hormone administration to patients. Drug Test Anal. 2014;6(3):234-238. [4] ESQUELA-KERSCHER A, SLACK FJ. Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259-269. [5] LANFORD RE, HILDEBRANDT-ERIKSEN ES, PETRI A, et al. Therapeutic silencing of microRNA-122 in primates with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Science. 2010;327:198-201. [6] HA M, KIM VN. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:509-524. [7] FABBRI M, PAONE A, CALORE F, et al. MicroRNAs bind to Toll-like receptors to induce prometastatic inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2012;109:2110-2116. [8] FRIEDMAN RC, FARH KK, BURGE CB, et al. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009;19(1):92-105. [9] FEINBERG MW, MOORE KJ. MicroRNA Regulation of Atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2016;118(4):703-720. [10] WILLIAMS AH, LIU N, VAN ROOIJ E, et al. MicroRNA control of muscle development and disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21(3): 461-469. [11] ZHANG C. MicroRNAs in vascular biology and vascular disease. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2010;3(3):235-240. [12] DAVIDSEN PK, GALLAGHER IJ, HARTAM JW, et al. High responders to resistance exercise training demonstrate differential regulation of skeletal muscle microRNA expression. J Appl Physiol. 2011;110(2):309-317. [13] BRONZE-DA-ROCHA E. MicroRNAs expression profiles in cardiovascular diseases. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:985408. [14] Hergenreider E, Heydt S, Tréguer K, et al. Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(3):249-256. [15] Jansen F, Yang X, Hoelscher M, et al. Endothelial micro particle-mediated transfer of microRNA-126 promotes vascular endothelial cell repair via SPRED1 and is abrogated in glucose-damaged endothelial micro particles. Circulation. 2013;128(18):2026-2038. [16] 满朝来,杨美玲.体液循环miRNA的研究进展[J].中国生物工程杂志,2014,34(2):104-108. [17] LAWRIE CH, GAL S, DUNLOP HM, et al. Detection of elevated levels of tumour-associated microRNAs in serum of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2008;141(5):672-675. [18] WANG H, TAN G, DONG L, et al. Circulating miR-125b as a marker predicting chemo resistance in breast cancer. Plos One. 2012;7(4): 34210. [19] FAYYAD-KAZAN H, BITAR N, NAJAR M, et al. Circulating miR-150 and miR-342 in plasma are novel potential biomarkers for acute myeloid leukemia. J Transl Med. 2013;11:31. [20] RODERBURG C, LUEDDE M, VARGAS CARDENAS D, et al. Circulating miR-150 serum levels predict survival in patients with critical illness and sepsis. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):54612. [21] CHEN X, BA Y, MA L, et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008;18(10):997-1006. [22] CHEN X, LIANG H, ZHANG J, et al. Secreted microRNAs: a new form of inter-cellular communication. Trends Cell Biol. 2012;22:125-132. [23] LEE EJ, BAEK M, GUSEV Y, et al. Systematic evaluation of microRNA processing patterns in tissues, cell lines, and tumors. RNA. 2007;14:35-42. [24] DINIZ GP, WANG DZ. Regulation of skeletal muscle by microRNAs. Compr Physiol. 2016;6:1279-1294. [25] LIU N, WILLIAMS AH, KIM Y, et al. An intragenic MEF2-dependent enhancer directs muscle-specific expression of microRNAs 1 and 133. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2007;104:20844-20849. [26] RAO PK, KUMAR RM, FARKHONDEH M, et al. Myogenic factors that regulate expression of muscle-specific microRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2006;103:8721-8726. [27] SWEETMAN D, GOLJANEK K, RATHJEN T, et al. Specific requirements of MRFs for the expression of muscle specific microRNAs, miR-1, miR-206 and miR-133. Dev Biol. 2008;321:491-499. [28] YEUNG F, CHUNG E, GUESS MG, et al. Myh7b/miR-499 gene expression is transcriptionally regulated by MRFs and Eos. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012; 40:7303-7318. [29] AOI W, ICHIKAWA H, MUNE K, et al. Muscle-enriched microRNA miR-486 decreases in circulation in response to exercise in young men. Front Physiol. 2013;4:80. [30] BANZET S, CHENNAOUI M, GIRARD O, et al. Changes in circulating microRNAs levels with exercise modality. J Appl Physiol. 2013;115:1237-1244. [31] FABBRI M, PAONE A, CALORE F, et al. MicroRNAs bind to Toll-like receptors to induce prometastatic inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2012;109:2110-2116. [32] LOVETT JAC, DURCAN PJ, MYBURGH KH. Investigation of Circulating Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNA Following Two Consecutive Bouts of Muscle-Damaging Exercise. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1149. [33] MOOREN FC, VIERECK J, KRÜGER K, et al. Circulating micrornas as potential biomarkers of aerobic exercise capacity. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014;306(4):H557-563. [34] SIRACUSA J, KOULMANN N, BANZET S. Circulating myomiRs: a new class of biomarkers to monitor skeletal muscle in physiology and medicine. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2018;9(1):20-27. [35] MCCARTHY JJ, ESSER KA. MicroRNA-1 and microRNA-133a expression are decreased during skeletal muscle hypertrophy. J Appl Physiol. 2006; 102:306-313. [36] DRUMMOND MJ, MC CARTHY JJ, FRY CS, et al. Aging differentially affects human skeletal muscle microRNA expression at rest and after an anabolic stimulus of resistance exercise and essential amino acids. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008;295:1333-1340. [37] RIVAS DA, LESSARD SJ, RICE NP, et al. Diminished skeletal muscle microRNA expression with aging is associated with attenuated muscle plasticity and inhibition of IGF-1 signaling. FASEB J. 2014;28:4133-4147. [38] ZACHAREWICZ E, DELLA GATTA P, REYNOLDS J, et al. Identification of microRNAs linked to regulators of muscle protein synthesis and regeneration in young and old skeletal muscle. PLoS One. 2014;9:114009. [39] NIELSEN S, SCHEELE C, YFANTI C, et al. Muscle specific microRNAs are regulated by endurance exercise in human skeletal muscle: Muscle specific microRNAs and exercise. J Physiol. 2010;588:4029-4037. [40] RUSSELL AP, LAMON S, BOON H, et al. Regulation of miRNAs in human skeletal muscle following acute endurance exercise and short-term endurance training: miRNA in muscle after exercise. J Physiol. 2013; 591:4637-4653. [41] BAGGISH AL, HALE A, WEINER RB, et al. Dynamic regulation of circulating microRNA during acute exhaustive exercise and sustained aerobic exercise training: circulating microRNA in exercise. J Physiol. 2011;589:3983-3994. [42] UHLEMANN M, MOBIUS-WINKLER S, FIKENZER S, et al. Circulating microRNA-126 increases after different forms of endurance exercise in healthy adults. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2014;21:484-491. [43] BAGGISH AL, PARK J, MIN PK, et al. Rapid upregulation and clearance of distinct circulating microRNAs after prolonged aerobic exercise. J Appl Physiol. 2014;116:522-531. [44] GOMES CPC, OLIVEIRA-JR GP, MADRID B, et al. Circulating miR-1, miR-133a, and miR-206 levels are increased after a half-marathon run. Biomarkers. 2014;19:585-589. [45] 李新.中等强度跑步对心率变异性和肌肉特异性miRNAs的影响[D].南京:南京大学,2019. [46] 孙庭汉,刘美,孙晓.耐力运动对人外周血微RNA表达谱的影响[J].中国医科大学学报,2021,50(8):737-741,751. [47] WARDLE SL, BAILEY ME, KILIKEVICIUS A, et al. Plasma microRNA levels differ between endurance and strength athletes. PLoS One. 2015;10(4): e0122107. [48] DENHAM J, PRESTES PR. Muscle-enriched microRNAs isolated from whole blood are regulated by exercise and are potential biomarkers of cardio respiratory fitness. Front Genet. 2016;7:196,. [49] 刘源.运动诱导miRNAs调控线粒体自噬的研究进展[J].体育科技, 2021,42(3):19-21. [50] 侯作旭,秦兴华,王立锋,等.有氧运动减轻心肌缺血/再灌注损伤新机制:循环外泌体miR-342-5p[J].中华航空航天医学杂志,2017, 28(2):15. [51] 闫冬.运动预处理通过外泌体介导miR146a对脑缺血再灌注大鼠炎症因子的影响[D].成都:成都体育学院,2021. [52] 毛彩凤.四周运动结合饮食干预改变肥胖男性青少年血清HDL亚型分布及MicroRNA-223水平[D].武汉:武汉体育学院,2020. [53] HOROWITZ JF, KLEIN S. Lipid metabolism during endurance exercise. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;72 Suppl:558S-563S. [54] MARGOLIS LM, LESSARD SJ, EZZYAT Y, et al. Circulating microRNA are predictive of aging and acute adaptive response to resistance exercise in men. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017;72(10):1319-1326. [55] 徐琳,王金之,郑益丽,等.小鼠过度训练模型肌肉特异性miRNAs在循环和不同组织中的变化研究[J].南京师大学报(自然科学版), 2019,42(4):103-110. [56] 曲振琳,李萌,刘凯.有氧运动训练前后循环血液中microRNA-146a 和222的动态变化及其对心血管功能的调节作用[J].重庆医学,2016,45(36):5081-5084,5087. [57] 陈圣菊,王飞,李文炯,等.小鼠运动敏感型血清 miRNA的筛选[J].航天医学与医学工程,2018,31(2):224-228. [58] 殷鑫.上坡、下坡跑对大鼠骨骼肌和循环中特异性miRNAs表达水平的影响[G].南京:第十一届全国体育科学大会,2019. [59] NAGUIBNEVA I, AMEYAR-ZAZOUA M, POLESSKAYA A, et al. The microRNA miR-181 targets the homeobox protein Hox-A1 during mammalian myoblast differentiation. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8(3):278-284. [60] CHEN Y, MELTON DW, GELFOND JA, et al. MiR-351 transiently increases during muscle regeneration and promotes progenitor cell proliferation and survival upon differentiation. Physiol Genomics. 2012;44(21): 1042-1051. [61] LIU N, WILLIAMS AH, MAXEINER JM, et al. microRNA-206 promotes skeletal muscle regeneration and delays progression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in mice. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(6):2054-2065. [62] DEY BK, GAGAN J, YAN Z, et al. miR-26a is required for skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration in mice. Genes Dev. 2012;26(19):2180-2191. [63] 徐玉明,曹建民,李俊平,等.大鼠运动性肌损伤特征 microRNA 表达及其膜损伤调控靶点的预测[J].生理学报,2017,69(3):276-284. [64] 徐玉明,曹建民,陈玉平,等.低氧调控大鼠运动性肌损伤的特征 miRNA 表达[J].中国运动医学杂志,2016,35(10):913-920. [65] CUI SF, WANG C, YIN X, et al. Similar responses of circulating microRNAs to acute high-intensity interval exercise and vigorous-intensity continuous exercise. Front Physiol. 2016;7:102,. [66] KILIAN Y, WEHMEIER UF, WAHL P, et al. Acute response of circulating vascular regulating microRNAs during and after high-intensity and high-volume cycling in children. Front Physiol. 2016;7:92,. [67] MONDADORI DOS SANTOS A, METZINGER L, HADDAD O, et al. miR-126 Is involved in vascular remodeling under laminar shear stress. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:497280,. [68] CASTAÑO C, MIRASIERRA M, VALLEJO M, et al. Delivery of muscle-derived exosomal miRNAs induced by HIIT improves insulin sensitivity through down-regulation of hepatic FoxO1 in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(48):30335-30343. [69] SCHMITZ B, BREULMANN FL, JUBRAN B, et al. A three-step approach identifies novel shear stress-sensitive endothelial microRNAs involved in vasculoprotective effects of high-intensity interval training (HIIT). Oncotarget. 2019;10(38):3625-3640. [70] 孙漾丽,顾迎春,李征艳,等.高强度间歇训练对冠心病患者心肺功能、生活质量及miRNA表达谱的影响[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2020,12(10):1185-1189. [71] HASHIDA R, MATSUSE H, KAWAGUCHI T, et al. Effects of a low-intensity resistance exercise program on serum miR-630, miR-5703, and Fractalkine/CX3CL1 expressions in subjects with No exercise habits: A preliminary study. Hepatol Res. 2021;51(7):823-833. [72] AMELING S, KACPROWSKI T, CHILUKOTI RK, et al. Associations of circulating plasma microRNAs with age, body mass index and sex in a population-based study. BMC Med Genomics. 2015;8:61. [73] SHARMA S, EGHBALI M. Influence of sex differences on microRNA gene regulation in disease. Biol Sex Differ. 2014;5:3. [74] BYE A, RØSJØ H, ASPENES ST, et al. Circulating microRNAs and aerobic fitness-the HUNT-Study. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57496. [75] BACKES C, LEIDINGER P, KELLER A, et al. Blood born miRNAs signatures that can serve as disease specific biomarkers are not significantly affected by overall fitness and exercise. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e102183. [76] SILVER JL, ALEXANDER SE, DILLON HT, et al. Extracellular vesicular miRNA expression is not a proxy for skeletal muscle miRNA expression in males and females following acute, moderate intensity exercise. Physiol Rep. 2020;8(16):e14520. [77] VAN CRAENENBROECK AH, LEDEGANCK KJ, VAN ACKEREN K, et al. Plasma levels of microRNA in chronic kidney disease: patterns in acute and chronic exercise. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015;309(12): H2008-H2016. [78] VAN CRAENENBROECK AH, VAN CRAENENBROECK EM, VAN ACKEREN K, et al. Impaired vascular function contributes to exercise intolerance in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016;31(12):2064-2072. [79] MARTINELLI NC, COHEN CR, SANTOS KG, et al. An analysis of the global expression of microRNAs in an experimental model of physiological left ventricular hypertrophy. PLoS One. 2014;9:e93271,. [80] XU T, ZHOU Q, DAS S, et al. Circulating miR-21, miR-378, and miR-940increase in response to an acute exhaustive exercise in chronic heart failure patients. Oncotarget. 2016;7:12414-12425,. [81] SARKAR J, GOU D, TURAKA P, et al.MicroRNA-21 plays a role in hypoxia-mediated pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010;299:L861-L871. [82] RADOM-AIZIK S, ZALDIVAR F JR, LEU SY, et al. Effects of exercise on microRNA expression in young males peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Clin Transl Sci. 2012;5:32-38. [83] GUESCINI M, CANONICO B, LUCERTINI F, et al. Muscle releases alpha-sarcoglycan positive extracellular vesicles carrying miRNAs in the bloodstream. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0125094. [84] CUI SF, LI W, NIU J, et al. Acute responses of circulating microRNAs to low-volume sprint interval cycling. Front Physiol. 2015;6:311,. [85] FISH JE, SANTORO MM, MORTON SU, et al. miR-126 regulates angiogenic signaling and vascular integrity. Dev Cell. 2008;15:272-284. [86] DA SILVA ND JR, ROSEGUINI BT, CHEHUEN M, et al. Effects of oral N-acetylcysteine on walking capacity, leg reactive hyperemia, and inflammatory and angiogenic mediators in patients with intermittent claudication. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015;309:H897-H905. |
| [1] | 刘金玉, 张晗硕, 崔洪鹏, 潘灵之, 赵博然, 李 菲, 丁 宇. 脊柱微创治疗脊髓型颈椎病的有限元生物力学分析及精准化运动康复方案[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1359-1364. |
| [2] | 吴东哲, 高晓嶙, 李闯涛, 王 昊. 根据心肺最佳点构建反向传播神经网络最大摄氧量预测模型[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1224-1231. |
| [3] | 杨九杰, 李 治, 王树杰, 田 野, 赵 伟. 神经电生理监测硬脊膜切开减压治疗急性脊髓损伤过程中脊髓的功能变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [4] | 王 继, 张 敏, 杨中亚, 张 龙. 体力活动干预2型糖尿病肌少症的研究现状[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [5] | 梁家琪, 刘恒旭, 阳金鑫, 杨 椅, 邓旭辉, 谭明健, 罗 炯. 运动与肠道菌健康效益的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1292-1299. |
| [6] | 黄林科, 韦林华, 蒋 捷, 刘 倩, 陈蔚蔚. 雌激素与跑台运动干预卵巢切除模型小鼠骨量和关节软骨的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [7] | 毕耕超, 张彦龙, 李秋月, 胡龙威, 张 愉. 不同高度和间距下跳深动作中膝关节力学和周围肌肉的激活特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1211-1218. |
| [8] | 阮 凌, 王光华, 吴荣平, 晋 战, 吕镇庆, 张 楠, 李寿邦. 运动强度与高脂饮食模型大鼠脂代谢紊乱和氧化应激的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1149-1155. |
| [9] | 张 艳, 何瑞波, 王庆博, 皮亦华, 陆春敏, 徐传仪, 马 刚, 彭 朋. 不同负荷量有氧运动对肥胖大鼠骨骼肌炎症反应和胰岛素信号途径的影响及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1237-1244. |
| [10] | 国婷婷, 谢 红, 徐光华. 弹性护踝防护性能的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1031-1037. |
| [11] | 杨怡天, 王 璐, 姚 蔚, 赵 彬. 生物支架与巨噬细胞在骨再生中的相互影响及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1071-1079. |
| [12] | 王金玲, 黄夏荣, 屈萌艰, 黄福锦, 尹林伟, 钟培瑞, 刘 静, 孙光华, 廖 阳, 周 君. 运动训练老年骨质疏松大鼠骨量及骨微结构的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(5): 676-682. |
| [13] | 卢会秀, 曹海育, 娄 丹, 李建英, 刘宏远, 孙 静. 咪喹莫特联合光动力疗法治疗增生性瘢痕的免疫应答与预后[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(5): 690-694. |
| [14] | 李玉娇, 苏坤霞. 高强度耐力运动影响高脂诱导肥胖模型小鼠白色脂肪棕色化相关蛋白的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(5): 707-713. |
| [15] | 游国鹏, 王健清, 刘 飞, 袁 强, 柳皓严, 吴 瑛. 基于机器学习的速度攀岩关键技术动作指标筛选[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(5): 738-744. |
至今,研究者们在各物种中发现了 7 597 种微小核糖核酸(microRNAs,miRNAs),其中,在人类基因组中已发现3 000 多种 miRNAs[1],对 miRNAs 的发现使学者们对基因表达调控有了全新认识,目前已是生物科学领域颇受关注的焦点。miRNAs不仅参与各种生理生化过程,包括细胞生长、分化、凋亡、糖代谢、脂肪代谢、胰岛素分泌、脑形成、心脏发生和干细胞分化,与许多疾病(包括癌症)的发生也密切相关[2]。在外周体液中已经发现有稳定存在的循环miRNAs (circulating microRNAs,ci-miRNAs),很多疾病已将其作为诊断和治疗的生物标志物[3]。据报道,循环中表达异常的miRNAs至少与70种疾病相关,且易于获得、高稳定性、易于扩增,被广泛作为有用的疾病生物标记进行研究[4]。
基于ci-miRNAs的治疗性干预措施的潜在应用也大有前景。如在黑猩猩体内,通过静脉注射补充miR-122拮抗剂,可以长期抑制丙型肝炎病毒[5]。这种疗法和其他基于miRNAs的疗法已用于对诸如冠心病、心脏衰竭和心肌梗死等疾病的临床前发展和临床测试中。大多数研究都集中在疾病环境中ci-miRNAs的表达水平上,对其他生理变化的影响也进行了研究,只是报道更少。运动对机体是一种压力源,会引起良好反应,若重复训练生理功能产生有益适应。然而,急性运动和长期运动训练中ci-miRNAs的研究已经滞后,只是最近才研究兴趣高涨。考虑到运动训练对心血管系统、骨骼肌及整个身体的良好影响,因此认为ci-miRNAs会随运动而改变,并可能参与调节部分或全部运动适应过程。近年来,研究者们也确实发现各种形式的急性运动和长期运动训练对机体产生刺激和适应的同时,ci-miRNAs会发生相应变化,因此研究逐渐关注在运动训练中ci-miRNAs的生物学意义。尽管最近的“组学”研究(如基因组学、蛋白组学、转录组学、代谢组学)已被用于探寻训练适应的生理途径,但这些研究结果仍值得考究。在这方面,ci-miRNAs可能是重要的缺失环节,赋予了它们在调节运动训练适应的上游路径的潜力。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2021年5月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2011年5月至2021年5月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 CNKI、万方、维普、PubMed及Web of Science数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“Exercise;ci-miRNAs;myomiRs;response;eccentric contraction;biomarker”; 中文检索词为“运动;循环miRNAs;myomiR;反应;离心收缩;生物标志物”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述、述评、经验交流、病例报告、荟萃分析等。
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
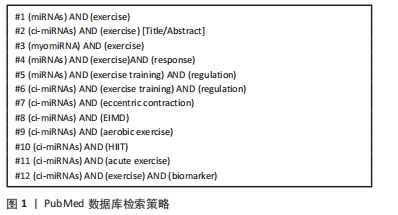
1.1.7 检索文献数量 共收集到256篇相关文献。
1.2 入选标准
纳入标准:涉及运动引起miRNAs表达水平改变的相关研究,和运动对ci-miRNAs表达水平影响的相关研究,以及纳入文献中的引用文献。
排除标准:与研究目的不相关的文献;内容重复或论点陈旧性的文献。
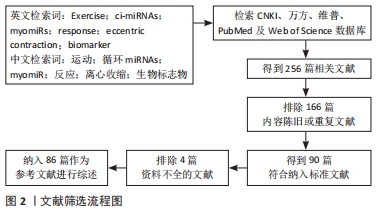
1.3 文献筛选过程 对收集到的资料进行初审,并查看每篇文献后的参考文献,重点选择介绍运动对ci-miRNAs表达水平影响的文献,共收集到256篇相关文献,90篇文献符合纳入标准,排除166篇文献多数为内容重复或观点陈旧,部分研究对象为动物,少数为综述或摘要。90篇文献中,涉及运动对骨骼肌miRNA (myomiRs)的影响、人体运动、不同运动方式等内容,选择86篇作为参考文献进行综述。文献筛选流程图,见图2。
文章与其他综述不同的是,搜集了miRNAs影响运动诱导的健康和表现适应的诸多证据,重点分析ci-miRNAs负责细胞间的通信作用,分析其作为疾病和运动相关性状的生物标志物的重要意义,这些生物标志物将有助于运动筛查、监测和个性化运动处方的开发。然而,由于目前的研究进展和搜索标准,无法保证可以搜索到所有ci-miRNAs相关的文献,在今后的研究过程中需继续关注具体运动方式对具体miRNAs表达水平的影响。
传统的生物标志物研究是通过骨骼肌活检,对肌组织刺激较大,受试者难以接受,ci-miRNAs的应用将显著降低研究中取材、测试的难度。目前的研究业已表明,运动对ci-miRNAs有影响,其表达水平的改变因运动项目、运动强度、运动时间、骨骼肌收缩类型不同而不同,因其反应敏感,与传统生物学指标相比有极大潜力成为新的运动过程中的生物标志物;但涉及到不同年龄段、不同性别进行不同运动项目时ci-miRNAs表达水平改变的差异研究还比较缺乏。
循环中miRNAs的来源有可能是骨骼肌细胞、心肌细胞或者血液中的免疫细胞,参与了某些生理生化连锁反应中的重要环节,调节这些miRNAs可以对整个生理过程起到一定干预作用。未来的研究应专注于确定ci-miRNAs对急性运动反应和长时间运动训练适应的机制和途径。虽然在ci-miRNAs研究过程中的生物学作用仍有待阐明,血浆、血清miRNAs释放的方式还不清楚,其对应的蛋白分子靶标、起到的具体生理功能也需要更多研究来证实;但是,一旦这些生物过程被揭示,ci-miRNAs可能会为未来运动训练过程中的有效干预和疾病治疗手段的发展提供新机遇。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程

文题释义:
运动:运动通过调节蛋白质平衡和调节卫星细胞的命运来诱导人类骨骼肌质量变化,发挥转录、翻译和翻译后的调节,并诱导表观遗传修饰和控制mRNA的稳定性,这些都有助于蛋白质合成的调节。骨骼肌是一种动态组织,能根据生长、衰老、身体活动、营养和健康状况而肥大或萎缩。运动的类型有多种,主要分为有氧运动、无氧运动,运动也有多种方式,如马拉松、中长跑、高强度间歇训练、抗阻训练等,各种运动方式通过miRNAs以不同的机制调节肌肉质量和机体健康。
循环miRNAs:微小核糖核酸(microRNAs,miRNAs)是一类重要的生命活动调控因子,已证实循环miRNAs是多种疾病新的生物标志物,与疾病的发生发展密切相关。近年来研究发现miRNAs可以通过被微囊泡包裹的形式稳定存在于血液和其他体液中,它们被称为循环miRNAs(ci-miRNAs)。除了病理条件导致的机体变化外,循环miRNAs也参与调节了体育运动导致的反应和适应,从而可能有助于体育运动观察到的有益影响。
在外周体液中已经发现有稳定存在的循环miRNAs (circulating microRNAs,ci-miRNAs),很多疾病已将其作为诊断和治疗的生物标志物。据报道,循环中表达异常的miRNAs至少与70种疾病相关,且易于获得、高稳定性、易于扩增,被广泛作为有用的疾病生物标记进行研究。本文搜集了miRNAs影响运动诱导的健康和表现适应的诸多证据,重点分析ci-miRNAs负责细胞间的通信作用,分析其作为疾病和运动相关性状的生物标志物的重要意义,这些生物标志物将有助于运动筛查、监测和个性化运动处方的开发。
传统的生物标志物研究是通过骨骼肌活检,对肌组织刺激较大,受试者难以接受,ci-miRNAs的应用将显著降低研究中取材、测试的难度。目前的研究业已表明,运动对ci-miRNAs有影响,其表达水平的改变因运动项目、运动强度、运动时间、骨骼肌收缩类型不同而不同,因其反应敏感,与传统生物学指标相比有极大潜力成为新的运动过程中的生物标志物;但涉及到不同年龄段、不同性别进行不同运动项目时ci-miRNAs表达水平改变的差异研究还比较缺乏,在今后的研究过程中需继续关注具体运动方式对具体miRNAs表达水平的影响。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||