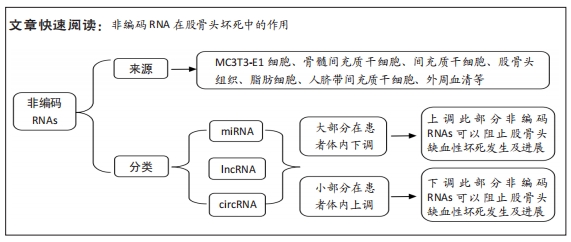
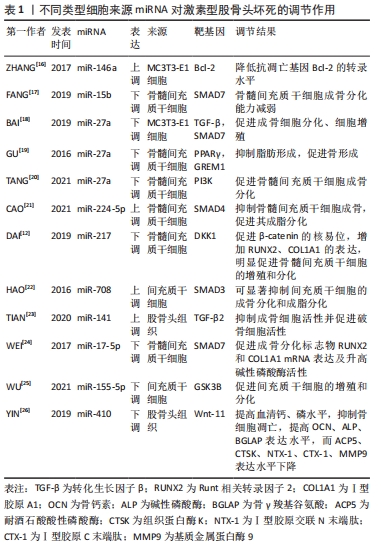
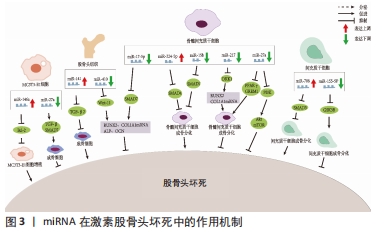
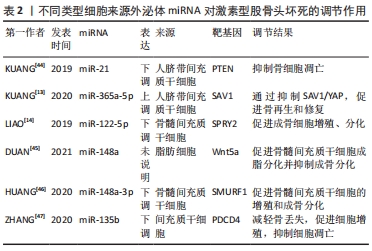
[1] MA J, HUA XY, ZHENG MX, et al. Surface-based map plasticity of brain regions related to sensory motor and pain information processing after osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(4):806-811.
[2] 中国医师协会骨科医师分会骨循环与骨坏死专业委员会,中华医学会骨科分会骨显微修复学组,国际骨循环学会中国区.中国成人股骨头坏死临床诊疗指南(2020)[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,40(20):1365-1376.
[3] XIE K, MAO Y, QU X, et al. High-energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy for nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):25.
[4] BEERMANN J, PICCOLI MT, VIERECK J, et al. Non-coding RNAs in Development and Disease: Background, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Approaches. Physiol Rev. 2016;96(4):1297-1325.
[5] HASHEMIAN SM, POURHANIFEH MH, FADAEI S, et al. Non-coding RNAs and Exosomes: Their Role in the Pathogenesis of Sepsis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;21:51-74.
[6] LI Z, HUANG C, YANG B, et al. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNAs in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(9):5984-5991.
[7] LANDER ES. Initial impact of the sequencing of the human genome. Nature. 2011;470(7333):187-197.
[8] 李崇,缪季峰,林秋宁,等.外泌体非编码RNA在骨关节炎软骨损伤修复中的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2021,41(3):186-194.
[9] SUN Q, YANG Z, LI P, et al. A novel miRNA identified in GRSF1 complex drives the metastasis via the PIK3R3/AKT/NF-κB and TIMP3/MMP9 pathways in cervical cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(9):636.
[10] CHANG C, GREENSPAN A, GERSHWIN ME. The pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical manifestations of steroid-induced osteonecrosis. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102460.
[11] LI P, ZHAI P, YE Z, et al. Differential expression of miR-195-5p in collapse of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Oncotarget. 2017;8(26): 42638-42647.
[12] DAI Z, JIN Y, ZHENG J, et al. MiR-217 promotes cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by targeting DKK1 in steroid-associated osteonecrosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:1112-1119.
[13] KUANG MJ, ZHANG KH, QIU J, et al. Exosomal miR-365a-5p derived from HUC-MSCs regulates osteogenesis in GIONFH through the Hippo signaling pathway. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;23:565-576.
[14] LIAO W, NING Y, XU HJ, et al. BMSC-derived exosomes carrying microRNA-122-5p promote proliferation of osteoblasts in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019;133(18):1955-1975.
[15] XU HJ, LIAO W, LIU XZ, et al. Down-regulation of exosomal microRNA-224-3p derived from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells potentiates angiogenesis in traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. FASEB J. 2019; 33(7):8055-8068.
[16] ZHANG B, YI J, ZHANG CL, et al. MiR-146a inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in murine osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 by regulating Bcl2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(17):3754-3762.
[17] FANG SH, CHEN L, CHEN HH, et al. MiR-15b ameliorates SONFH by targeting Smad7 and inhibiting osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(22):9761-9771.
[18] BAI Y, LIU Y, JIN S, et al. Expression of microRNA‑27a in a rat model of osteonecrosis of the femoral head and its association with TGF‑β/Smad7 signalling in osteoblasts. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(2):850-860.
[19] GU C, XU Y, ZHANG S, et al. miR-27a attenuates adipogenesis and promotes osteogenesis in steroid-induced rat BMSCs by targeting PPARγ and GREM1. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38491.
[20] TANG J, YU H, WANG Y, et al. miR-27a promotes osteogenic differentiation in glucocorticoid-treated human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targeting PI3K. J Mol Histol. 2021;52(2):279-288.
[21] CAO Y, JIANG C, WANG X, et al. Reciprocal effect of microRNA-224 on osteogenesis and adipogenesis in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Bone. 2021;145:115844.
[22] HAO C, YANG S, XU W, et al. MiR-708 promotes steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head, suppresses osteogenic differentiation by targeting SMAD3. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22599.
[23] TIAN L, SUN S, LI W, et al. Down-regulated microRNA-141 facilitates osteoblast activity and inhibits osteoclast activity to ameliorate osteonecrosis of the femoral head via up-regulating TGF-β2. Cell Cycle. 2020;19(7):772-786.
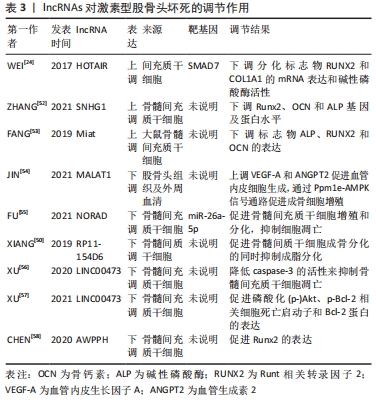
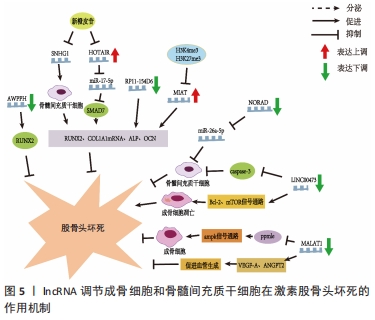
[24] WEI B, WEI W, ZHAO B, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits miR-17-5p to regulate osteogenic differentiation and proliferation in non-traumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head. PLoS One. 2017;12(2):e0169097.
[25] WU F, HUANG W, YANG Y, et al. miR-155-5p regulates mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis and proliferation by targeting GSK3B in steroid-associated osteonecrosis. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(1):83-91.
[26] YIN Y, DING L, HOU Y, et al. Upregulating MicroRNA-410 or Downregulating Wnt-11 Increases Osteoblasts and Reduces Osteoclasts to Alleviate Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2019;14(1):383.
[27] MIAO C, ZHOU W, WANG X, et al. The Research Progress of Exosomes in Osteoarthritis, With Particular Emphasis on the Mediating Roles of miRNAs and lncRNAs. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:685623.
[28] MATHIEU M, MARTIN-JAULAR L, LAVIEU G, et al. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(1):9-17.
[29] PATHAN M, FONSEKA P, CHITTI SV, et al. Vesiclepedia 2019: a compendium of RNA, proteins, lipids and metabolites in extracellular vesicles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D516-D519.
[30] VAN BALKOM BW, EISELE AS, PEGTEL DM, et al. Quantitative and qualitative analysis of small RNAs in human endothelial cells and exosomes provides insights into localized RNA processing, degradation and sorting. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:26760.
[31] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977.
[32] HE C, ZHENG S, LUO Y, et al. Exosome Theranostics: Biology and Translational Medicine. Theranostics. 2018;8(1):237-255.
[33] SULLIVAN R, SAEZ F, GIROUARD J, et al. Role of exosomes in sperm maturation during the transit along the male reproductive tract. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2005;35(1):1-10.
[34] LUDWIG AK, GIEBEL B. Exosomes: small vesicles participating in intercellular communication. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012;44(1):11-15.
[35] ASGHAR S, LITHERLAND GJ, LOCKHART JC, et al. Exosomes in intercellular communication and implications for osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59(1):57-68.
[36] ZHANG C, SU Y, DING H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived and siRNAs-encapsulated exosomes inhibit osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(17):9605-9612.
[37] 刘超,曾昭穆,温稀超,等.外泌体非编码RNA在胶质瘤发生发展中的作用及其临床应用前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(24):3928-3936.
[38] CHEN J, YU X, ZHANG X. Advances on biological functions of exosomal non-coding RNAs in osteoarthritis. Cell Biochem Funct. 2022;40(1):49-59.
[39] JAQUENOD DE GIUSTI C, SANTALLA M, DAS S. Exosomal non-coding RNAs (Exo-ncRNAs) in cardiovascular health. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019;137:143-151.
[40] LIU Q. The emerging roles of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in bladder cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26(4):966-976.
[41] XIA H, HUANG Z, LIU S, et al. Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs: Regulatory and Therapeutic Target of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2021;11:653846.
[42] VALADI H, EKSTRÖM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659.
[43] ZHANG M, CHEN D, ZHANG F, et al. Serum exosomal hsa-miR-135b-5p serves as a potential diagnostic biomarker in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(5):2136-2154.
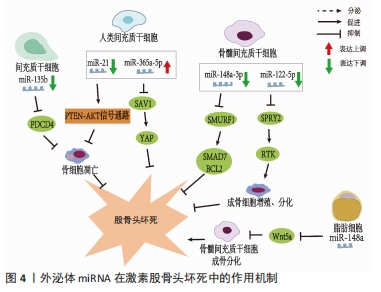
[44] KUANG MJ, HUANG Y, ZHAO XG, et al. Exosomes derived from Wharton’s jelly of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce osteocyte apoptosis in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats via the miR-21-PTEN-AKT signalling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(9):1861-1871.
[45] DUAN DY, TANG J, TIAN HT, et al. Adipocyte-secreted microvesicle-derived miR-148a regulates adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation by targeting Wnt5a/Ror2 pathway. Life Sci. 2021;278:119548.
[46] HUANG S, LI Y, WU P, et al. microRNA-148a-3p in extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppresses SMURF1 to prevent osteonecrosis of femoral head. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(19):11512-11523.
[47] ZHANG X, YOU JM, DONG XJ, et al. Administration of mircoRNA-135b-reinforced exosomes derived from MSCs ameliorates glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head (ONFH) in rats. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(23): 13973-13983.
[48] FATICA A, BOZZONI I. Long non-coding RNAs: new players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15(1):7-21.
[49] ZHENG YL, SONG G, GUO JB, et al. Interactions Among lncRNA/circRNA, miRNA, and mRNA in Musculoskeletal Degenerative Diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:753931.
[50] XIANG S, LI Z, WENG X. The role of lncRNA RP11-154D6 in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head through BMSC regulation. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(10):18435-18445.
[51] LI T, XIAO K, XU Y, et al. Identification of long non‑coding RNAs expressed during the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow‑derived mesenchymal stem cells obtained from patients with ONFH. Int J Mol Med. 2020;46(5):1721-1732.
[52] ZHANG C, YUAN S, CHEN Y, et al. Neohesperidin promotes the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells by inhibiting the histone modifications of lncRNA SNHG1. Cell Cycle. 2021;20(19):1953-1966.
[53] FANG B, LI Y, CHEN C, et al. Huo Xue Tong Luo capsule ameliorates osteonecrosis of femoral head through inhibiting lncRNA-Miat. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019;238:111862.
[54] JIN Y, ZHU HX, WEI BF. Reduced serum and local LncRNA MALAT1 expressions are linked with disease severity in patients with non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Technol Health Care. 2021;29(3):479-488.
[55] FU D, YANG S, LU J, et al. LncRNA NORAD promotes bone marrow stem cell differentiation and proliferation by targeting miR-26a-5p in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):18.
[56] XU Y, JIANG Y, WANG Y, et al. LINC00473 regulated apoptosis, proliferation and migration but could not reverse cell cycle arrest of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by a high-dosage of dexamethasone. Stem Cell Res. 2020;48:101954.
[57] XU Y, JIANG Y, WANG Y, et al. LINC00473 rescues human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from apoptosis induced by dexamethasone through the PEBP1‑mediated Akt/Bad/Bcl‑2 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(1):171-182.
[58] CHEN X, LI J, LIANG D, et al. LncRNA AWPPH participates in the development of non-traumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head by upregulating Runx2. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19(1):153-159.
[59] YUAN S, ZHANG C, ZHU Y, et al. Neohesperidin Ameliorates Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head by Inhibiting the Histone Modification of lncRNA HOTAIR. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:5419-5430.
[60] YU QS, GUO WS, CHENG LM, et al. Glucocorticoids Significantly Influence the Transcriptome of Bone Microvascular Endothelial Cells of Human Femoral Head. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(14):1956-1963.
[61] SHI S, WU X, WANG X, et al. Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Cardiomyocyte-Like Cells Is Regulated by the Combined Low Dose Treatment of Transforming Growth Factor-β1 and 5-Azacytidine. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:3816256.
[62] ZHANG L, LI S, LI J, et al. LncRNA ORLNC1 Promotes Bone Marrow Mesenchyml Stem Cell Pyroptosis Induced by Advanced Glycation End Production by Targeting miR-200b-3p/Foxo3 Pathway. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021;17(6):2262-2275.
[63] PRUUNSILD P, BENGTSON CP, BADING H. Networks of Cultured iPSC-Derived Neurons Reveal the Human Synaptic Activity-Regulated Adaptive Gene Program. Cell Rep. 2017;18(1):122-135.
[64] TANG YH, YUE ZS, LI GS, et al. Effect of beta-ecdysterone on glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis and autophagy in osteoblasts. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(1): 158-164.
[65] KUANG MJ, XING F, WANG D, et al. CircUSP45 inhibited osteogenesis in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head by sponging miR-127-5p through PTEN/AKT signal pathway: Experimental studies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;509(1):255-261.
[66] XIN W, YUAN S, WANG B, et al. Hsa_circ_0066523 promotes the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells by repressing PTEN. Bone Joint Res. 2021;10(8):526-535.
[67] JIANG B, ZHU SH, ZENG JY, et al. Plasma and local expressions of CircRNA CDR1as are linked with disease severity in patients with non-traumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):592.
|