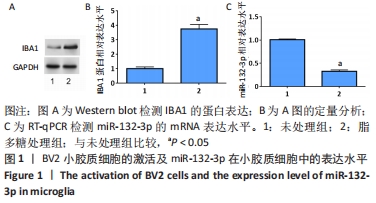
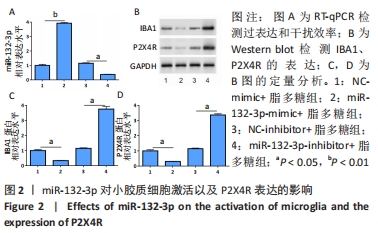
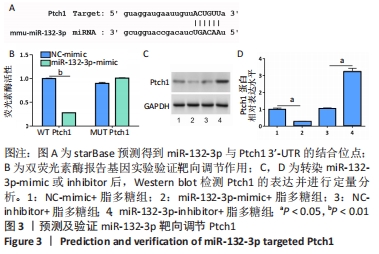
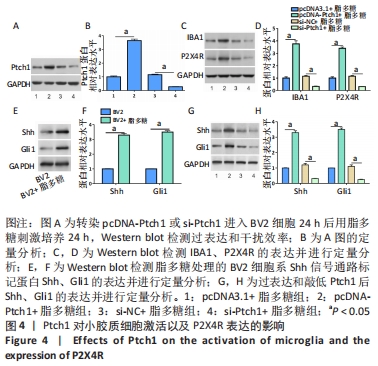
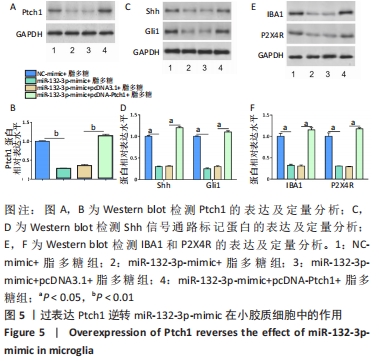
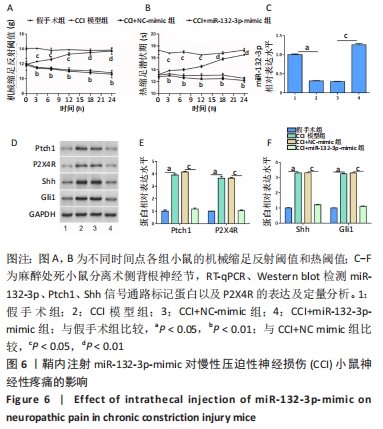
[1] BICKER S, LACKINGER M, WEIß K, et al. MicroRNA-132, -134, and -138: a microRNA troika rules in neuronal dendrites. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014;71(20):3987-4005.
[2] CHEN D, HU S, WU Z, et al. The Role of MiR-132 in Regulating Neural Stem Cell Proliferation, Differentiation and Neuronal Maturation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(6):2319-2330.
[3] ATEN S, PAGE CE, KALIDINDI A, et al. miR-132/212 is induced by stress and its dysregulation triggers anxiety-related behavior. Neuropharmacology. 2019;144:256-270.
[4] LIU G, YIN F, ZHANG C, et al. Effects of regulating miR-132 mediated GSK-3β on learning and memory function in mice. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(2):1191-1197.
[5] ARAI M, GENDA Y, ISHIKAWA M, et al. The miRNA and mRNA changes in rat hippocampi after chronic constriction injury. Pain Med. 2013;14(5): 720-729.
[6] 施燕渲,朱涛.微RNA-132在神经病理性疼痛中的研究进展[J].医学综述,2017,23(16):3170-3173.
[7] 施燕渲,朱涛.miR-132在神经病理性疼痛传导通路中的表达[J].实用医学杂志,2017,33(19):3189-3192.
[8] ZHANG R, HUANG M, CAO Z, et al. MeCP2 plays an analgesic role in pain transmission through regulating CREB / miR-132 pathway. Mol Pain. 2015;11:19.
[9] WU B, LI J, WANG H, et al. MiR-132-3p serves as a tumor suppressor in mantle cell lymphoma via directly targeting SOX11. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020;393(11):2197-2208.
[10] GE Y, SONG X, LIU J, et al. The Combined Therapy of Berberine Treatment with lncRNA BACE1-AS Depletion Attenuates Aβ25-35 Induced Neuronal Injury Through Regulating the Expression of miR-132-3p in Neuronal Cells. Neurochem Res. 2020;45(4):741-751.
[11] 杨秀方,褚凯丽,李媛,等.miR-132调节非小细胞肺癌hedgehog信号通路受体基因PTCH1及细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭[J].复旦学报(医学版),2015,42(3):291-299,306.
[12] YANG Z, GAO L, JIA H, et al. The Expression of Shh, Ptch1, and Gli1 in the Developing Caudal Spinal Cord of Fetal Rats With Anorectal Malformations. J Surg Res. 2019;233:173-182.
[13] TUKACHINSKY H, PETROV K, WATANABE M, et al. Mechanism of inhibition of the tumor suppressor Patched by Sonic Hedgehog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(40):E5866-E5875.
[14] MOREAU N, MAUBORGNE A, BOURGOIN S, et al. Early alterations of Hedgehog signaling pathway in vascular endothelial cells after peripheral nerve injury elicit blood-nerve barrier disruption, nerve inflammation, and neuropathic pain development. Pain. 2016;157(4):827-839.
[15] MOREAU N, BOUCHER Y. Hedging against Neuropathic Pain: Role of Hedgehog Signaling in Pathological Nerve Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(23):9115.
[16] FURUBE E, KAWAI S, INAGAKI H, et al. Brain Region-dependent Heterogeneity and Dose-dependent Difference in Transient Microglia Population Increase during Lipopolysaccharide-induced Inflammation. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2203.
[17] LV R, DU L, ZHANG L, et al. Polydatin attenuates spinal cord injury in rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and microglia apoptosis via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Life Sci. 2019;217:119-127.
[18] 李永丰,任维,刘一辉.CB1受体通过钾离子通道介导外周镇痛作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2019,35(4):92-98.
[19] 刘宇临.Sonic hedgehog信号通路在神经病理性疼痛模型大鼠中的表达及其意义的研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2017.
[20] COLLOCA L, LUDMAN T, BOUHASSIRA D, et al. Neuropathic pain. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17002.
[21] BARON R, MAIER C, ATTAL N, et al. Peripheral neuropathic pain: a mechanism-related organizing principle based on sensory profiles. Pain. 2017;158(2):261-272.
[22] NI HD, YAO M, HUANG B, et al. Glial activation in the periaqueductal gray promotes descending facilitation of neuropathic pain through the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. J Neurosci Res. 2016;94(1):50-61.
[23] KUAN YH, SHYU BC. Nociceptive transmission and modulation via P2X receptors in central pain syndrome. Mol Brain. 2016;9(1):58.
[24] CHEN L, LIU YW, YUE K, et al. Differential expression of ATP-gated P2X receptors in DRG between chronic neuropathic pain and visceralgia rat models. Purinergic Signal. 2016;12(1):79-87.
[25] ZHANG WJ, LUO HL, ZHU ZM. The role of P2X4 receptors in chronic pain: A potential pharmacological target. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020; 129:110447.
[26] INOUE K, TSUDA M. Nociceptive signaling mediated by P2X3, P2X4 and P2X7 receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;187:114309.
[27] 陈桂玲,张加强.右美托咪定对神经病理性痛大鼠脊髓P2X3和P2X4受体表达的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志,2017,27(6):27-31.
[28] TRANG M, SCHMALZING G, MÜLLER CE, et al. Dissection of P2X4 and P2X7 Receptor Current Components in BV-2 Microglia. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(22):8489.
[29] INOUE K. Role of the P2X4 receptor in neuropathic pain. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2019;47:33-39.
[30] ZHANG WJ, ZHU ZM, LIU ZX. The role of P2X4 receptor in neuropathic pain and its pharmacological properties. Pharmacol Res. 2020;158:104875.
[31] HALIEVSKI K, GHAZISAEIDI S, SALTER MW. Sex-Dependent Mechanisms of Chronic Pain: A Focus on Microglia and P2X4R. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020;375(1):202-209.
[32] XU R, YANG F, LI L, et al. CB2/miR-124 signaling down-regulate the expression of purinergic P2X4 and P2X7 receptor in dorsal spinal cord of CCI rats. 2020.
[33] GONG X, HUANG MY, CHEN L. Mechanism of miR-132-3p Promoting Neuroinflammation and Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. eNeuro. 2022;9(1):ENEURO.0393-21.2021.
[34] WANG X, WANG H, ZHANG T, et al. Inhibition of MicroRNA-195 Alleviates Neuropathic Pain by Targeting Patched1 and Inhibiting SHH Signaling Pathway Activation. Neurochem Res. 2019;44(7):1690-1702.
[35] COHEN M, KICHEVA A, RIBEIRO A, et al. Ptch1 and Gli regulate Shh signalling dynamics via multiple mechanisms. Nat Commun. 2015;6: 6709.
[36] 孙艳.2,5-己二酮致人卵巢颗粒细胞凋亡及Sonichedgehog信号通路调控机制的研究[D].福州:福建医科大学,2012.
[37] CHOUDHRY Z, RIKANI AA, CHOUDHRY AM, et al. Sonic hedgehog signalling pathway: a complex network. Ann Neurosci. 2014;21(1):28-31.
[38] 牛小莉.丁苯酞对血管性痴呆大鼠认知功能及Shh/Ptch1信号通路和内质网应激相关蛋白表达的影响[D].石家庄:河北医科大学, 2019.
[39] BELGACEM YH, HAMILTON AM, SHIM S, et al. The Many Hats of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Nervous System Development and Disease. J Dev Biol. 2016;4(4):35.
[40] HE W, CUI L, ZHANG C, et al. Sonic Hedgehog Promotes Neurite Outgrowth of Primary Cortical Neurons Through Up-Regulating BDNF Expression. Neurochem Res. 2016;41(4):687-695.
[41] LI X, LI Y, LI S, et al. The role of Shh signalling pathway in central nervous system development and related diseases. Cell Biochem Funct. 2021;39(2):180-189.
[42] 刘宇临,刘丹彦.Sonic hedgehog信号通路在神经病理性疼痛模型大鼠中的表达及其意义[J].重庆医科大学学报,2016,41(1):61-65.
[43] 冯晓雪,蔡孟,杨晓秋,等.大鼠神经病理性痛时脊髓Sonic hedgehog信号通路与炎症反应的关系[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2018, 38(11):1347-1350.
[44] 冯晓雪,杨晓秋,刘丹彦. 环巴明抑制SHH信号通路缓解大鼠神经病理性疼痛[J].基础医学与临床,2016,36(5):661-665.
|