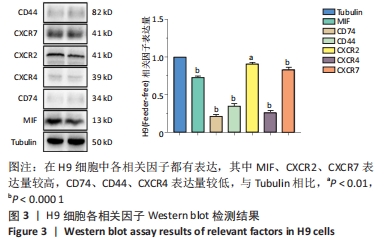
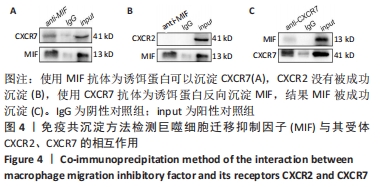
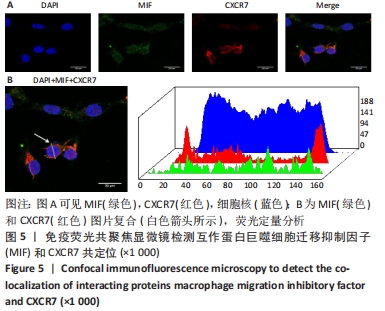
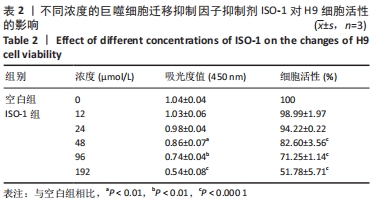
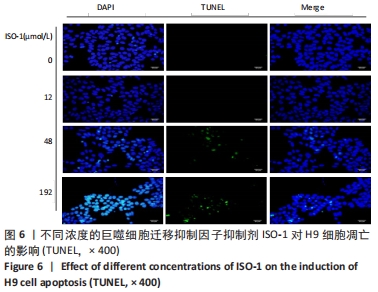
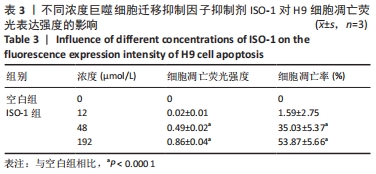
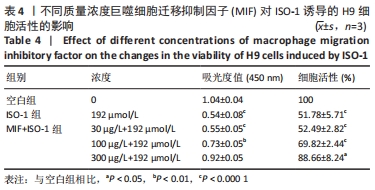
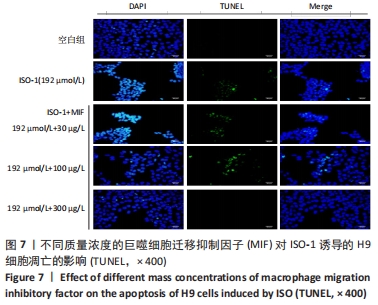
[1] CHEN J, WANG Y, WANG C, et al. LncRNA Functions as a New Emerging Epigenetic Factor in Determining the Fate of Stem Cells. Front Genet. 2020;11:277.
[2] THOMSON JA, ITSKOVITZ-ELDOR J, SHAPIRO SS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science.1998;282(5391):1145-1147.
[3] ZAKRZEWSKI W, DOBRZYNSKI M, SZYMONOWICZ M, et al. Stem cells: past, present, and future. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):68.
[4] NERI S. Genetic Stability of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Regenerative Medicine Applications: A Fundamental Biosafety Aspect. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(10):2406.
[5] TILLMANN S, BERNHAGEN J, NOELS H. Arrest Functions of the MIF Ligand/Receptor Axes in Atherogenesis. Front Immunol. 2013;4:115.
[6] GUNTHER S, FAGONE P, JALCE G, et al. Role of MIF and D-DT in immune-inflammatory, autoimmune, and chronic respiratory diseases: from pathogenic factors to therapeutic targets. Drug Discov Today. 2019;24(2):428-439.
[7] KLEMKE L, DE OLIVEIRA T, WITT D, et al. Hsp90-stabilized MIF supports tumor progression via macrophage recruitment and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(2):155.
[8] NAGARAJAN P, TOBER KL, RIGGENBACH JA, et al. MIF antagonist (CPSI-1306) protects against UVB-induced squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer Res. 2014; 12(9):1292-1302.
[9] GORDON-WEEKS AN, LIM SY, YUZHALIN AE, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: a key cytokine and therapeutic target in colon cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015;26(4):451-461.
[10] OLIVEIRA CS, DE BOCK CE, MOLLOY TJ, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor engages PI3K/Akt signalling and is a prognostic factor in metastatic melanoma. BMC Cancer. 2014;14: 630.
[11] LIAO B, ZHONG BL, LI Z, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor contributes angiogenesis by up-regulating IL-8 and correlates with poor prognosis of patients with primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2010;102(7):844-851.
[12] WADGAONKAR R, SOMNAY K, GARCIA JG. Thrombin induced secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) and its effect on nuclear signaling in endothelium. J Cell Biochem. 2008;105(5):1279-1288.
[13] AMIN MA, HAAS CS, ZHU K, et al. Migration inhibitory factor up-regulates vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 via Src, PI3 kinase, and NFkappaB. Blood. 2006;107(6):2252-2261.
[14] XIE J, YANG L, TIAN L, et al. Macrophage Migration Inhibitor Factor Upregulates MCP-1 Expression in an Autocrine Manner in Hepatocytes during Acute Mouse Liver Injury. Sci Rep. 2016;6:27665.
[15] MA H, WANG J, THOMAS DP, et al. Impaired macrophage migration inhibitory factor-AMP-activated protein kinase activation and ischemic recovery in the senescent heart. Circulation. 2010;122(3):282-292.
[16] LUE H, THIELE M, FRANZ J, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) promotes cell survival by activation of the Akt pathway and role for CSN5/JAB1 in the control of autocrine MIF activity. Oncogene. 2007;26(35):5046-5059.
[17] LANG T, FOOTE A, LEE J P, et al. MIF: Implications in the Pathoetiology of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front Immunol. 2015;6:577.
[18] SINITSKI D, KONTOS C, KRAMMER C, et al. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF)-Based Therapeutic Concepts in Atherosclerosis and Inflammation. Thromb Haemost. 2019;119(4):553-566.
[19] KANG I, BUCALA R. The immunobiology of MIF:function, genetics and prospects for precision medicine. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(7):427-437.
[20] ALAMPOUR-RAJABI S, EL BO, ROT A, et al. MIF interacts with CXCR7 to promote receptor internalization, ERK1/2 and ZAP-70 signaling, and lymphocyte chemotaxis. FASEB J. 2015;29(11):4497-4511.
[21] KLASEN C, OHL K, STERNKOPF M, et al. MIF promotes B cell chemotaxis through the receptors CXCR4 and CD74 and ZAP-70 signaling. J Immunol. 2014; 192(11):5273-5284.
[22] JANKAUSKAS SS, WONG D, BUCALA R, et al. Evolving complexity of MIF signaling. Cell Signal. 2019;57:76-88.
[23] XU X, PANG J, CHEN Y, et al. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) Deficiency Exacerbates Aging-Induced Cardiac Remodeling and Dysfunction Despite Improved Inflammation: Role of Autophagy Regulation. Sci Rep. 2016;6: 22488.
[24] LIU Y, ZHAO L, JU Y, et al. A novel androstenedione derivative induces ROS-mediated autophagy and attenuates drug resistance in osteosarcoma by inhibiting macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1361.
[25] YAO Y, DENG Q, SONG W, et al. MIF Plays a Key Role in Regulating Tissue-Specific Chondro-Osteogenic Differentiation Fate of Human Cartilage Endplate Stem Cells under Hypoxia. Stem Cell Reports. 2016;7(2):249-262.
[26] CUI J, ZHANG F, WANG Y, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes cardiac stem cell proliferation and endothelial differentiation through the activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and AMPK pathways. Int J Mol Med. 2016;37(5):1299-1309.
[27] ZHANG X, CHEN L, WANG Y, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes proliferation and neuronal differentiation of neural stem/precursor cells through Wnt/beta-catenin signal pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2013;9(10):1108-1120.
[28] GILFILLAN M, DAS P, SHAH D, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-451 is associated with increased expression of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor and mitgation of the cardio-pulmonary phenotype in a murine model of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Respir Res. 2020;21(1):92.
[29] BAYRAKTAR S, TANYERI BB, KILIC U. Umbilical cord levels of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. Turk J Med Sci. 2021; 51(2):722-726.
[30] SUMAIYA K, LANGFORD D, NATARAJASEENIVASAN K, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF): A multifaceted cytokine regulated by genetic and physiological strategies. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;108024. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.108024.
[31] VERJANS E, NOETZEL E, BEKTAS N, et al. Dual role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in human breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:230.
[32] FUJIHARA Y, HIKITA A, TAKATO T, et al. Roles of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in cartilage tissue engineering. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(2):1490-1499.
[33] YAO J, LENG L, SAULER M, et al. Transcription factor ICBP90 regulates the MIF promoter and immune susceptibility locus. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(2):732-744.
[34] KIM J, GEE HY, LEE MG. Unconventional protein secretion - new insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutic targets of human diseases. J Cell Sci. 2018; 131(12):jcs213686.
[35] EICKHOFF R, WILHELM B, RENNEBERG H, et al. Purification and characterization of macrophage migration inhibitory factor as a secretory protein from rat epididymis: evidences for alternative release and transfer to spermatozoa. Mol Med. 2001;7(1):27-35.
[36] BILSBORROW JB, DOHERTY E, TILSTAM P V, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) as a therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019.23(9):733-744.
[37] TILSTAM PV, PANTOURIS G, CORMAN M, et al. A selective small-molecule inhibitor of macrophage migration inhibitory factor-2 (MIF-2), a MIF cytokine superfamily member, inhibits MIF-2 biological activity. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(49):18522-18531.
[38] STADTMANN A, ZARBOCK A. CXCR2: From Bench to Bedside. Front Immunol. 2012;3:263.
[39] PUCHERT M, ENGELE J. The peculiarities of the SDF-1/CXCL12 system: in some cells, CXCR4 and CXCR7 sing solos, in others, they sing duets. Cell Tissue Res. 2014;355(2):239-253.
[40] CHATTERJEE M, BORST O, WALKER B, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor limits activation-induced apoptosis of platelets via CXCR7-dependent Akt signaling. Circ Res. 2014;115(11):939-949.
[41] STARLETS D, GORE Y, BINSKY I, et al. Cell-surface CD74 initiates a signaling cascade leading to cell proliferation and survival. Blood. 2006;107(12):4807-4816.
[42] GORE Y, STARLETS D, MAHARSHAK N, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor induces B cell survival by activation of a CD74-CD44 receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(5):2784-2792.
[43] COURNIA Z, LENG L, GANDAVADI S, et al. Discovery of human macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)-CD74 antagonists via virtual screening. J Med Chem. 2009;52(2):416-424.
[44] SHAUL YD, SEGER R. The MEK/ERK cascade: from signaling specificity to diverse functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1773(8):1213-1226.
[45] STAMATIADES GA, KAISER UB. Gonadotropin regulation by pulsatile GnRH: Signaling and gene expression. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018;463:131-141.
[46] VOSKAS D, LING LS, WOODGETT JR. Signals controlling un-differentiated states in embryonic stem and cancer cells: role of the phosphatidylinositol 3’ kinase pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2014;229(10):1312-1322.
[47] SATO N, SANJUAN IM, HEKE M, et al. Molecular signature of human embryonic stem cells and its comparison with the mouse. Dev Biol. 2003;260(2):404-413.
[48] PALING NR, WHEADON H, BONE HK, et al. Regulation of embryonic stem cell self-renewal by phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent signaling. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(46):48063-48070.
[49] SHPARBERG RA, GLOVER HJ, MORRIS MB. Modeling Mammalian Commitment to the Neural Lineage Using Embryos and Embryonic Stem Cells. Front Physiol. 2019;10:705.
[50] BRAZIL DP, YANG ZZ, HEMMINGS BA. Advances in protein kinase B signalling: AKTion on multiple fronts. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004;29(5):233-242.
[51] TAHIR SA, GAO J, MIURA Y, et al. Autoimmune antibodies correlate with immune checkpoint therapy-induced toxicities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(44): 22246-22251.
[52] RAJASEKARAN D, GRONING S, SCHMITZ C, et al. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor-CXCR4 Receptor Interactions: EVIDENCE FOR PARTIAL ALLOSTERIC AGONISM IN COMPARISON WITH CXCL12 CHEMOKINE. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(30):15881-15895.
|