[1] FERRARO R, LATINA JM, ALFADDAGH A, et al. Evaluation and Management of Patients With Stable Angina: Beyond the Ischemia Paradigm: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020; 76(19):2252-2266.
[2] WANG JC, LU L, CHEN SS, et al. PERK Overexpression-Mediated Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway Alleviates Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Injury in Neonatal Murine Cardiomyocytes via Improving Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6458060.
[3] HUANG XW, PAN MD, DU PH, et al. Arginase-2 protects myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via NF-κB/TNF-α pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(19):6529-6537.
[4] LI T, TAN Y, OUYANG S, et al. Resveratrol protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via attenuating ferroptosis. Gene. 2022; 808:145968.
[5] XIA M, ZU XY, CHEN ZY, et al. Noncoding RNAs in triple negative breast cancer: Mechanisms for chemoresistance. Cancer Lett. 2021;523:100-110.
[6] ARYAL B, SUÁREZ Y. Non-coding RNA regulation of endothelial and macrophage functions during atherosclerosis. Vascul Pharmacol. 2019; 114:64-75.
[7] ZHANG L, XU X, SU X. Noncoding RNAs in cancer immunity: functions, regulatory mechanisms, and clinical application. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):48.
[8] WADLEY GD, LAMON S, ALEXANDER SE, et al. Noncoding RNAs regulating cardiac muscle mass. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;127(2):633-644.
[9] CHEN HY, XIAO ZZ, LING X, et al. ELAVL1 is transcriptionally activated by FOXC1 and promotes ferroptosis in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating autophagy. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):14.
[10] WANG JP, CHI RF, WANG K, et al. Oxidative stress impairs myocyte autophagy, resulting in myocyte hypertrophy. Exp Physiol. 2018;103(4): 461-472.
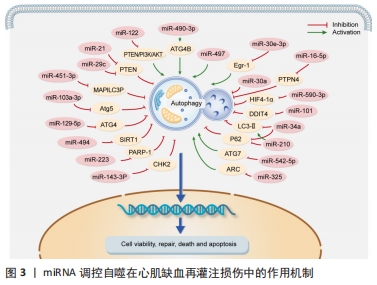
[11] SUN T, LI MY, LI PF, et al. MicroRNAs in Cardiac Autophagy: Small Molecules and Big Role. Cells. 2018;7(8):104.
[12] OHSUMI Y. Historical landmarks of autophagy research. Cell Res. 2014; 24(1):9-23.
[13] MA S, WANG Y, CHEN Y, et al. The role of the autophagy in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1852(2):271-276.
[14] CĂTANĂ CS, ATANASOV AG, BERINDAN-NEAGOE I. Natural products with anti-aging potential: Affected targets and molecular mechanisms. Biotechnol Adv. 2018;36(6):1649-1656.
[15] WU X, IROEGBU CD, PENG J, et al. Cell Death and Exosomes Regulation After Myocardial Infarction and Ischemia-Reperfusion. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:673677.
[16] HUANG J, QING W, PAN Y. NPAS2 ameliorates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury in rats via CX3CL1 pathways and regulating autophagy. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(16):20569-20584.
[17] KHAN SH, KUMAR R. Role of an intrinsically disordered conformation in AMPK-mediated phosphorylation of ULK1 and regulation of autophagy. Mol Biosyst. 2012;8(1):91-96.
[18] YANG L, XIE P, WU J, et al. Deferoxamine Treatment Combined With Sevoflurane Postconditioning Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Restoring HIF-1/BNIP3-Mediated Mitochondrial Autophagy in GK Rats. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:6.
[19] KALUDERCIC N, MAIURI MC, KAUSHIK S, et al. Comprehensive autophagy evaluation in cardiac disease models. Cardiovasc Res. 2020;116(3):483-504.
[20] HALUSHKA PV, GOODWIN AJ, HALUSHKA MK. Opportunities for microRNAs in the Crowded Field of Cardiovascular Biomarkers. Annu Rev Pathol. 2019;14:211-238.
[21] LU TX, ROTHENBERG ME. MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018; 141(4):1202-1207.
[22] WU P. Inhibition of RNA-binding proteins with small molecules. Nat Rev Chem. 2020;4(9):441-458.
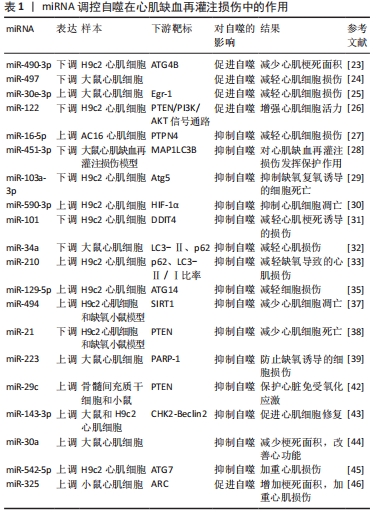
[23] WU Y, MAO Q, LIANG X. Targeting the MicroRNA-490-3p-ATG4B-Autophagy Axis Relieves Myocardial Injury in Ischemia Reperfusion. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2021;14(1):173-183.
[24] LI X, ZENG Z, LI Q, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-497 ameliorates anoxia/reoxygenation injury in cardiomyocytes by suppressing cell apoptosis and enhancing autophagy. Oncotarget. 2015;6(22):18829-18844.
[25] SU B, WANG X, SUN Y, et al. miR-30e-3p Promotes Cardiomyocyte Autophagy and Inhibits Apoptosis via Regulating Egr-1 during Ischemia/Hypoxia. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:7231243.
[26] ZHANG Z, LI H, CHEN S, et al. Knockdown of MicroRNA-122 Protects H9c2 Cardiomyocytes from Hypoxia-Induced Apoptosis and Promotes Autophagy. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:4284-4290.
[27] CAO Z, LIU J, ZHAO Z, et al. miR-16-5p Regulates PTPN4 and Affects Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis and Autophagy Induced by Hypoxia/Reoxygenation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021: 5599031.
[28] LV XW, HE ZF, ZHU PP, et al. miR-451-3p alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting MAP1LC3B-mediated autophagy. Inflamm Res. 2021;70(10-12):1089-1100.
[29] ZHANG C, LU J, WANG H, et al. Effects of miR-103a-3p on the autophagy and apoptosis of cardiomyocytes by regulating Atg5. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(5):1951-1960.
[30] GONG N, YANG X, LI X, et al. MicroRNA-590-3p relieves hypoxia/reoxygenation induced cardiomyocytes apoptosis and autophagy by targeting HIF-1α. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(4):1077.
[31] LI Q, GAO Y, ZHU J, et al. MiR-101 Attenuates Myocardial Infarction-induced Injury by Targeting DDIT4 to Regulate Autophagy. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2020;17(2):123-130.
[32] SHAO H, YANG L, WANG L, et al. MicroRNA-34a protects myocardial cells against ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibiting autophagy via regulating TNF alpha expression. Biochem Cell Biol. 2018;96(3):349-354.
[33] WU TY, LENG Q, TIAN LQ. The microRNA-210/Casp8ap2 Axis Alleviates Hypoxia-Induced Myocardial Injury by Regulating Apoptosis and Autophagy. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2021;161(3-4):132-142.
[34] LIU L, JIN X, HU CF, et al. Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Rescue Myocardial Ischaemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inducing Cardiomyocyte Autophagy Via AMPK and Akt Pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(1):52-68.
[35] ZHANG H, ZHANG X, ZHANG J. MiR-129-5p inhibits autophagy and apoptosis of H9c2 cells induced by hydrogen peroxide via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by targeting ATG14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;506(1):272-277.
[36] LUO G, JIAN Z, ZHU Y, et al. Sirt1 promotes autophagy and inhibits apoptosis to protect cardiomyocytes from hypoxic stress. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(5):2033-2043.
[37] NING S, LI Z, JI Z, et al. MicroRNA-494 suppresses hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and autophagy via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by targeting SIRT1. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(6):5231-5242.
[38] HUANG Z, WU S, KONG F, et al. MicroRNA-21 protects against cardiac hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting excessive autophagy in H9c2 cells via the Akt/mTOR pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(3):467-474.
[39] LIU X, DENG Y, XU Y, et al. MicroRNA-223 protects neonatal rat cardiomyocytes and H9c2 cells from hypoxia-induced apoptosis and excessive autophagy via the Akt/mTOR pathway by targeting PARP-1. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018;118:133-146.
[40] MA W, ZHOU Y, LIU M, et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC00470 in serum derived exosome: a critical regulator for proliferation and autophagy in glioma cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21(1):149.
[41] NASSER MI, MASOOD M, ADLAT S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome microRNA as therapy for cardiac ischemic injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;143:112118.
[42] LI T, GU J, YANG O, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal miRNA-29c Decreases Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Inhibition of Excessive Autophagy via the PTEN/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Circ J. 2020;84(8):1304-1311.
[43] CHEN G, WANG M, RUAN Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-143-3p suppresses myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating autophagy. Life Sci. 2021;280:119742.
[44] XU YQ, XU Y, WANG SH. Effect of exosome-carried miR-30a on myocardial apoptosis in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury rats through regulating autophagy. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019; 23(16):7066-7072.
[45] WANG F, MIN X, HU SY, et al. Hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced upregulation of miRNA-542-5p aggravated cardiomyocyte injury by repressing autophagy. Hum Cell. 2021;34(2):349-359.
[46] BO L, SU-LING D, FANG L, et al. Autophagic program is regulated by miR-325. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(6):967-977.
[47] CHEN G, YUE A, WANG M, et al. The Exosomal lncRNA KLF3-AS1 From Ischemic Cardiomyocytes Mediates IGF-1 Secretion by MSCs to Rescue Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:671610.
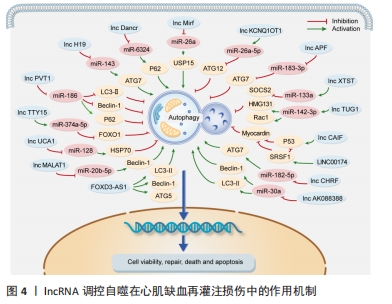
[48] TONG X, CHEN J, LIU W, et al. LncRNA LSINCT5/miR-222 regulates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through PI3K/AKT pathway. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021;52(3):720-729.
[49] ZHAO G, HAILATI J, MA X, et al. LncRNA Gm4419 Regulates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Targeting the miR-682/TRAF3 Axis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020;76(3):305-312.
[50] LV XW, WANG MJ, QIN QY, et al. 6-Gingerol relieves myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury by regulating lncRNA H19/miR-143/ATG7 signaling axis-mediated autophagy. Lab Invest. 2021;101(7):865-877.
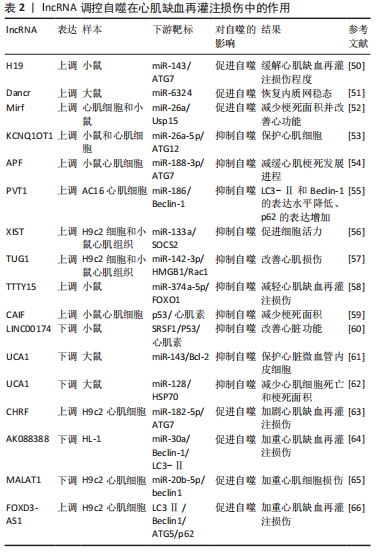
[51] LI J, XIE J, WANG YZ, et al. Overexpression of lncRNA Dancr inhibits apoptosis and enhances autophagy to protect cardiomyocytes from endoplasmic reticulum stress injury via sponging microRNA-6324. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(2):116.
[52] LIANG H, SU X, WU Q, et al. LncRNA 2810403D21Rik/Mirf promotes ischemic myocardial injury by regulating autophagy through targeting Mir26a. Autophagy. 2020;16(6):1077-1091.
[53] LI J, TONG Y, ZHOU Y, et al. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 as a miR-26a-5p sponge regulates ATG12-mediated cardiomyocyte autophagy and aggravates myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2021;338:14-23.
[54] WANG K, LIU CY, ZHOU LY, et al. APF lncRNA regulates autophagy and myocardial infarction by targeting miR-188-3p. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6779.
[55] OUYANG M, LU J, DING Q, et al. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA PVT1 protects human AC16 cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis and autophagy by regulating miR-186/Beclin-1 axis. Gene. 2020;754:144775.
[56] LI Z, ZHANG Y, DING N, et al. Inhibition of lncRNA XIST Improves Myocardial I/R Injury by Targeting miR-133a through Inhibition of Autophagy and Regulation of SOCS2. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;18:764-773.
[57] SU Q, LIU Y, LV XW, et al. Inhibition of lncRNA TUG1 upregulates miR-142-3p to ameliorate myocardial injury during ischemia and reperfusion via targeting HMGB1-and Rac1-induced autophagy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019;133:12-25.
[58] CHEN YQ, YANG X, XU W, et al. Knockdown of lncRNA TTTY15 alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through the miR-374a-5p/FOXO1 axis. IUBMB Life. 2021;73(1):273-285.
[59] LIU CY, ZHANG YH, LI RB, et al. LncRNA CAIF inhibits autophagy and attenuates myocardial infarction by blocking p53-mediated myocardin transcription. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):29.
[60] SU Q, LV XW, XU YL, et al. Exosomal LINC00174 derived from vascular endothelial cells attenuates myocardial I/R injury via p53-mediated autophagy and apoptosis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;23:1304-1322.
[61] DIAO L, ZHANG Q. Transfer of lncRNA UCA1 by hUCMSCs-derived exosomes protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury through impairing miR-143-targeted degradation of Bcl-2. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(4):5967-5985.
[62] CHEN Z, LIU R, NIU Q, et al. Morphine Postconditioning alleviates autophage in ischemia-reperfusion induced cardiac injury through up-regulating lncRNA UCA1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;108:1357-1364.
[63] MO Y, WU H, ZHENG X, et al. LncRNA CHRF aggravates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by enhancing autophagy via modulation of the miR-182-5p/ATG7 pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021;35(4): e22709.
[64] WANG JJ, BIE ZD, SUN CF. Long noncoding RNA AK088388 regulates autophagy through miR-30a to affect cardiomyocyte injury. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(6):10155-10163.
[65] WANG S, YAO T, DENG F, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 Promotes Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation and Reoxygenation Induced Cardiomyocytes Injury Through Sponging miR-20b to Enhance beclin1-Mediated Autophagy. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2019;33(6):675-686.
[66] TONG G, WANG Y, XU C, et al. Long non-coding RNA FOXD3-AS1 aggravates ischemia/reperfusion injury of cardiomyocytes through promoting autophagy. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(9):5634-5644.
[67] SUN Z, YU T, JIAO Y, et al. Expression Profiles and Ontology Analysis of Circular RNAs in a Mouse Model of Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury (vol 2020, 2346369, 2020). Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:2346369.
[68] YU J, KANG X, XIONG Y, et al. Gene Expression Profiles of Circular RNAs and MicroRNAs in Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:643504.
[69] BEERMANN J, PICCOLI MT, VIERECK J, et al. Non-coding RNAs in Development and Disease: Background, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Approaches. Physiol Rev. 2016;96(4):1297-1325.
[70] BAI XF, NIU RZ, LIU J, et al. Roles of noncoding RNAs in the initiation and progression of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Epigenomics. 2021;13(9):715-743.
[71] YAO H, HAN B, ZHANG Y, et al.Non-coding RNAs and Autophagy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1206:199-220.
[72] FAN G, CHEN MJ, WEI J. Involvement of phosphatase and tensin homolog-induced putative kinase 1/Parkin-mediated autophagy in angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy in C57BL/6 mice. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(5):300060519896143.
[73] ZHOU LY, ZHAI M, HUANG Y, et al. The circular RNA ACR attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing autophagy via modulation of the Pink1/FAM65B pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2019; 26(7):1299-1315.
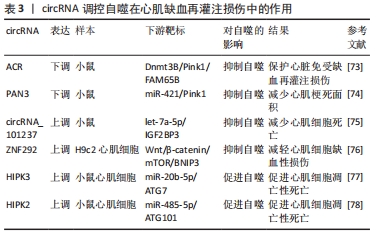
[74] ZHANG CL, LONG TY, BI SS, et al. CircPAN3 ameliorates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury by targeting miR-421/Pink1 axis-mediated autophagy suppression (vol 63, pg 717, 2021). Lab Invest. 2021;101(1): 89-103.
[75] GAN J, YUAN J, LIU Y, et al. Circular RNA_101237 mediates anoxia/reoxygenation injury by targeting let-7a-5p/IGF2BP3 in cardiomyocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2020;45(2):451-460.
[76] REN Q, LI H, WANG X. The circular RNA ZNF292 alleviates OGD-induced injury in H9c2 cells via targeting BNIP3. Cell Cycle. 2019;18(23):3365-3377.
[77] QIU Z, WANG Y, LIU W, et al. CircHIPK3 regulates the autophagy and apoptosis of hypoxia/reoxygenation-stimulated cardiomyocytes via the miR-20b-5p/ATG7 axis. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):64.
[78] ZHOU J, LI L, HU H, et al. Circ-HIPK2 Accelerates Cell Apoptosis and Autophagy in Myocardial Oxidative Injury by Sponging miR-485-5p and Targeting ATG101. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020;76(4):427-436.
|