中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (36): 5826-5830.doi: 10.12307/2022.787
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 上一篇 下一篇
不同模式平衡障碍康复机器人训练老年全髋关节置换后的效果比较
袁 博1,李开南1,2,贾子善3
- 1遵义医科大学,贵州省遵义市 563006;2成都大学附属医院骨科,四川省成都市 610000;3中国人民解放军军区总医院康复科,北京市 100000
Comparison of the effects of different modes of balance disorder rehabilitation robots after total hip arthroplasty in the elderly
Yuan Bo1, Li Kainan1, 2, Jia Zishan3
- 1Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563006, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China; 3Department of Rehabilitation, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100000, China
摘要:
文题释义:
减重步行训练:通过减重装置和步行训练装置,在跑台即训练装置上进行的一种康复功能训练。通过训练可纠正患者步态,提高患者行走能力,减轻神经组织损伤,改善患肢功能,是针对下肢功能障碍改善步行能力的一种新的康复治疗技术。
平衡障碍康复机器人:由中国人民解放军总医院联合北京航空航天大学等相关单位研制的下肢康复机器人,该平台包括减重步行训练装置、足底压力传感器、位置监控装置、位置警示装置、控制柜、软件组件,附件包括打印机(选配)、电池充电器、DE-A、3D视觉模拟系统、深感觉仿真平台等系统及配件组成。该机器人结合人体生物力学特点,可实现多功能、多场景、多方案康复训练。
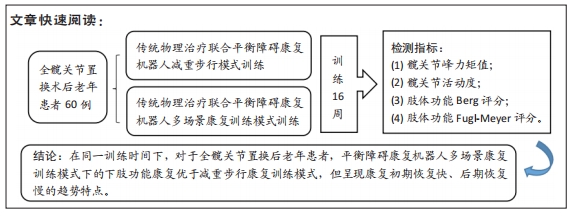
背景:髋关节置换不但改善了股骨颈骨折患者的生活质量、下肢功能,还降低了死亡率,但因术后康复手法单一、康复医师分配不均,总体人群疗效不明,因此康复机器人运用于髋关节置换后不失为一种更有效及安全的方式。
目的:研究基于平衡障碍康复机器人多场景康复模式对全髋关节置换后老年人下肢功能的影响。
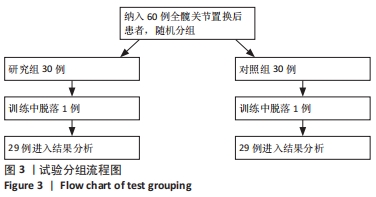
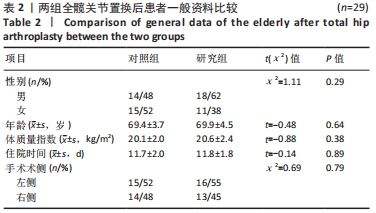
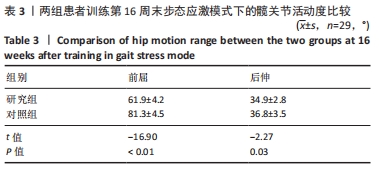
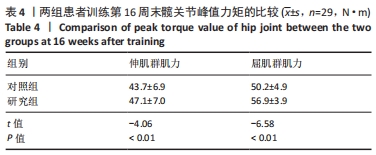
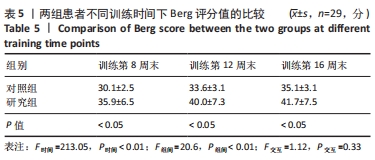
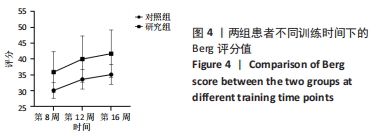
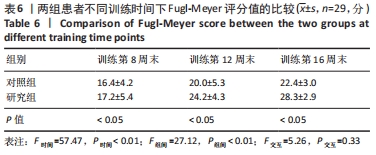
方法:招募中国人民解放军军区总医院及成都大学附属医院骨科病区,2021年1-6月收治的60岁以上股骨颈骨折行全髋关节置换后患者60例为研究对象,利用随机数字表法分为研究组30例和对照组30例。对照组进行传统物理治疗联合平衡障碍康复机器人减重步行模式训练,研究组进行传统物理治疗联合平衡障碍康复机器人多场景康复训练模式训练。训练16周后,采集受试者髋关节峰力矩值数据及步态应激模式下的髋关节活动度;训练8,12,16周后,评估患者肢体功能Berg平衡量表评分与Fugl-Meyer评分。
结果与结论:①训练过程中两组各脱落1例,其余58例在训练过程中未发生意外损伤,顺利完成训练治疗;②训练16周后,研究组患者步态应激模式下的髋关节活动度小于对照组(P < 0.05),髋关节峰值力矩大于对照组(P < 0.05);③随着训练时间的延长,两组患者的肢体功能Berg平衡量表评分与Fugl-Meyer评分升高;相同训练时间下,研究组患者的肢体功能Berg平衡量表评分与Fugl-Meyer评分均高于对照组(P < 0.05);④结果表明,在同一训练时间下,对于全髋关节置换后老年患者,平衡障碍康复机器人多场景康复训练模式下的下肢功能康复优于减重步行康复训练模式,但呈现康复初期恢复快、后期恢复慢的趋势特点。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0612-7072 (袁博)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: