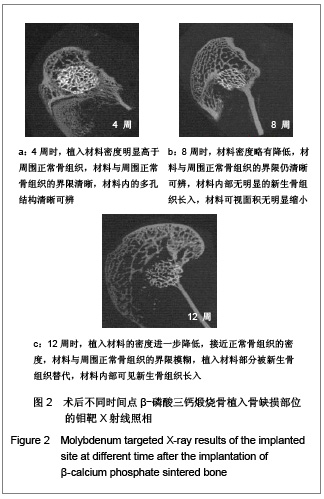
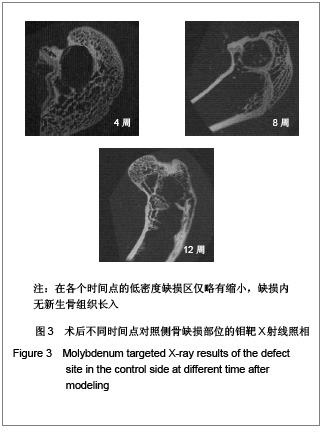
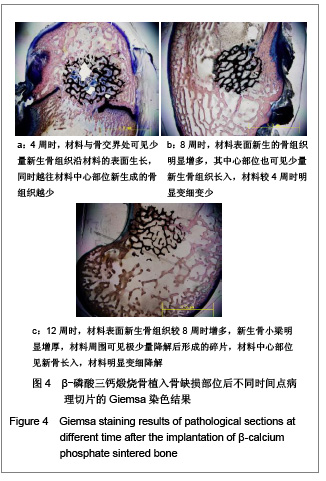
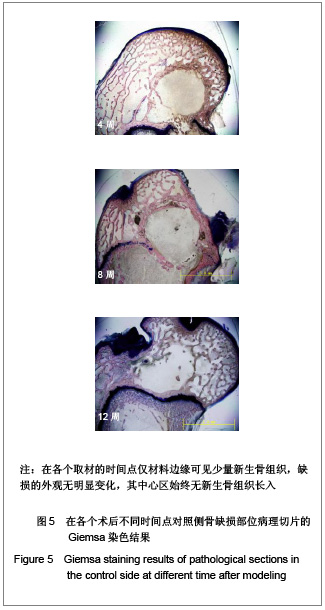
| [1] Boyde A, Corsi A, Quarto R,et al. Osteoconduction in large macroporous hydroxyapatite ceramic implants: evidence for a complementary integration and disintegration mechanism. Bone. 1999;24(6):579-589.[2] Muschler GF, Nitto H, Matsukura Y,et al. Spine fusion using cell matrix composites enriched in bone marrow-derived cells. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(407):102-118.[3] Greenwald AS, Boden SD, Goldberg VM,et al. Bone-graft substitutes: facts, fictions, and applications. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A Suppl 2 Pt 2:98-103.[4] Eggli PS, Müller W, Schenk RK. Porous hydroxyapatite and tricalcium phosphate cylinders with two different pore size ranges implanted in the cancellous bone of rabbits. A comparative histomorphometric and histologic study of bony ingrowth and implant substitution. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; (232):127-138.[5] Mandelkow HK, Hallfeldt KK, Kessler SB,et al. New bone formation following implantation of various hydroxyapatite ceramics. Animal experiment with bore hole models of the sheep tibia. Unfallchirurg. 1990;93(8):376-379.[6] Lai C,Tang XQ. Taoci Gongcheng. 2000;34(6):41-43.赖琛,唐绍裘.生物陶瓷材料在生物材料中的应用[J].陶瓷工程,2000,34(6):41-43. [7] Jiang X,Fang F,Yan YH. Guowai Jiancai Keji. 2001;22(4): 11-15. 江昕,方芳,闫玉华.磷酸钙多孔生物陶瓷的降解机理[J]. 国外建材科技,2001,22(4):11-15. [8] Chen Q,He JP,Zheng QX,et al. Shengwu Wuli Xuebao. 1999;15(2):294-300. 陈勤,何季平,郑启新,等.多孔β-TCP生物陶瓷骨内植入后的显微红外光谱[J].生物物理学报,1999,15(2):294-300.[9] Arai E, Nakashima H, Tsukushi S,et al. Regenerating the fibula with beta-tricalcium phosphate minimizes morbidity after fibula resection. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;(431): 233-237.[10] Delécrin J, Takahashi S, Gouin F,et al. A synthetic porous ceramic as a bone graft substitute in the surgical management of scoliosis: a prospective, randomized study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(5):563-569.[11] Gunzburg R, Szpalski M.Use of a novel beta-tricalcium phosphate-based bone void filler as a graft extender in spinal fusion surgeries.Orthopedics. 2002;25(5 Suppl):s591-595.[12] Fujibayashi S, Shikata J, Tanaka C, et al. Lumbar posterolateral fusion with biphasic calcium phosphate ceramic. J Spinal Disord. 2001;14(3):214-221.[13] Ignatius AA, Wolf S, Augat P,et al. Composites made of rapidly resorbable ceramics and poly(lactide) show adequate mechanical properties for use as bone substitute materials. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;57(1):126-131.[14] Arts JJ, Gardeniers JW, Welten ML,et al. No negative effects of bone impaction grafting with bone and ceramic mixtures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;438:239-247.[15] Bolder SB, Verdonschot N, Schreurs BW,et al. Acetabular defect reconstruction with impacted morsellized bone grafts or TCP/HA particles. A study on the mechanical stability of cemented cups in an artificial acetabulum model. Biomaterials. 2002;23(3):659-666.[16] Bolder SB, Verdonschot N, Schreurs BW,et al. The initial stability of cemented acetabular cups can be augmented by mixing morsellized bone grafts with tricalciumphosphate/hydroxyapatite particles in bone impaction grafting.J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(8):1056-1063.[17] Le Nihouannen D, Daculsi G, Saffarzadeh A,et al. Ectopic bone formation by microporous calcium phosphate ceramic particles in sheep muscles.Bone. 2005;36(6):1086-1093.[18] Benke D, Olah A, Möhler H. Protein-chemical analysis of Bio-Oss bone substitute and evidence on its carbonate content. Biomaterials. 2001;22(9):1005-1012.[19] Rodrigues CV, Serricella P, Linhares AB,et al. Characterization of a bovine collagen-hydroxyapatite composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2003;24(27):4987-4997.[20] Tsuruga E, Takita H, Itoh H,et al. Pore size of porous hydroxyapatite as the cell-substratum controls BMP-induced osteogenesis. J Biochem. 1997;121(2):317-324.[21] Lu JX, Flautre B, Anselme K,et al. Role of interconnections in porous bioceramics on bone recolonization in vitro and in vivo. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1999;10(2):111-120.[22] Reif D, Leuner B, Hotz G. Temporäre Knochenersatzmaterialien auf Basis von Calciumphosphat. In: Claes L, Ignatius A, eds.Biodegradierbare Implantate und Materialien. Berlin: Springer. 1998: 270-277 |