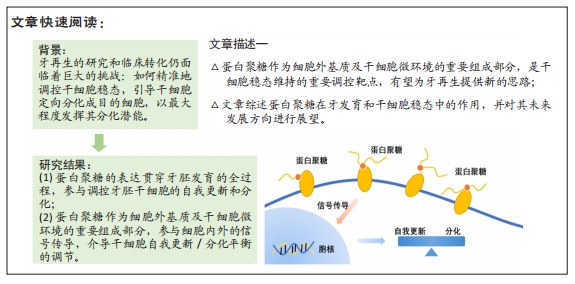
[1] WANG F, WU Z, FAN Z, et al. The cell re-association-based whole-tooth regeneration strategies in large animal, Sus scrofa. Cell Prolif. 2018; 51(4):e12479.
[2] WU Z, WANG F, FAN Z, et al. Whole-Tooth Regeneration by Allogeneic Cell Reassociation in Pig Jawbone. Tissue Eng Part A. 2019;25(17-18): 1202-1212.
[3] YANG KC, KITAMURA Y, WU CC, et al. Tooth Germ-Like Construct Transplantation for Whole-Tooth Regeneration: An In Vivo Study in the Miniature Pig. Artif Organs. 2016;40(4):E39-50.
[4] YU T, KLEIN OD. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of tooth development, homeostasis and repair. Development. 2020;147(2): dev184754.
[5] HU L, LIU Y, WANG S. Stem cell-based tooth and periodontal regeneration. Oral Dis. 2018;24(5):696-705.
[6] Baranova J, Büchner D, Götz W, et al. Tooth Formation: Are the Hardest Tissues of Human Body Hard to Regenerate? Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(11): 4031.
[7] ABDEL MEGUID E, KE Y, Ji J, et al. Stem cells applications in bone and tooth repair and regeneration: New insights, tools, and hopes. J Cell Physiol. 2018; 233(3):1825-1835.
[8] BALIC A, THESLEFF I. Tissue Interactions Regulating Tooth Development and Renewal. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015;115:157-186.
[9] CAPURRO M, IZUMIKAWA T, SUAREZ P, et al. Glypican-6 promotes the growth of developing long bones by stimulating Hedgehog signaling. J Cell Biol. 2017; 216(9):2911-2926.
[10] TOWNLEY RA, BÜLOW HE. Deciphering functional glycosaminoglycan motifs in development. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2018;50:144-154.
[11] THESLEFF I, JALKANEN M, VAINIO S, et al. Cell surface proteoglycan expression correlates with epithelial-mesenchymal interaction during tooth morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 1988;129(2):565-572.
[12] YAMADA K, YAMADA T, SASAKI T, et al. Light and electron microscopical immunohistochemical localization of large proteoglycans in human tooth germs at the bell stage. Histochem J. 1997;29(2):167-175.
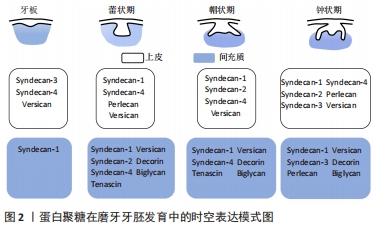
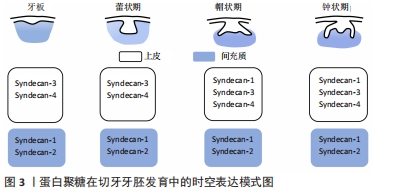
[13] WU J, LI H, HAN L, et al. The spatiotemporal expression pattern of Syndecans in murine embryonic teeth. Gene Expr Patterns. 2020;36:119109.
[14] WU J, TIAN Y, HAN L, et al. FAM20B-catalyzed glycosaminoglycans control murine tooth number by restricting FGFR2b signaling. BMC Biol. 2020;18(1):87.
[15] IOZZO RV, SCHAEFER L. Proteoglycan form and function: A comprehensive nomenclature of proteoglycans. Matrix Biol. 2015;42:11-55.
[16] MIKAMI T, KITAGAWA H. Sulfated glycosaminoglycans: their distinct roles in stem cell biology. Glycoconj J. 2017;34(6):725-735.
[17] SMOCK RG, MEIJERS R. Roles of glycosaminoglycans as regulators of ligand/receptor complexes. Open Biol. 2018;8(10):180026.
[18] YU P, PEARSON CS, GELLER HM. Flexible Roles for Proteoglycan Sulfation and Receptor Signaling. Trends Neurosci. 2018;41(1):47-61.
[19] ZONG C, VENOT A, LI X, et al. Heparan Sulfate Microarray Reveals That Heparan Sulfate-Protein Binding Exhibits Different Ligand Requirements. J Am Chem Soc. 2017;139(28):9534-9543.
[20] BIRBRAIR A. Stem Cell Microenvironments and Beyond. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1041:1-3.
[21] BALIC A. Biology Explaining Tooth Repair and Regeneration: A Mini-Review. Gerontology. 2018;64(4):382-388.
[22] THESLEFF I. From understanding tooth development to bioengineering of teeth. Eur J Oral Sci. 2018;126 Suppl 1:67-71.
[23] LIU Z, CHEN T, BAI D, et al. Smad7 Regulates Dental Epithelial Proliferation during Tooth Development. J Dent Res. 2019;98(12):1376-1385.
[24] KLEIN OD, MINOWADA G, PETERKOVA R, et al. Sprouty genes control diastema tooth development via bidirectional antagonism of epithelial-mesenchymal FGF signaling. Dev Cell. 2006;11(2):181-190.
[25] NAKATO H, LI JP. Functions of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans in Development: Insights From Drosophila Models. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2016;325:275-293.
[26] DÍAZ-BALZAC CA, LÁZARO-PEÑA MI, TECLE E, et al. Complex cooperative functions of heparan sulfate proteoglycans shape nervous system development in Caenorhabditis elegans. G3 (Bethesda). 2014; 4(10):1859-1870.
[27] SOARES DA COSTA D, REIS RL, PASHKULEVA I. Sulfation of Glycosaminoglycans and Its Implications in Human Health and Disorders. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2017;19:1-26.
[28] HAYES AJ, MITCHELL RE, BASHFORD A, et al. Expression of glycosaminoglycan epitopes during zebrafish skeletogenesis. Dev Dyn. 2013;242(6):778-789.
[29] YAN Z, CHEN G, YANG Y, et al. Expression and roles of syndecan-4 in dental epithelial cell differentiation. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(5):1301-1308.
[30] RANDILINI A, FUJIKAWA K, SHIBATA S. Expression, localization and synthesis of small leucine-rich proteoglycans in developing mouse molar tooth germ. Eur J Histochem. 2020;64(1):3092.
[31] GOLDBERG M, SEPTIER D, OLDBERG A, et al. Fibromodulin-deficient mice display impaired collagen fibrillogenesis in predentin as well as altered dentin mineralization and enamel formation. J Histochem Cytochem. 2006;54(5):525-537.
[32] GOLDBERG M, SEPTIER D, RAPOPORT O, et al. Targeted disruption of two small leucine-rich proteoglycans, biglycan and decorin, excerpts divergent effects on enamel and dentin formation. Calcif Tissue Int. 2005;77(5):297-310.
[33] KERO D, BILANDZIJA TS, ARAPOVIC LL, et al. Syndecans and Enzymes Involved in Heparan Sulfate Biosynthesis and Degradation Are Differentially Expressed During Human Odontogenesis. Front Physiol. 2018;9:732.
[34] GALBRAITH DB, CUTLER LS, KOLLAR EJ. The correlation of temporal regulation of glycosaminoglycan synthesis with morphogenetic events in mouse tooth development. Arch Oral Biol. 1992;37(8):623-628.
[35] JIANG B, XU F, LI L, et al. The inhibition of glycosaminoglycan incorporation influences the cell proliferation and cytodifferentiation in cultured embryonic mouse molars. J Mol Histol. 2019;50(1):11-19.
[36] LIU L, CHEN W, LI L, et al. Inhibition of chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycans incorporation affected odontoblast differentiation in cultured embryonic mouse molars. J Mol Histol. 2017;48(5-6):337-345.
[37] KOIKE T, IZUMIKAWA T, TAMURA J, et al. FAM20B is a kinase that phosphorylates xylose in the glycosaminoglycan-protein linkage region. Biochem J. 2009; 421(2):157-162.
[38] ZHANG H, ZHU Q, CUI J, et al. Structure and evolution of the Fam20 kinases. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1218.
[39] TIAN Y, MA P, LIU C, et al. Inactivation of Fam20B in the dental epithelium of mice leads to supernumerary incisors. Eur J Oral Sci. 2015;123(6):396-402.
[40] JUURI E, JUSSILA M, SEIDEL K, et al. Sox2 marks epithelial competence to generate teeth in mammals and reptiles. Development. 2013;140(7): 1424-1432.
[41] JUURI E, SAITO K, AHTIAINEN L, et al. Sox2+ stem cells contribute to all epithelial lineages of the tooth via Sfrp5+ progenitors. Dev Cell. 2012; 23(2):317-328.
[42] SAEI AREZOUMAND K, ALIZADEH E, PILEHVAR-SOLTANAHMADI Y, et al. An overview on different strategies for the stemness maintenance of MSCs. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2017;45(7):1255-1271.
[43] JIN S, COLLIN J, ZHU L, et al. A Novel Role for miR-1305 in Regulation of Pluripotency-Differentiation Balance, Cell Cycle, and Apoptosis in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cells. 2016;34(9):2306-2317.
[44] KRAUSHAAR DC, YAMAGUCHI Y, WANG L. Heparan sulfate is required for embryonic stem cells to exit from self-renewal. J Biol Chem. 2015; 290(38):23023.
[45] IZUMIKAWA T, SATO B, KITAGAWA H. Chondroitin sulfate is indispensable for pluripotency and differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Sci Rep. 2014;4:3701.
[46] HELLEDIE T, DOMBROWSKI C, RAI B, et al. Heparan sulfate enhances the self-renewal and therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells from human adult bone marrow. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(11):1897-1910.
[47] LING L, REN X, CAO X, et al. Enhancing the Efficacy of Stem Cell Therapy with Glycosaminoglycans. Stem Cell Reports. 2020;14(1):105-121.
[48] KRAUSHAAR DC, DALTON S, WANG L. Heparan sulfate: a key regulator of embryonic stem cell fate. Biol Chem. 2013;394(6):741-751.
[49] KRAUSHAAR DC, RAI S, CONDAC E, et al. Heparan sulfate facilitates FGF and BMP signaling to drive mesoderm differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(27):22691-22700.
[50] QU C, RILLA K, TAMMI R, et al. Extensive CD44-dependent hyaluronan coats on human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells produced by hyaluronan synthases HAS1, HAS2 and HAS3. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;48:45-54.
[51] CHEN PY, HUANG LL, HSIEH HJ. Hyaluronan preserves the proliferation and differentiation potentials of long-term cultured murine adipose-derived stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;360(1):1-6.
[52] WONG TY, CHANG CH, YU CH, et al. Hyaluronan keeps mesenchymal stem cells quiescent and maintains the differentiation potential over time. Aging Cell. 2017;16(3):451-460.
[53] AI X, DO AT, LOZYNSKA O, et al. QSulf1 remodels the 6-O sulfation states of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans to promote Wnt signaling. J Cell Biol. 2003;162(2):341-351.
[54] LANNER F, LEE KL, SOHL M, et al. Heparan sulfation-dependent fibroblast growth factor signaling maintains embryonic stem cells primed for differentiation in a heterogeneous state. Stem Cells. 2010; 28(2):191-200.
[55] HUANG ML, MICHALAK AL, FISHER CJ, et al. Small Molecule Antagonist of Cell Surface Glycosaminoglycans Restricts Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells in a Pluripotent State. Stem Cells. 2018;36(1):45-54.
[56] TITMARSH DM, TAN CL, GLASS NR, et al. Microfluidic Screening Reveals Heparan Sulfate Enhances Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth by Modulating Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 Transport. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(4):1178-1190.
[57] YAMADA T, KEREVER A, YOSHIMURA Y, et al. Heparan sulfate alterations in extracellular matrix structures and fibroblast growth factor-2 signaling impairment in the aged neurogenic niche. J Neurochem. 2017;142(4):534-544.
[58] QIU H, SHI S, YUE J, et al. A mutant-cell library for systematic analysis of heparan sulfate structure-function relationships. Nat Methods. 2018;15(11):889-899.
[59] WANG X, CORNELIS FMF, LORIES RJ, et al. Exostosin-1 enhances canonical Wnt signaling activity during chondrogenic differentiation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(11):1702-1710.
[60] MORIMOTO-TOMITA M, UCHIMURA K, WERB Z, et al. Cloning and characterization of two extracellular heparin-degrading endosulfatases in mice and humans. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(51):49175-49185.
[61] DHOOT GK, GUSTAFSSON MK, AI X, et al. Regulation of Wnt signaling and embryo patterning by an extracellular sulfatase. Science. 2001; 293(5535):1663-1666.
[62] SASAKI N, OKISHIO K, UI-TEI K, et al. Heparan sulfate regulates self-renewal and pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283(6):3594-3606.
[63] CHEN YH, NARIMATSU Y, CLAUSEN TM, et al. The GAGOme: a cell-based library of displayed glycosaminoglycans. Nat Methods. 2018; 15(11):881-888.
[64] ZHANG X, PAGADALA V, JESTER HM, et al. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of heparan sulfate and heparin oligosaccharides and NMR analysis: paving the way to a diverse library for glycobiologists. Chem Sci. 2017; 8(12):7932-7940.
|