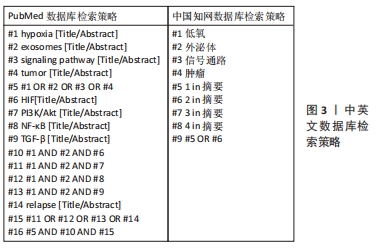
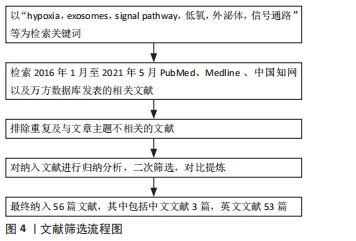
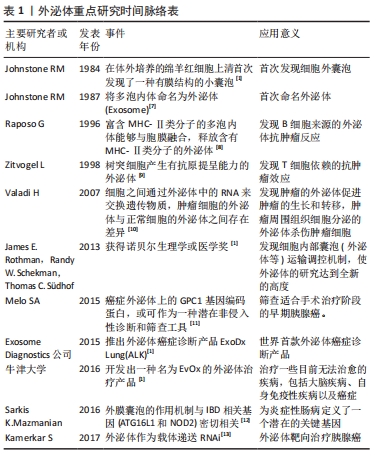
[1] PAN B, TENG K, WU C, et al. Electron Microscopic Evidence for Externalization of the Transferrin Receptor in Vesicular Form in Sheep Reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1985;101(3):942-948.
[2] 张灏,赵立波,叶国栋.外泌体研究、转化和临床应用专家共识[J].转化医学杂志,2018,7(6):321-325.
[3] DUAN P, TAN J, MIAO Y, et al. Potential role of exosomes in the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of hypoxic diseases. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(3):1184-1201.
[4] 顾霞,赵敏,王平义,等.低氧诱导因子1α与低氧相关疾病信号通路的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(8):1284-1289.
[5] EMANUELI C, SHEARN AIU, ANGELINI GD, et al. Exosomes and exosomal miRNAs in cardiovascular protection and repair. Vasc Pharmacol. 2015;71:24-30.
[6] SHAO C, YANG F, MIAO S, et al. Role of hypoxia-induced exosomes in tumor biology. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):120.
[7] JOHNSTONE RM, ADAM M, HAMMOND JR, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412-9420.
[8] RAPOSO G, NIJMAN HW, STOORVOGEL W, et al. B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med. 1996;183(3):1161-1172.
[9] ZITVOGEL L, REGNAULT A, LOZIER A, et al. Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat Med. 1998;4(5):594-600.
[10] VALADI H, EKSTROM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659.
[11] MELO SA, LUECKE LB, KAHLERT C, et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2015;523(7559):177-182.
[12] CHU H, KHOSRAVI A, KUSUMAWARDHANI IP, et al. Gene-microbiota interactions contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Science. 2016;352(6289):1116-1120.
[13] KAMERKAR S, LEBLEU VS, SUGIMOTO H, et al. Exosomes facilitate therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2017;546(7659):498-503.
[14] Wu Y, Wang X, Meng L, et al. Changes of miRNA expression profiles from cervical-vaginal fluid-derived exosomes in response to HPV16 infection. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020(17):1-8.
[15] BELTING M, CHRISTIANSON HC. Role of exosomes and microvesicles in hypoxia-associated tumour development and cardiovascular disease. J Intern Med. 2015,278(3):251-263.
[16] MIZUTA Y, AKAHOSHI T, GUO J, et al. Exosomes from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate histone-induced acute lung injury by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway in endothelial cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):508.
[17] LI J, DENG X, JI X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes reverse acute lung injury through Nrf-2/ARE and NF-κB signaling pathways. Peer J. 2020;8(1):e9928.
[18] CAI L, CHAO G, LI W, et al. Activated CD4(+) T cells-derived exosomal miR-142-3p boosts post-ischemic ventricular remodeling by activating myofibroblast. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(8):7380-7396.
[19] LI D, ZHANG D, TANG B, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce damage from oxidative stress and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal epithelial cells exposed to oxalate and calcium oxalate monohydrate. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:1-10.
[20] KUMAR A, DEEP G. Exosomes in hypoxia-induced remodeling of the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Lett. 2020;488:1-8.
[21] TIRPE AA, GULEI D, CIORTEA SM, et al. Hypoxia: overview on hypoxia-mediated mechanisms with a focus on the role of HIF genes. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6140.
[22] MCGETTRICK AF, O NEILL LAJ. The role of HIF in immunity and inflammation. Cell Metab. 2020;32(4):524-536.
[23] HOXHAJ G, MANNING BD. The PI3K-AKT network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020; 20(2):74-88.
[24] 曲畅,吴云红,穆靖洲,等.核转录因子κB在缺氧导致的炎症中的作用[J].生理科学进展,2018,49(1):39-43.
[25] TZAVLAKI K, MOUSTAKAS A. TGF-β Signaling. Biomolecules. 2020;10(3): 487.
[26] ZHANG Z, YAO L, YANG J, et al. PI3K/Akt and HIF1 signaling pathway in hypoxiaischemia (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(4):3547-3554.
[27] CHOUDHRY H, HARRIS AL. Advances in hypoxia-inducible factor biology. Cell Metab. 2018;27(2):281-298.
[28] ZHANG W, ZHOU X, YAO Q, et al. HIF-1-mediated production of exosomes during hypoxia is protective in renal tubular cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017;313(4):F906-F913.
[29] LIU W, LI L, Rong Y, et al. Hypoxic mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote bone fracture healing by the transfer of miR-126. Acta Biomater. 2020;103:196-212.
[30] YING C, WANG R, WANG Z, et al. BMSC-exosomes carry mutant hif-1α for improving angiogenesis and osteogenesis in critical-sized calvarial defects. Front Bioeng Biotech. 2020. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2020.565561.
[31] SUN J, SHEN H, SHAO L, et al. HIF-1α overexpression in mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes mediates cardioprotection in myocardial infarction by enhanced angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):373.
[32] GONZALEZ-KING H, GARCIA N A, ONTORIA-OVIEDO I, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha potentiates jagged 1-mediated angiogenesis by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Stem Cells. 2017;35(7):1747-1759.
[33] XIA X, WANG S, NI B, et al. Hypoxic gastric cancer-derived exosomes promote progression and metastasis via MiR-301a-3p/PHD3/HIF-1α positive feedback loop. Oncogene. 2020;39(39):6231-6244.
[34] LIU Y, TAN J, OU S, et al. Adipose-derived exosomes deliver miR-23a/b to regulate tumor growth in hepatocellular cancer by targeting the VHL/HIF axis. J Physiol Biochem. 2019;75(3):391-401.
[35] PAKRAVAN K, BABASHAH S, SADEGHHIZADEH M, et al. MicroRNA-100 shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes suppresses in vitro angiogenesis through modulating the mTOR/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling axis in breast cancer cells. Cell Oncol. 2017;40(5):457-470.
[36] LIU XN, ZHANG CB, LIN H, et al. microRNA-204 shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes inhibits the migration and invasion of non-small-cell lung cancer cells via the KLF7/AKT/HIF-1alpha axis. Neoplasma. 2021. doi:10.4149/neo_2021_201208N1328.
[37] ZHANG J, ZHANG X. Ischaemic preconditioning‐induced serum exosomes protect against myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway. Cell Biochem Funct. 2021;39(2):287-295.
[38] ARSLAN F, LAI RC, SMEETS MB, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes increase ATP levels, decrease oxidative stress and activate PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance myocardial viability and prevent adverse remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2013;10(3):301-312.
[39] NING W, LI S, YANG W, et al. Blocking exosomal miRNA-153-3p derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates hypoxia-induced myocardial and microvascular damage by targeting the ANGPT1-mediated VEGF/PI3k/Akt/eNOS pathway. Cell Signal. 2021;77: 109812.
[40] PAN Q, KUANG X, CAI S, et al. miR-132-3p priming enhances the effects of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes on ameliorating brain ischemic injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):260.
[41] SUN X, WANG Y, LI G, et al. Serum-derived three-circRNA signature as a diagnostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. doi:10.1186/s12935-020-01302-y.
[42] WANG L, BO X, YI X, et al. Exosome-transferred LINC01559 promotes the progression of gastric cancer via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(9):723.
[43] ZHANG W, ZHOU Q, WEI Y, et al. The exosome-mediated PI3k/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in cervical cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019; 12(7):2474-2484.
[44] LI M, GUO H, WANG Q, et al. Pancreatic stellate cells derived exosomal miR-5703 promotes pancreatic cancer by downregulating CMTM4 and activating PI3K/Akt pathway. Cancer Lett. 2020;490:20-30.
[45] WANG H, WANG L, ZHOU X, et al. OSCC exosomes regulate miR-210-3p targeting EFNA3 to promote oral cancer angiogenesis through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:1-13.
[46] LIN F, YIN HB, LI XY, et al. Bladder cancer cellsecreted exosomal miR21 activates the PI3K/AKT pathway in macrophages to promote cancer progression. Int J Oncol. 2020;56(1):151-164.
[47] DAI Y, WANG S, CHANG S, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes carry microRNA-148a to alleviate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibiting TXNIP and the TLR4/NF-kappaB/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020;142:65-79.
[48] WANG K, RU J, ZHANG H, et al. Melatonin enhances the therapeutic effect of plasma exosomes against cerebral ischemia-induced pyroptosis through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Front Neurosci. 2020; 14:848.
[49] NAGPAL P, DESCALZI MONTOYA DB, LODHI N. The circuitry of the tumor microenvironment in adult and pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma: cellular composition, cytokine profile, EBV, and exosomes. Cancer Rep. 2021;4(2):e1311.
[50] WANG B, MAO JH, WANG BY, et al. Exosomal miR-1910-3p promotes proliferation, metastasis, and autophagy of breast cancer cells by targeting MTMR3 and activating the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2020;489:87-99.
[51] LI W, ZHANG L, GUO B, et al. Exosomal FMR1-AS1 facilitates maintaining cancer stem-like cell dynamic equilibrium via TLR7/NFκB/c-Myc signaling in female esophageal carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):22.
[52] DENG S, ZHOU X, GE Z, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate cardiac damage after myocardial infarction by activating S1P/SK1/S1PR1 signaling and promoting macrophage M2 polarization. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;114:105564.
[53] CAO Q, LIU Y, WU Y, et al. Profilin 2 promotes growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis of small cell lung cancer through cancer-derived exosomes. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(24):25981-25999.
[54] YIN Z, MA T, HUANG B, et al. Macrophage-derived exosomal microRNA-501-3p promotes progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through the TGFBR3-mediated TGF-β signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Canc Res. 2019;38(1):310.
[55] SHANG A, GU C, WANG W, et al. Exosomal circPACRGL promotes progression of colorectal cancer via the miR-142-3p/miR-506-3p- TGF-β1 axis. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):117.
[56] QU Z, FENG J, PAN H, et al. Exosomes derived from HCC cells with different invasion characteristics mediated EMT through TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. Oncotargets Ther. 2019;12:6897-6905.
|
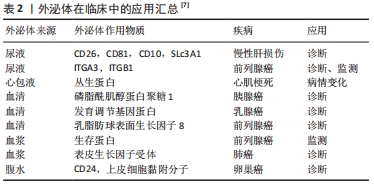
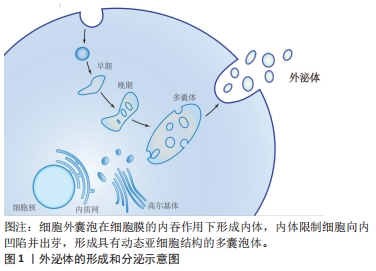 20世纪80年代,外泌体的发现被认为是细胞的“排泄物”,并未引起足够的重视[1]。随着时间流逝,外泌体的结构和功能逐渐清晰,越来越多的科学家发现了其有着不可忽视的作用。外泌体通过这几种方式将信息传递进入靶细胞:①与受体细胞膜直接融合;②其膜蛋白或其内容物转移至受体细胞;③其跨膜蛋白直接作用于受体细胞膜表面的信号分子,见图2。
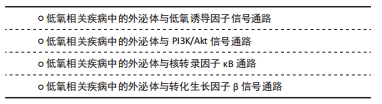
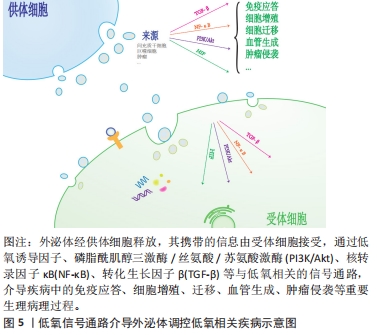
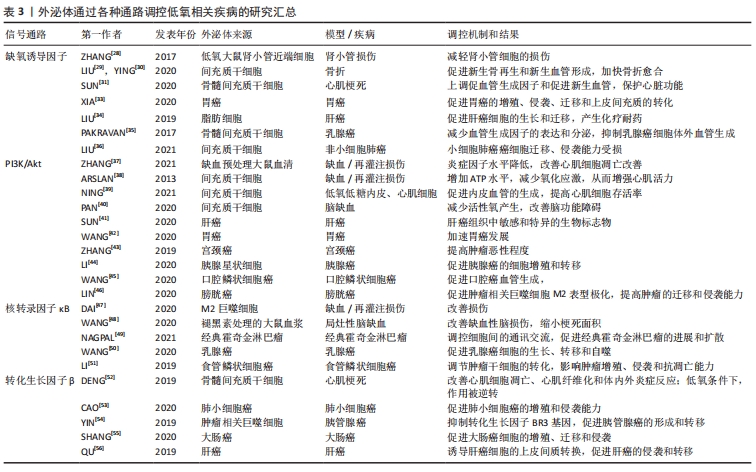
20世纪80年代,外泌体的发现被认为是细胞的“排泄物”,并未引起足够的重视[1]。随着时间流逝,外泌体的结构和功能逐渐清晰,越来越多的科学家发现了其有着不可忽视的作用。外泌体通过这几种方式将信息传递进入靶细胞:①与受体细胞膜直接融合;②其膜蛋白或其内容物转移至受体细胞;③其跨膜蛋白直接作用于受体细胞膜表面的信号分子,见图2。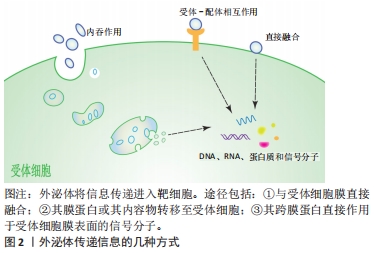 在上述过程中,靶细胞的表型和功能发生变化,靶细胞的信号通路被激活,从而介导免疫和炎症等重要生理病理过程[2]。目前,外泌体在低氧相关疾病及肿瘤疾病中取得瞩目的研究进展[3]。磷脂酰肌醇三激酶/丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶(PI3K/Akt)、核转录因子κB、转化生长因子β等信号通路在低氧环境下与低氧诱导因子关系密切,受低氧诱导因子的调节改变自身的分子表达水平,从而影响细胞周期、形态结构、代谢、增殖、分化、自噬和凋亡等方面,是较为确切的低氧相关信号通路[4]。
在上述过程中,靶细胞的表型和功能发生变化,靶细胞的信号通路被激活,从而介导免疫和炎症等重要生理病理过程[2]。目前,外泌体在低氧相关疾病及肿瘤疾病中取得瞩目的研究进展[3]。磷脂酰肌醇三激酶/丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶(PI3K/Akt)、核转录因子κB、转化生长因子β等信号通路在低氧环境下与低氧诱导因子关系密切,受低氧诱导因子的调节改变自身的分子表达水平,从而影响细胞周期、形态结构、代谢、增殖、分化、自噬和凋亡等方面,是较为确切的低氧相关信号通路[4]。