[1] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715.
[2] CONAGHAN PG, COOK AD, HAMILTON JA, et al. Therapeutic options for targeting inflammatory osteoarthritis pain. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(6):355-363.
[3] KOLASINSKI SL, NEOGI T, HOCHBERG MC, et al. 2019 American college of rheumatology/arthritis foundation guideline for the management of osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020;72(2):149-162.
[4] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393(10182):1745-1759.
[5] SHARMA L. Osteoarthritis of the Knee. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(1):51-59.
[6] ZHANG Z, HUANG C, JIANG Q, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis in China (2019 edition). Ann Transl Med. 2020; 8(19):1213.
[7] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis: a review. JAMA. 2020;325(6):568-578.
[8] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072.
[9] ZHENG L, ZHANG Z, SHENG P, et al. The role of metabolism in chondrocyte dysfunction and the progression of osteoarthritis. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;66:101249.
[10] PENG Z, SSUN H, BUNPETCH V, et al. The regulation of cartilage extracellular matrix homeostasis in joint cartilage degeneration and regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;268:120555.
[11] SZUSTAK M, GENDASZEWSKA-DARMACH E. Extracellular nucleotides selectively induce migration of chondrocytes and expression of type II collagen. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(15):5227.
[12] HUBER AK, PATEL N, PAGANI CA, et al. Immobilization after injury alters extracellular matrix and stem cell fate. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(10):5444-5460.
[13] FANG T, ZHOU X, JIN M, et al. Molecular mechanisms of mechanical load-induced osteoarthritis. Int Orthop. 2021;45(5):1125-1136.
[14] RELLMANN Y, EIDHOF E, DREIER R. Review: ER stress-induced cell death in osteoarthritic cartilage. Cell Signal. 2021;78:109880.
[15] 翟中和,王喜忠,丁明孝.细胞生物学.第4版[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2011:5-7,30-42.
[16] LOEWI G. Changes in the ground substance of ageing cartilage. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953;65(2):381-388.
[17] GUNSTON FH. Polycentric knee arthroplasty: prosthetic simulation of normal knee movement. 1971. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;446:11-12.
[18] GREEN WT JR. Articular cartilage repair. Behavior of rabbit chondrocytes during tissue culture and subsequent allografting. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977;124:237-250.
[19] BELL E, EHRLICH HP, SHER S, et al. Development and use of a living skin equivalent. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1981;67(3):386-392.
[20] KATO Y, IWAMOTO M, KOIKE T, et al. Terminal differentiation and calcification in rabbit chondrocyte cultures grown in centrifuge tubes: regulation by transforming growth factor beta and serum factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988;85(24):9552-9556.
[21] OXFORD JT, REECK JC, HARDY MJ. Extracellular matrix in development and disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(1):205.
[22] HAMIDI H, LVASKA J. Every step of the way: integrins in cancer progression and metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18(9):533-548.
[23] PICKUP MW, MOUW JK, WEAVER VM. The extracellular matrix modulates the hallmarks of cancer. EMBO Rep. 2014;15(12):1243-1253.
[24] ZILE MR, O’MEARA E, CLAGGETT B, et al. Effects of Sacubitril/Valsartan on Biomarkers of Extracellular Matrix Regulation in Patients With HFrEF. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019; 73(7):795-806.
[25] KLINGBERG F, CHAU G, WALRAVEN M, et al. The fibronectin ED-A domain enhances recruitment of latent TGF-β-binding protein-1 to the fibroblast matrix. J Cell Sci. 2018;131(5):jcs201293.
[26] WALRAVEN M, HINZ B. Therapeutic approaches to control tissue repair and fibrosis: extracellular matrix as a game changer. Matrix Biol. 2018;71-72:205-224.
[27] WINKLER J, ABISOYE-OGUNNIYAN A, METCALF KJ, et al. Concepts of extracellular matrix remodelling in tumour progression and metastasis. Nat Commun. 2020; 11(1):5120.
[28] TERPOS E, CHRISTOULAS D, KASTRITIS E, et al. High levels of periostin correlate with increased fracture rate, diffuse MRI pattern, abnormal bone remodeling and advanced disease stage in patients with newly diagnosed symptomatic multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2016;6(10):e482.
[29] THOMPSON BJ. YAP/TAZ: Drivers of tumor growth, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Bioessays. 2020;42(5):e1900162.
[30] LAMAR JM, XIAO Y, NORTON E, et al. SRC tyrosine kinase activates the YAP/TAZ axis and thereby drives tumor growth and metastasis. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(7):2302-2317.
[31] CHAKKALAKAL SA, HEILIG J, BAUMANN U, et al. Impact of arginine to cysteine mutations in collagen ii on protein secretion and cell survival. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(2):541.
[32] NYSTROM A, BERNASCONI R, BORNERT O. Therapies for genetic extracellular matrix diseases of the skin. Matrix Biol. 2018;71-72:330-347.
[33] KAUR A, ECKER BL, DOUGLASS SM, et al. Remodeling of the collagen matrix in aging skin promotes melanoma metastasis and affects immune cell motility. Cancer Discov. 2019;9(1):64-81.
[34] HAYDONT V, BERNARD BA, FORTUNER NO. Age-related evolutions of the dermis: clinical signs, fibroblast and extracellular matrix dynamics. Mech Ageing Dev. 2019; 177:150-156.
[35] FANE M, WEERARATNA AT. How the ageing microenvironment influences tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20(2):89-106.
[36] YOUNGSTROM DW, CAKSTINA I, JAKOBSONS E. Cartilage-derived extracellular matrix extract promotes chondrocytic phenotype in three-dimensional tissue culture. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016;44(3):1040-1047.
[37] MA TW, WEN YJ, SONG XP, et al. Puerarin inhibits the development of osteoarthritis through antiinflammatory and antimatrix-degrading pathways in osteoarthritis-induced rat model. Phytother Res. 2020. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6988.
[38] LIN X, CHEN J, QIU P, et al. Biphasic hierarchical extracellular matrix scaffold for osteochondral defect regeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3):433-444.
[39] MA P, YUE L, YANG H, et al. Chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of amurensin H by regulating TLR4/Syk/NF-κB signals. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(2): 1958-1968.
[40] YAO M, ZHANG J, LI Z, et al. Marein protects human nucleus pulposus cells against high glucose-induced injury and extracellular matrix degradation at least partly by inhibition of ROS/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;80:106126.
[41] LI P, FLEISCHHAUER L, NICOLAE C, et al. Mice lacking the matrilin family of extracellular matrix proteins develop mild skeletal abnormalities and are susceptible to age-associated osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(2):666.
[42] SANCHEZ-ADAMS J, LEDDY HA, MCNULTY AL, et al. The mechanobiology of articular cartilage: bearing the burden of osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2014;16(10):451.
[43] DENG Y, LU J, LI W, et al. Reciprocal inhibition of YAP/TAZ and NF-κB regulates osteoarthritic cartilage degradation. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4564.
[44] SONG H, PARK KH. Regulation and function of SOX9 during cartilage development and regeneration. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;67(Pt 1):12-23.
[45] SUN M, HUSSAIN S, HU Y, et al. Maintenance of SOX9 stability and ECM homeostasis by selenium-sensitive PRMT5 in cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(6):932-944.
[46] ZHOU Y, MING J, DENG M, et al. Chemically modified curcumin (CMC2.24) alleviates osteoarthritis progression by restoring cartilage homeostasis and inhibiting chondrocyte apoptosis via the NF-κB/HIF-2α axis. J Mol Med (Berl). 2020;98(10): 1479-1491.
[47] 武世勋,吴翠艳,郭雄.大骨节病和骨性关节炎软骨细胞外基质的降解差异[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2021,42(2):306-310, 316.
[48] HENROTIN Y, SANCHEZ C, BAY-JENSEN AC, et al. Osteoarthritis biomarkers derived from cartilage extracellular matrix: current status and future perspectives. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2016;59(3):145-148.
[49] BOER CG, RADJABZADEH D, MEDINA-GOMEZ C, et al. Intestinal microbiome composition and its relation to joint pain and inflammation. Nat Commun. 2019; 10(1):4881.
[50] LI X, WU D, HU Z, et al. The protective effect of ligustilide in osteoarthritis: an in vitro and in vivo study. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(6):2583-2595.
[51] ZHOU YAN, MING JIANGHUA, et al. Ligustilide attenuates nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in rat chondrocytes and cartilage degradation via inhibiting JNK and p38 MAPK pathways. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23:3357-3368.
[52] DUAN B, LIU Y, HU H, et al. Notch1-ADAM8 positive feed-back loop regulates the degradation of chondrogenic extracellular matrix and osteoarthritis progression. Cell Commun Signal. 2019;17(1):134.
[53] XING H, LEE H, LUO L, et al. Extracellular matrix-derived biomaterials in engineering cell function. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;42:107421.
[54] WANG Y, YU D, LIU Z, et al. Exosomes from embryonic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis through balancing synthesis and degradation of cartilage extracellular matrix. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):189.
[55] NOURI BARKESTANI M, NASERIAN S, UZAN G, et al. Post-decellularization techniques ameliorate cartilage decellularization process for tissue engineering applications. J Tissue Eng. 2021;12:2041731420983562.
[56] MAYORCA-GUILIANI AE, WILLACY O, MADSEN CD, et al. Decellularization and antibody staining of mouse tissues to map native extracellular matrix structures in 3D. Nat Protoc. 2019;14(12):3395-3425.
[57] XIA C, MEI S, GU C, et al. Decellularized cartilage as a prospective scaffold for cartilage repair. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;101:588-595.
[58] WANG Z, HAN L, SUN T, et al. Extracellular matrix derived from allogenic decellularized bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheets for the reconstruction of osteochondral defects in rabbits. Acta Biomater. 2020;118:54-68.
[59] ROSADI I, KARINA K, ROSLIANA I, et al. In vitro study of cartilage tissue engineering using human adipose-derived stem cells induced by platelet-rich plasma and cultured on silk fibroin scaffold. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):369.
[60] SAEEDI GARAKANI S, KHANMOHAMMADI M, AYOUFI Z, et al. Fabrication of chitosan/agarose scaffolds containing extracellular matrix for tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;143:533-545.
[61] MONIBI FA, COOK JL. Tissue-derived extracellular matrix bioscaffolds: emerging applications in cartilage and meniscus repair. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2017;23(4):386-398.
|

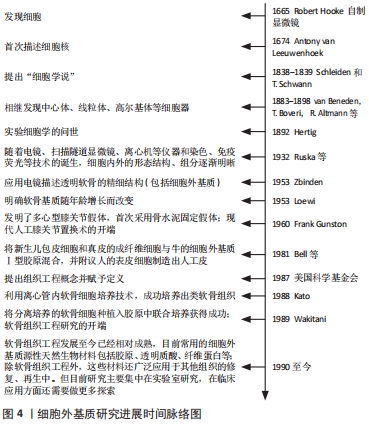
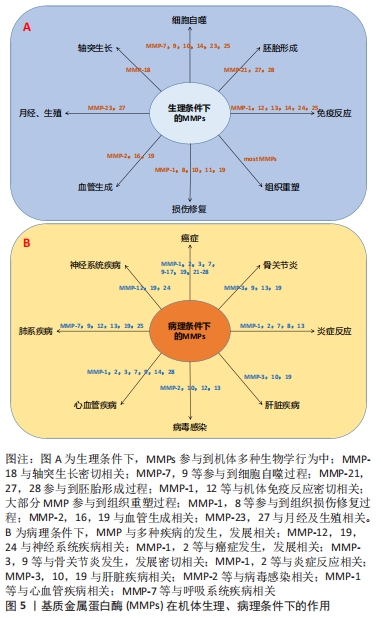
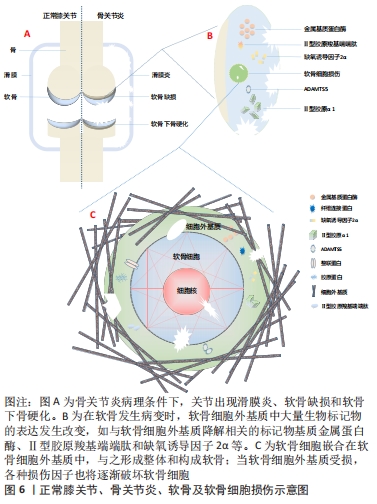
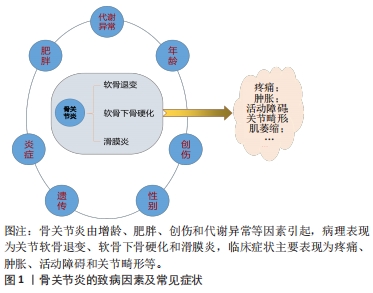 抛开繁杂的病理机制,研究者们发现软骨代谢失衡,即关节软骨的分解代谢明显大于合成代谢是骨关节炎发生、发展的重要特征[9],其中,软骨细胞是软骨的主要组成部分,其功能包括分泌、合成以及维持软骨细胞外基质的稳定。细胞外基质是一种由水、胶原及蛋白多糖等组成的复杂网络结构,与关节软骨的生物力学特性等理化性质密切相关[10]。蛋白多糖是一种带高度负电荷的物质,通过吸收组织中的水和盐增加其渗透性和抗压能力;而胶原则是位于关节软骨的纤维蛋白,特别是Ⅱ型胶原,使软骨能够抵抗剪切应力和获得良好的生物力学特性[11]。
抛开繁杂的病理机制,研究者们发现软骨代谢失衡,即关节软骨的分解代谢明显大于合成代谢是骨关节炎发生、发展的重要特征[9],其中,软骨细胞是软骨的主要组成部分,其功能包括分泌、合成以及维持软骨细胞外基质的稳定。细胞外基质是一种由水、胶原及蛋白多糖等组成的复杂网络结构,与关节软骨的生物力学特性等理化性质密切相关[10]。蛋白多糖是一种带高度负电荷的物质,通过吸收组织中的水和盐增加其渗透性和抗压能力;而胶原则是位于关节软骨的纤维蛋白,特别是Ⅱ型胶原,使软骨能够抵抗剪切应力和获得良好的生物力学特性[11]。