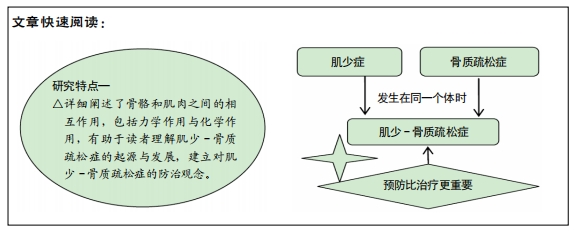
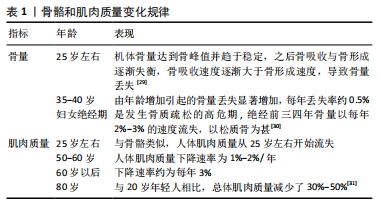
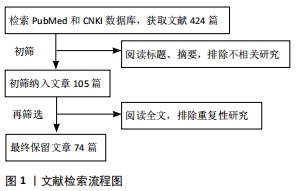
[1] COLLINS FL, RIOS-ARCE ND, SCHEPPER JD, et al. The Potential of Probiotics as a Therapy for Osteoporosis. Microbiol Spectr. 2017;5(4): 10.1128/microbiolspec.BAD-0015-2016.
[2] 薛鹏, 李玉坤. 2017年版《原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南》解读[J].河北医科大学学报,2018,39(1):1-6.
[3] KANIS JA, GLÜER CC. An update on the diagnosis and assessment of osteoporosis with densitometry. Committee of Scientific Advisors, International Osteoporosis Foundation. Osteoporos Int. 2000;11(3): 192-202.
[4] WALSTON JD. Sarcopenia in older adults. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2012; 24(6):623-627.
[5] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.肌少症共识[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2016,9(3):215-227.
[6] BINKLEY N, BUEHRING B. Beyond FRAX®: It’s Time to Consider “Sarco-Osteopenia”. J Clin Densitom. 2009;12(4):413-416.
[7] CEVEI M, ONOFREI RR, CIOARA F, et al. Correlations between the Quality of Life Domains and Clinical Variables in Sarcopenic Osteoporotic Postmenopausal Women. J Clin Med. 2020;9(2):441.
[8] NIELSEN BR, ANDERSEN HE, HADDOCK B, et al. Prevalence of muscle dysfunction concomitant with osteoporosis in a home-dwelling Danish population aged 65–93years - The Copenhagen Sarcopenia Study.Exp Gerontol. 2020;138:110974.
[9] WANG YJ, WANG Y, ZHAN JK, et al. Sarco-Osteoporosis: Prevalence and Association with Frailty in Chinese Community-Dwelling Older Adults.Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015:482940.
[10] HIDA T, ISHIGURO N, SHIMOKATA H, et al. International, High prevalence of sarcopenia and reduced leg muscle mass in Japanese patients immediately after a hip fracture. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2013;13(2):413-420.
[11] DREY M, SIEBER CC, BERTSCH T, et al. Osteosarcopenia is more than sarcopenia and osteopenia alone. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2016;28(5):895-899.
[12] DI MONACO M, CASTIGLIONI C, BARDESONO F, et al. Sarcopenia, osteoporosis and the burden of prevalent vertebral fractures: a cross-sectional study of 350 women with hip fracture. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2020;56(2):184-190.
[13] 林华, 谢忠建, 朱梅, 等. 肌肉和骨骼的相互调节[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2016,9(3):236-239.
[14] MANSKE SL, BOYD SK, ZERNICKE RF. Vertical ground reaction forces diminish in mice after botulinum toxin injection.J Biomech. 2011;44(4): 637-643.
[15] LAM H, QIN YX. The effects of frequency-dependent dynamic muscle stimulation on inhibition of trabecular bone loss in a disuse model.Bone. 2008;43(6):1093-1100.
[16] TAGLIAFERRI C, WITTRANT Y, DAVICCO MJ, et al. Muscle and bone, two interconnected tissues. Ageing Res Rev. 2015;21:55-70.
[17] KAWAO N, KAJI H. Interactions between muscle tissues and bone metabolism. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(5):687-695.
[18] BUEHRING B, BINKLEY N. Myostatin--the holy grail for muscle, bone, and fat?. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2013;11(4):407-414.
[19] BREN-MATTISON Y, HAUSBURG M, OLWIN BB. Growth of limb muscle is dependent on skeletal-derived Indian hedgehog. Dev Biol. 2011;356(2):486-495.
[20] SHEN H, GRIMSTON S, CIVITELLI R, et al. Thomopoulos, Deletion of Connexin43 in Osteoblasts/Osteocytes Leads to Impaired Muscle Formation in Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(4):596-605.
[21] BINKLEY N, KRUEGER D, BUEHRING B. What’s in a name revisited: should osteoporosis and sarcopenia be considered components of “dysmobility syndrome?”. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(12):2955-2959.
[22] 陈锦成, 朱国涛, 刘洪文,等. “肌少-骨质疏松症”的共同发病机制[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2020,13(1):95-102.
[23] KARASIK D, CUPPLES LA, HANNAN MT, et al. Genome screen for a combined bone phenotype using principal component analysis: the Framingham study. Bone. 2004;34(3):547-556.
[24] HUANG J, HSU YH, MO C, et al. METTL21C is a potential pleiotropic gene for osteoporosis and sarcopenia acting through the modulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(7):1531-1540.
[25] MERA P, LAUE K, FERRON M, et al. Osteocalcin Signaling in Myofibers Is Necessary and Sufficient for Optimum Adaptation to Exercise. Cell Metab. 2017;25(1):218.
[26] PAGNOTTI GM, STYNER M, UZER G, et al. Combating osteoporosis and obesity with exercise: leveraging cell mechanosensitivity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15(6):339-355.
[27] 刘长江. 废用性骨质疏松症的防治研究进展[J].科技资讯,2020, 18(3):224-226.
[28] PHU S, BOERSMA D, DUQUE G. Exercise and Sarcopenia. J Clin Densitom. 2015;18(4):488- 492.
[29] 陈梦阳,谢菊英.骨质疏松症发病机制的研究进展[J].湘南学院学报(医学版),2018,20(1):63-66.
[30] 张琚, 曾果.运动对骨量影响的研究进展[J].环境卫生学杂志, 2006,33(4):238-243.
[31] MORLEY JE. Frailty and sarcopenia in elderly. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2016;128(Suppl 7):439-445.
[32] 钟静,王秀华.老年人肌少症非药物干预的研究进展[J].中国护理管理, 2019,19(8):144-150.
[33] 王泽洲,万和平,张天晔, 等. 海市部分社区居民骨质疏松预防知识、自我效能、行为状况及健康宣教效果分析[J].上海预防医学, 2017,29(12):922-925.
[34] 甘萍, 迟中海, 李培杰, 等. 新形式健康教育对老年骨质疏松病人生活质量影响[J].齐鲁医学杂志,2017,32(1):78-81.
[35] 杨红旗, 赵欣, 陈燕, 等. 骨质疏松症的健康管理[J].中国临床保健杂志, 2018,21(5):718-720.
[36] 朱赛, 苏昕, 辛妮, 等. 信息化技术在慢病管理中的研究进展[J].中国医学装备,2019,16(5):143-146.
[37] 王德杰, 郑傲, 潘杰.电网男职工骨质疏松症现状调查及危险因素分析[J].中国现代药物应用,2019,13(12):28-30.
[38] 竹盈, 陈浩, 刘凤娟.生活方式与大学教师骨密度水平的相关性分析[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2019,18(11):1230-1233.
[39] 刘金彦, 刘娜, 任宛丽.女性医护人员骨质疏松患病率调查及影响因素分析[J].实用预防医学,2019,26(2):95-97.
[40] WANG H, HAI S, LIU Y, et al. Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Associated Factors in Community-dwelling Elderly Populations in Chengdu China. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019;50(2):224-228.
[41] ALEXANDRE TDA S, DUARTE YA, SANTOS JL, et al. Prevalence and associated factors of sarcopenia among elderly in Brazil: Findings from the SABE study. J Nutr Health Aging. 2014;18(3):284-290.
[42] 张琼, 陈慎.不同年龄段医务人员对骨质疏松症认知程度的比较[J].中国全科医学,2017,20(7):257-260.
[43] 李百云, 熊东林, 熊毅丰.不同年龄段医务人员对骨质疏松症认知程度的比较[C].江西省中西医结合骨质疏松与骨矿盐疾病学术交流会资料汇编,2018.
[44] HASSAN EB, DUQUE G. Osteosarcopenia: A new geriatric syndrome.Aust Fam Physician. 2017;46(11):849-853.
[45] HONG AR, KIM SW. Effects of Resistance Exercise on Bone Health.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2018;33(4):435-444.
[46] LIU Y, CHU JMT, YAN T, et al. Short-term resistance exercise inhibits neuroinflammation and attenuates neuropathological changes in 3xTg Alzheimer’s disease mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):4.
[47] CSAPO R, ALEGRE LM. Effects of resistance training with moderate vs heavy loads on muscle mass and strength in the elderly: A meta‐analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2016;26(9):995-1006.
[48] LICHTENBERG T, VON STENGEL S, SIEBER C, et al. The Favorable Effects of a High-Intensity Resistance Training on Sarcopenia in Older Community-Dwelling Men with Osteosarcopenia: The Randomized Controlled FrOST Study. Clin Interv Aging. 2019;14:2173-2186.
[49] World Health Organization. Global recommendations on phys-ical activity for health. Geneva: World Health Organiza-tion. 2010:9-10.
[50] KERR D, MORTON A, DICK I, et al.Exercise effects on bone mass in postmenopausal women are site-specific and load-dependent. J Bone Miner Res. 1996;11(2):218-225.
[51] ILICH JZ, KELLY OJ, INGLIS JE, et al.Ormsbee, Interrelationship among muscle, fat, and bone: Connecting the dots on cellular, hormonal, and whole body levels.Ageing Res Rev. 2014;15:51-60.
[52] FRANCIS RM, PEACOCK M, STORER JH, et al.Calcium malabsorption in the elderly: the effect of treatment with oral 25-hydroxyvitamin D3.Eur J Clin Invest. 1983;13(5):391-396.
[53] SUZUKI T, NAKAMURA Y, KATO H. Calcium and vitamin D supplementation with 3-year denosumab treatment is beneficial to enhance bone mineral density in postmenopausal patients with osteoporosis and rheumatoid arthritis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018;15:15-22.
[54] YANG A, LV Q, CHEN F, et al.The effect of vitamin D on sarcopenia depends on the level of physical activity in older adults.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020;11(3):678-689.
[55] MEDICINE IO. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D, National Academies Press Washington, DC National Academies Press. 2011.
[56] VAES AMM, TIELAND M, DE REGT MF, et al. Dose–response effects of supplementation with calcifediol on serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D status and its metabolites: A randomized controlled trial in older adults. Clin Nutr. 2018;37(3):808-814.
[57] TIELAND M, DIRKS ML, VAN DER ZWALUW N, et al. Protein Supplementation Increases Muscle Mass Gain During Prolonged Resistance-Type Exercise Training in Frail Elderly People: A Randomized, Double-Blind. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2012;13(8):713-719.
[58] GROENENDIJK I, DEN BOEFT L, VAN LOON LJC, et al. High Versus low Dietary Protein Intake and Bone Health in Older Adults: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019;17:1101-1112.
[59] LONNIE M, HOOKER E, BRUNSTROM JM, et al.Protein for Life: Review of Optimal Protein Intake, Sustainable Dietary Sources and the Effect on Appetite in Ageing Adults.Nutrients. 2018;10(3):360.
[60] 肌肉衰减综合征营养与运动干预中国专家共识(节录)[J].营养学报, 2015(4):320-324.
[61] KONG SH, KIM JH, LEE JH, et al. Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate and Free Testosterone but not Estradiol are Related to Muscle Strength and Bone Microarchitecture in Older Adults. Calcif Tissue Int. 2019; 105(3):285-293.
[62] FERRANDO AA, TIPTON KD, DOYLE D, et al. Testosterone injection stimulates net protein synthesis. Am J Physiol. 1998;275(5):E864-871.
[63] SNYDER PJ, KOPPERDAHL DL, STEPHENS-SHIELDS AJ, et al. Effect of Testosterone Treatment on Volumetric Bone Density and Strength in Older Men With Low Testosterone: A Controlled Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177(4):471-479.
[64] LINDBERG MK, VANDENPUT L, MOVÈRARE SKRTIC S, et al. Androgens and the skeleton. Minerva Endocrinol. 2005;30(1):15-25.
[65] GERBER C, MEYER DC, FLÜCK M, et al. Anabolic Steroids Reduce Muscle Degeneration Associated With Rotator Cuff Tendon Release in Sheep.Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(10):2393-2400.
[66] PAPANICOLAOU DA, ATHER SN, ZHU H, et al. A phase IIA randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial to study the efficacy and safety of the selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM), MK-0773 in female participants with sarcopenia. J Nutr Health Aging. 2013;17(6):533-543.
[67] WELLE S, THORNTON C, STATT M, et al. Growth hormone increases muscle mass and strength but does not rejuvenate myofibrillar protein synthesis in healthy subjects over 60 years old. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81(9):3239-3243.
[68] BLACKMAN MR, SORKIN JD, MÜNZER T, et al. Growth hormone and sex steroid administration in healthy aged women and men a randomized controlled trial.JAMA. 2002;288(18):2282-2292.
[69] WILHELM B, KANN PH. Long-term effects of 7-year growth hormone substitution on bone metabolism, bone density, and bone quality in growth hormone-deficient adults. Med Klin (Munich). 2004;99(10):569-577.
[70] BINKLEY N, KRUEGER D, BUEHRING B. What’s in a name revisited: should osteoporosis and sarcopenia be considered components of “dysmobility syndrome?”. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(12):2955-2959.
[71] 杨艳芳, 徐红. 肌少症,骨质疏松的关系及研究进展[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(98):150-151+155.
[72] CHEN LK, LIU LK, WOO J, et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus Report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014; 15(2):95-101.
[73] LANE NE. Epidemiology, etiology, and diagnosis of osteoporosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;194(2 Suppl):S3-11.
[74] 赵瑾, 常晶.老年肌少-骨质疏松症相关研究进展[J].中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2020,19(9):713-716.
|