[1] KIHC Y, ÖZERr A, TATAR T, et al. Effect of picroside II on hind limb ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. J Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017;11: 1917-1925.
[2] CHENG Y, DI S, FAN C, et al.SIRT1 activation by pterostilbene attenuate the skeletal muscle oxidative stress injury and mitochondrial dysfunction induced by ischemia reperfusion injury. J Apoptosis. 2016; 21(8):905-916.
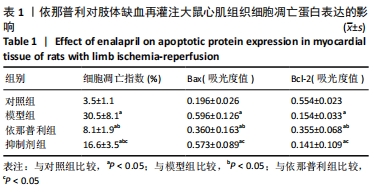
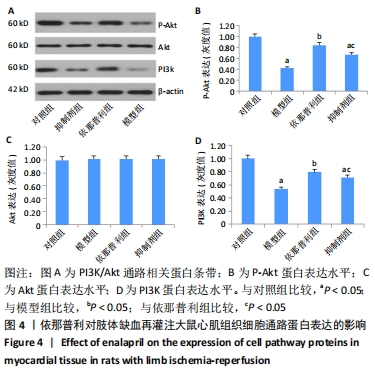
[3] 邢宏昶,姚鲲,赵宏,等.依那普利对大鼠肢体缺血-再灌注心肌细胞的影响[J].医药导报,2013,32(7):861-864.
[4] DING Y, DU J, CUI F, et al. The protective effect of ligustrazine on rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via activating PI3K/Akt pathway. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2019;38(10):1168-1177.
[5] CHEN S, LI X, WANG Y, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 attenualtes intestinal ischemia/reperfusion-induced inflammation and oxidative stress via activation of the PI3K∕Akt/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2019; 19(5):3633-3641.
[6] 赵立军,门秀丽,董淑云,等.骨骼肌缺血预适应对肢体缺血再灌注后心肌的远端保护作用[J].中国医科大学学报,2008,37(2):168-170.
[7] LIU Y, QIN XY, LU XF, et al. Effects of inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway on the pain of sciatic endometriosis in a rat mode. Cana J Physi Phar. 2019;97(10):963-970.
[8] STEIGER AK, PARDUE S, KEVIL CG, et al. Self-immolative thiocarbamates provide access to triggered H2S donors and analyte replacement fluorescent probes. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138(23):7256-7259.
[9] OZTURK L, DOGAN HT, KILICARSLAN A, et al. Effect of different doses of pregabalin on skeletal muscle ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2017;118(7):417-422.
[10] CHENG W, WANG M, PENG L, et al. Protective Effects of Dexmedetomidine and Oxycodone in Patients Undergoing Limb Ischemia-Reperfusion. Med Sci Mon. 2019;25:9073-9084.
[11] MANGUM LC, GARCIA GR, AKERS KS, et al. Duration of extremity tourniquet application profoundly impacts soft-tissue antibiotic exposure in a rat model of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Injury. 2019; 50(12):2203-2214.
[12] Heel K, Blennerhassett L, Kong SE, et al. Influence of isehaemia-repedusion injury on CD44 expression in ratsmall intestine. Br J Surg. 1998;85(8):1086-1089.
[13] Grace PA. Ischaemia reperfusion. Br J Surg. 1994;81(5):637-647.
[14] Knowles R, Keeping H, Graeber T, et al. Cytokinecontrol of PMN phagocytsis: regulatory effectsofhypoxtmia and hypoxemiareoxygenatio. Am J Physiol. 1997;272(41):1352-1364.
[15] Lum H, Roebuck KA. Oxidant stress andendothelial cell dysfunction. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001;280(4):C719-C741.
[16] Kun Y, Hong CX, Bin W, et al. Effect of TIEG1 on apoptosis and expressions of Bcl-2/Bax and pten in leukemic cell lines. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14(1):1968-1974.
[17] Beyersdorf F. The use of controlled reperfusion strategies in cardiac surgery to minimize ischaemia/reperfusion damage. Cardiovasc Res. 2009;83(2):262-268.
[18] Yasuda S, Kobayashi H, Iwasa M, et al. Antidiabetic drug pioglitazone protects the heart via activation of PPA receptors, PI3-kinase, Akt, and eNOS pathway in a rabbit model of myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009;296(5):H1558-H1565.
[19] Hoole SP, Heck PM, Sharples L, et al. Cardiac remote ischemic preconditioning in coronary stenting(CRISP Stent) study: a prospective,randomized control study. Circulation. 2009;119:820-827.
[20] 徐叔云.中华临床药物学(上册)[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2003:811.
[21] Srinivasan J, Jayadev S, Kumaran D, et al. Effect of losartan and enalapril on cognitive deficit caused by Goldblatt induced hy-pertension. Indian J Exp Biol. 2005;43(3):241.
[22] Winer N, Folker A, Murphy JA, et al. Effect of fixed dose ACE inhibitor/calcium channel blocker combina therapy vs ACE inhibitor monotherapy on arterial compliance in hypertensive patients with type 2 diadetes. Prev Cardiol.2005; 8(2):87.
[23] 邢宏昶, 姚鲲, 赵宏, 等.依那普利后处理对肢体缺血再灌注诱发大鼠心肌损伤的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2013,33(3):360-362.
[24] Dudek H, Datta SR, Franke TF, et al. Regulation of neurona1survival by the serinethreonine protein kinase Akt. Science. 1997;275(5300): 661-665.
[25] Shaw RJ, Cantley LC. Ras, PI(3)K and mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth. Nature. 2006;441(7092): 424 -430.
[26] Chan TO, Rittenhouse SE, Tsichlis PN. Phosphoinositide3-kinase signalling -which way to target. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003;24:366-376.
[27] LI GC, QIN XL, SONG HH, et al. Upregulated microRNA-15b alleviates ovarian cancer through inhitbition of the PI3K/Akt pathway by targeting LPAR3. J Cel Phy. 2019;234(12):22331-22342.
[28] FERNANDEZ MC, YU A, MOAWAD AR, et al. Peroxiredoxin 6 regulates the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway to maintain human sperm viability. Mol Hum Rep. 2019;25(12):787-796.
[29] SUN GQ, LI YB, JI ZY, et al. Up-regulation of MIAT aggravates the atherosclerotic damage in atherosclerosis mice through the activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Drug Del. 2019;26(1):641-649.
[30] LU YZ, LI LH, WANG GY, et al. Effect of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway on PRAS40Thr246 Phosphorylation in Gastric Cancer Cells. Ira J Pub Health. 2019;48(12):2196-2204.
[31] LUO X, LIN B, GAO YG, et al. Genipin attenuates mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and inflammation via the PI3K/AKT pathway in acute lung injury. Int Immun. 2019;76: 105842.
[32] Rosse T, Olivier R, Monney L, et al. Bcl-2 prolongs cell survival after bax-induced release of cytochromec. Nature. 1998;391(6666):496-499.
[33] MORRIS DL, KASTNER DW, JOHNSON S, et al. Humanin induces conformational changes in the apoptosis regulator BAX and sequesters it into fibers, preventing mitochondrial outer-membrane permeabilization. J Bio Chem. 2019;294(50):19055-19065.
[34] LIU SP, ZHU YY, YAN SS, et al. Phenethyl isothiocyanate induces IPEC-J2 cells cytotoxicity and apoptosis via S-G 2/M phase arrest and mitochondria-mediated Bax/Bcl-2 pathway. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2019;226:108574.
[35] WON M, LUO YY, LEE DH, et al. BAX is an essential key mediator of AP5M1-induced apoptosis in cervical carcinoma cells. Biochemical Biophysical Res Commu. 2019;518(2)368-373.
[36] Edlich F. BCL-2 proteins and apoptosis: Recent insights and unknowns.Bio Res Commu. 2018;500(1):26-34.
|