[1] 孙彦豹,金宝城,王静,等.颈椎病发病危险因素的调查研究[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2020,7(40):6+8.
[2] 魏庆华,张琼,胡屏,等.简阳市某三甲医院骨科住院患者颈椎病患病影响因素病例对照分析[J].预防医学情报杂志,2020,36(11): 1529-1534.
[3] 孙震,雷立健,刘鹏,等.大学生群体颈椎健康状况及影响因素分析[J].中国学校卫生,2019,40(4):631-633.
[4] 吴佳倩,陆一涵,张成钢.颈椎病的研究进展[J].健康教育与健康促进,2018,13(1):58-61.
[5] 冯超博,樊云山,贺石生.颈椎牵引的若干问题讨论[J].上海医药, 2020,41(2):3-5.
[6] YANG JD, TAM KW, HUANG TW, et al. Intermittent cervical traction for treating neck pain: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(13):959-965.
[7] 胡海,贾维中,刘沛然,等.仰卧间歇角度牵引治疗神经根型颈椎病的临床疗效分析[J].广西医科大学学报,2019,36(12):1942-1945.
[8] 木巴拉克·开赛尔,米勇.神经根型颈椎病近10年的研究进展[J].新疆中医药,2020,38(6):104-106.
[9] 李创,吴斌,郑启新.脊髓型颈椎病手术治疗研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2020,41(6):342-346.
[10] 周文芳,夏红.脊髓型颈椎病的治疗进展[J].医学理论与实践,2020, 33(4):553-554+552.
[11] 刘智斌,杨晓航,王渊,等.角度牵引对神经根型颈椎病家兔模型血清β-EP和CRP的影响[J].陕西中医,2009,30(5):628-630.
[12] 刘智斌,王卫刚.角度牵引治疗神经根型颈椎病30例[J].陕西中医,2009,30(9):1202-1203.
[13] 吕锐斌,戴胜良,王铮辉.推拿疗法联合坐位动态牵引法治疗神经根型颈椎病的效果分析[J].当代医药论丛,2017,15(8):126-127.
[14] 赖梦婷,周梦林,蔡树河.颈椎牵引治疗神经根型颈椎病的研究近况[J].按摩与康复医学,2018,9(2):6-8.
[15] 周志,倪海键,贺石生.颈椎牵引的体位探讨[J].上海医药,2020, 41(2):6-9.
[16] 王琳,孙月芳,陈宪福,等.彩色多普勒和经颅多普勒对椎动脉型颈椎病牵引治疗效果的评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(17):3094-3098.
[17] 胡国昌,安玉芳.牵引治疗椎动脉型颈椎病的研究进展[J].黑龙江中医药,2018,47(6):8-9.
[18] 姜瑛,于子娟,陈绍晋,等.颈椎牵引X线研究及临床应用[J].颈腰痛杂志,2000,21(4):274-277.
[19] 李琦,曾炳芳,朱立国.神经根型颈椎病中、西医综合疗法不同传承方式疗效评价的临床探索[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2017,25(5): 73-74.
[20] 瞿强.神经根型颈椎病的治疗研究进展[J].医学理论与实践,2020, 33(3):377-378+384.
[21] WU AY, HSU JT, CHEE W, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of one-piece and two-piece small-diameter dental implants: in vitro experimental and three-dimensional finite element analyses. J Formos Med Assoc. 2016;115(9):794-800.
[22] WANG XD, FENG MS, HU YC. Establishment and finite element analysis of a three‐dimensional dynamic model of upper cervical spine instability. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(3):500-509.
[23] 李斌,赵文志,陈秉智.有限元分析:椎间盘退变对颈椎生物力学的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(11):1748-1752.
[24] 杜诗尧,周风金,倪斌,等.新型后路寰枢椎限制性非融合内固定系统的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(3):383-389.
[25] HU Y, DONG WX, HANN S, et al. Construction of Finite Element Model for an Artificial Atlanto-Odontoid Joint Replacement and Analysis of Its Biomechanical Properties. Turkish Neurosurg. 2016;26(3):430-436.
[26] CAI C, MING G, NG LY, et al. Development of a clinical prediction rule to identify patients with neck pain who are likely to benefit from home-based mechanical cervical traction. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(6): 912-922.
[27] 薛召,吕毅,李小妹,等.一种磁悬浮颈椎牵引装置的设计与应用研究[A]. 中国医学装备协会(China Association of Medical Equipment).中国医学装备大会暨2020医学装备展览会论文汇编[C].中国医学装备协会(China Association of Medical Equipment):《中国医学装备》杂志社,2020:5.
[28] 崔颖,王兴亭,陈莹莹.不同颈椎牵引角度对纠正颈椎异常生理曲度的影响[J].中国社区医师,2019,35(18):87+89.
[29] 陈威烨,王辉昊,梁飞凡,等.牵引治疗颈椎病的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2016,31(5):599-601.
[30] 陈群响,倪斌,郭群峰,等.带肌肉组织全颈椎三维有限元模型的建立及分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(4):348-355.
[31] 谢天浩,卢玉昭,王在贵,等.带有枕骨全颈椎三维有限元模型的构建及生物力学分析[J].中国临床神经外科杂志,2019,24(11): 681-684.
[32] LI Y, LEWIS G. Influence of surgical treatment for disc degeneration disease at C5-6 on changes in some biomechanical parameters of the cervical spine. Med Eng Phys. 2010;6:595-603.
[33] MATTHEW BP, JANSON BF, DUANE SC. Cervical spine response in frontalcrash. Med Eng Phys. 2011;33(9):1147-1159.
[34] 刘峰,彭文,浣溢帆,等.新型颈椎多孔型(金属)网式融合器的三维有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(19):1785-1789.
[35] RONG X, WANG B, DING C, et al. The biomechanical impact of facet tropism on the intervertebral disc and facet joints in the cervical spine. Spine J. 2017;17(12):1926-1931.
[36] CAI XY, SANG DC, YUCHI CX, et al. Using finite element analysis to determine effects of the motion loading method on facet joint forces after cervical disc degeneration. Comput Biol Med. 2020; 116:103519.
[37] KLEINBERGER M. Application of finite element techniques to the study of cervical spine mechanics. In: Proceedings of the 37th Stapp Car Crash Conference. San Antonio, TX; 1993:261-272.
[38] 黎珂宇.基于有限元法的人体腰椎力学分析及其应用研究[D].南京:南京航空航天大学,2019.
[39] 刘鹏程,毕明顺.66例颈椎病的X线平片诊断价值[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2015,15(28):143.
[40] 刘治华,汤清,陶德岗,等.全颈椎三维有限元模型的建立及旋转牵引疗法研究[J].生物医学工程研究,2018,37(3):362-366+376.
[41] 刘治华,许伟超,张新民,等.颈椎C2-7三维有限元模型的建立与最优角度牵引仿真研究[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2016,51(3): 359-363.
[42] SWEZEY RL, SWEZEY AM, WARNER K. Efficacy of home cervical traction therapy. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1999;78(1):30-32.
[43] CHEN DS, CHEN HM. Analysis of Pain Scores and Rehabilitation of Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy Receiving Massage Combined with Traction and Ultrashort Wave. World J Integr Tradition Western Med. 2019;5(3):12-16.
[44] DELACERDA FG. Effect of angle of traction pull on upper trapezius muscle activity. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1980;1(4):205-209.
[45] 温剑涛,柳永明. 颈椎外科学[M].北京:科学技术文献出版社,2009.
[46] 高楚荣,王丹影,李志申.颈椎牵引的力学分析[J]. 中华理疗杂志, 1993,16(4):215.
[47] SHIGEKI I, IVANCIC PC, PANJABI MM, et al. Soft tissue injury threshold during simulated whiplash: a biomechanical investigation. Spine. 2004; 29(9):979-987.
[48] PANJABI MM, CRISCO JJ, VASAVADA A, et al. Mechanical properties of the human cervical spine as shown by three-dimensional load – displacement curves. Spine. 2001;26(24):2692-2700.
[49] PANJABI MM, NIBU K, CHOLEWICKI J. Whiplash injuries and the potential for mechanical instability. Euro Spine J. 1998;7(6): 484-492.
[50] 陈强.挥鞭样损伤的生物力学和临床研究[D].上海: 第二军医大学, 2005.
[51] FIDAN M, COBAN M. Design and application of a novel motorized traction device. 2015 9th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering,Bursa. 2015:1122-1125.
[52] 刘成,王霞,张啸,等.智能气囊式颈椎牵引器的设计及性能试验[J].吉林化工学院学报,2020,37(11):65-69.
[53] 黄梓聪,巫鑫炜,张基杭,等.颈椎舒缓牵引器功能创新研究及前景展望[J].科技经济导刊,2020,28(1):76. |
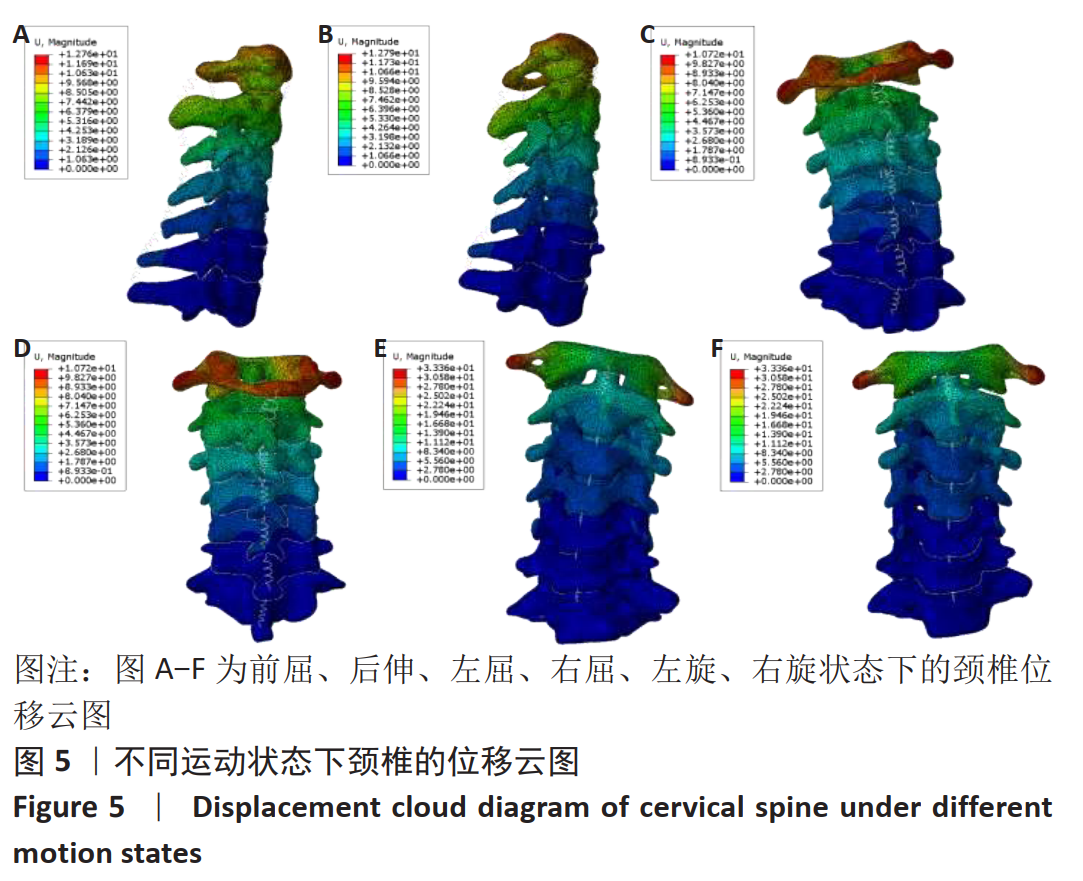
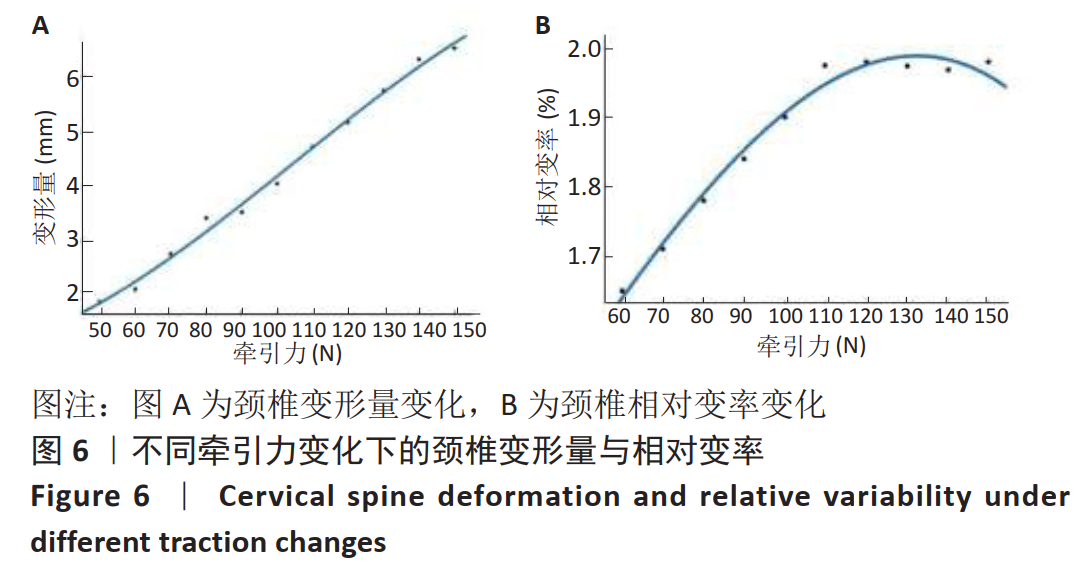

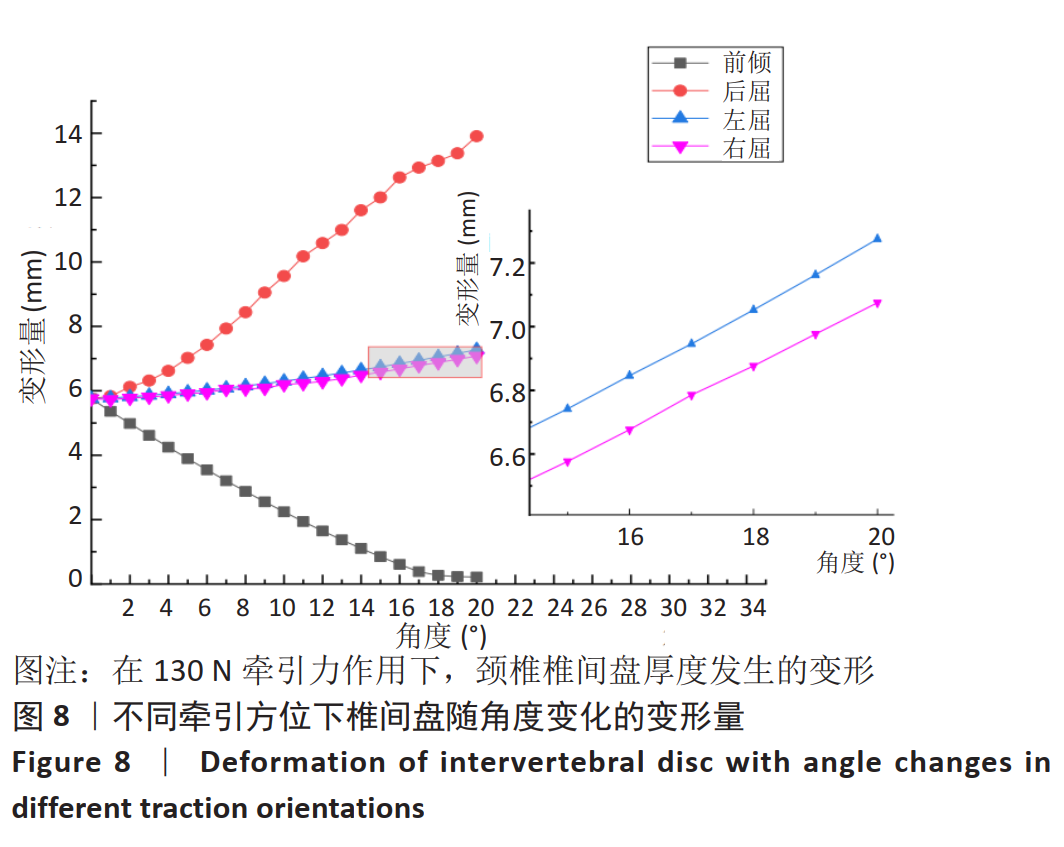
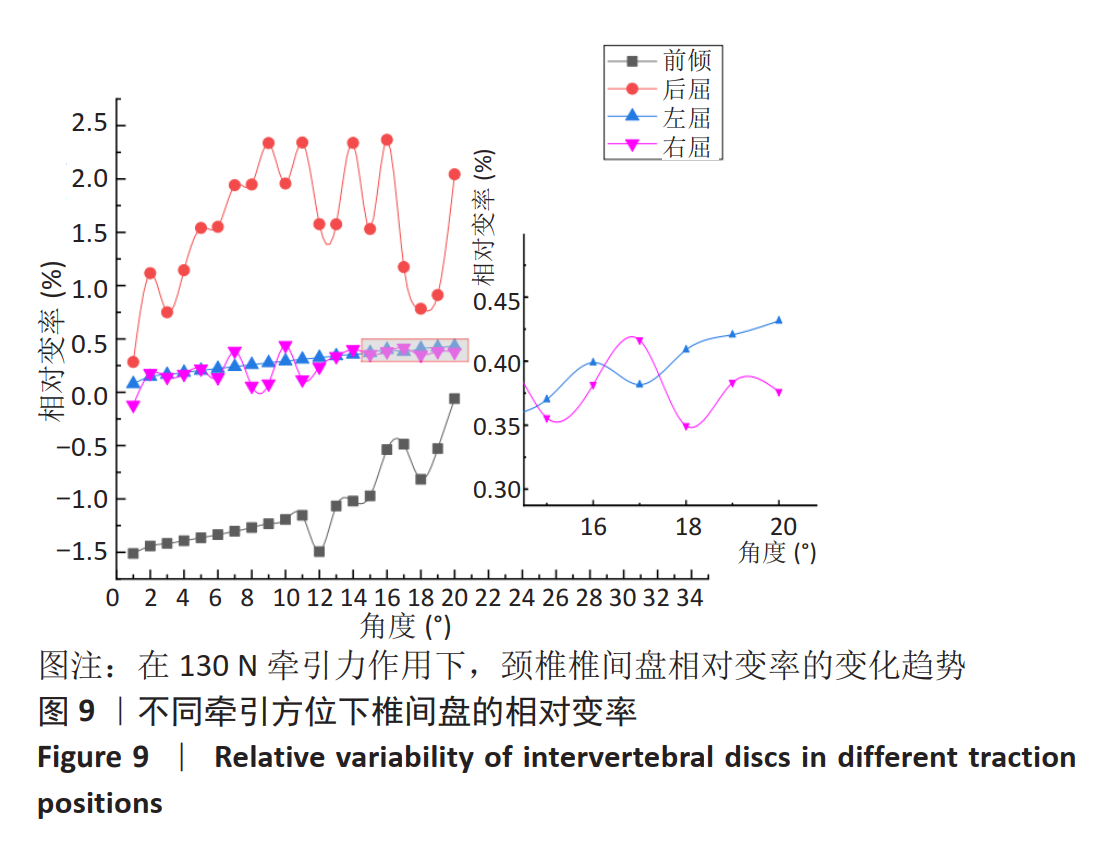
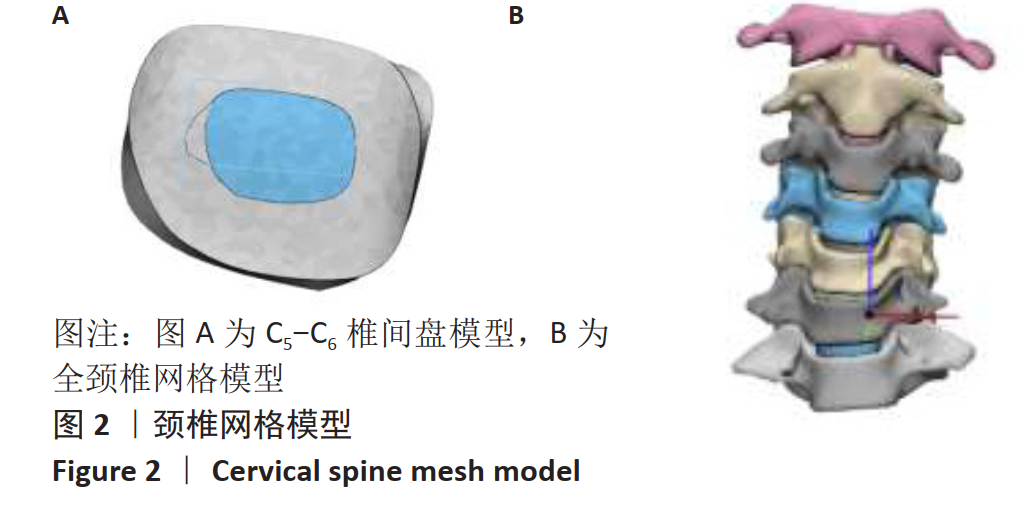
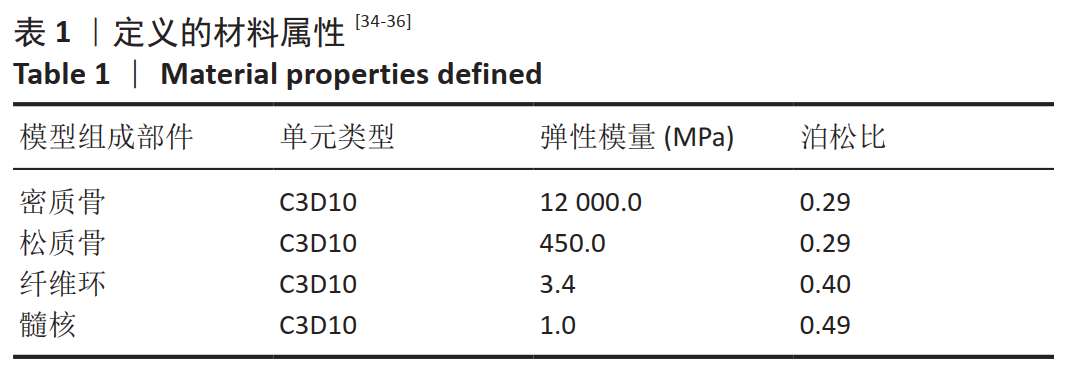
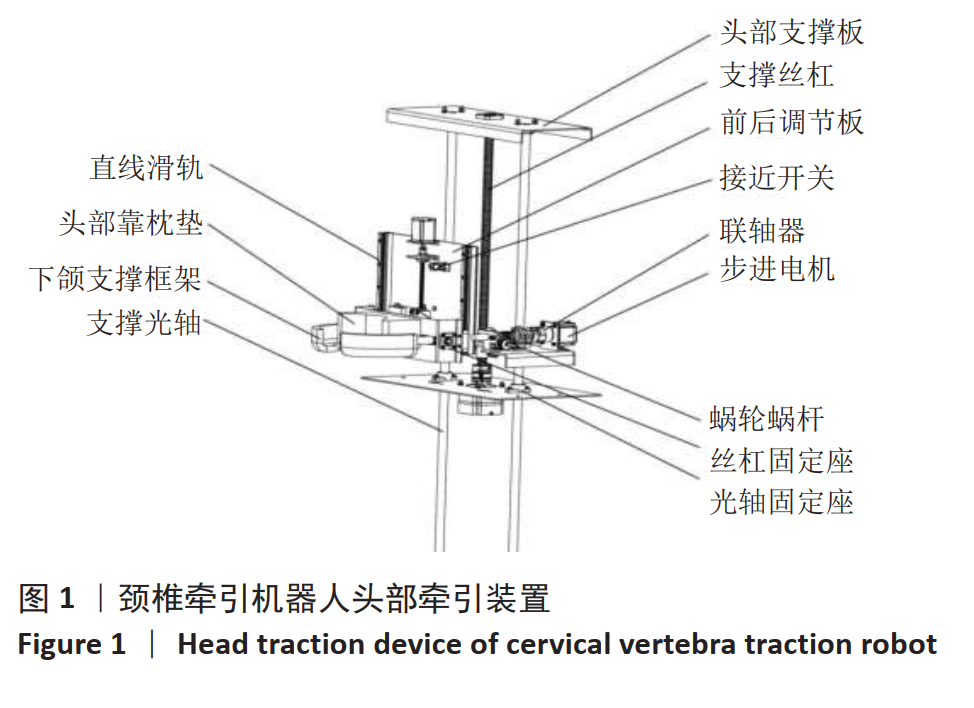 采用坐位牵引的方法,可以在一定程度上对人体颈椎进行不同角度的牵引,做到因人制宜,从而达到更好的治疗效果。多功能颈椎牵引机器人以颅骨的生理弧度为受力点,使用包裹着柔软物质的下颌支撑托着头颅,在进行牵引时通过下颌支撑给颈椎一个向上的牵引力,且下颌支撑可随相连的机械结构进行不同方位的调节,达到多角度牵引目的。近年来,生物力学分析在颈椎问题的研究中起到了越来越重要的作用,其中三维有限元分析因其可重复性高、可比性强,可方便获取内部结构应力数据等优势而备受青睐[21-25]。颈椎牵引角度与牵引力是影响牵引效果的主要因素,相关方面的研究虽多,但却没有统一的标准。大部分的牵引设备会将牵引中所施加的载荷量化处理,然而也有报道使用非量化力量牵引的牵引器械和方法,如新加坡研究人员设计的器械利用患者手动牵拉进行颈椎牵引[26];国内研究人员设计了一种利用磁性斥力对抗人体肌肉收缩力的颈椎牵引设备等[27]。有研究者认为,不同的牵引角度将对颈椎生理曲度的影响也不同[28],颈椎中立位、屈曲位以及过伸位牵引均有应用,也各有优缺点[29]。在颈椎模型中,韧带起到防止颈椎过度屈曲、维护颈椎各项活动动态平衡的作用。有的学者采用双节点的SPINGA单元模拟颈椎韧带[30],也有研究人员利用壳单元和弹簧单元建立相关的韧带[31],但是韧带采用弹簧单元模拟的模型较少。对于新型牵引设备存在的牵引参数难以确定,从而有效治疗颈椎病问题,此文通过对有限元模型的分析,模仿人体在新型牵引设备下进行牵引治疗的情况,分析颈椎在什么牵引力范围内可以最大程度牵开椎间隙,对于牵引力大小的选择提供了参考。此外对颈椎进行前屈、后屈、左屈、右屈等不同牵引力加载方向的仿真,模拟患者在新型设备不同牵引方位下的情景,为该设备不同牵引方位的角度选择提供了理论依据,确定了这种新型牵引设备医治颈椎病的牵引力和牵引角度范围。在文中使用了相对变率的概念来分析牵引力和牵引角度对颈椎的影响,为牵引参数的细化比较提供了参考。
采用坐位牵引的方法,可以在一定程度上对人体颈椎进行不同角度的牵引,做到因人制宜,从而达到更好的治疗效果。多功能颈椎牵引机器人以颅骨的生理弧度为受力点,使用包裹着柔软物质的下颌支撑托着头颅,在进行牵引时通过下颌支撑给颈椎一个向上的牵引力,且下颌支撑可随相连的机械结构进行不同方位的调节,达到多角度牵引目的。近年来,生物力学分析在颈椎问题的研究中起到了越来越重要的作用,其中三维有限元分析因其可重复性高、可比性强,可方便获取内部结构应力数据等优势而备受青睐[21-25]。颈椎牵引角度与牵引力是影响牵引效果的主要因素,相关方面的研究虽多,但却没有统一的标准。大部分的牵引设备会将牵引中所施加的载荷量化处理,然而也有报道使用非量化力量牵引的牵引器械和方法,如新加坡研究人员设计的器械利用患者手动牵拉进行颈椎牵引[26];国内研究人员设计了一种利用磁性斥力对抗人体肌肉收缩力的颈椎牵引设备等[27]。有研究者认为,不同的牵引角度将对颈椎生理曲度的影响也不同[28],颈椎中立位、屈曲位以及过伸位牵引均有应用,也各有优缺点[29]。在颈椎模型中,韧带起到防止颈椎过度屈曲、维护颈椎各项活动动态平衡的作用。有的学者采用双节点的SPINGA单元模拟颈椎韧带[30],也有研究人员利用壳单元和弹簧单元建立相关的韧带[31],但是韧带采用弹簧单元模拟的模型较少。对于新型牵引设备存在的牵引参数难以确定,从而有效治疗颈椎病问题,此文通过对有限元模型的分析,模仿人体在新型牵引设备下进行牵引治疗的情况,分析颈椎在什么牵引力范围内可以最大程度牵开椎间隙,对于牵引力大小的选择提供了参考。此外对颈椎进行前屈、后屈、左屈、右屈等不同牵引力加载方向的仿真,模拟患者在新型设备不同牵引方位下的情景,为该设备不同牵引方位的角度选择提供了理论依据,确定了这种新型牵引设备医治颈椎病的牵引力和牵引角度范围。在文中使用了相对变率的概念来分析牵引力和牵引角度对颈椎的影响,为牵引参数的细化比较提供了参考。