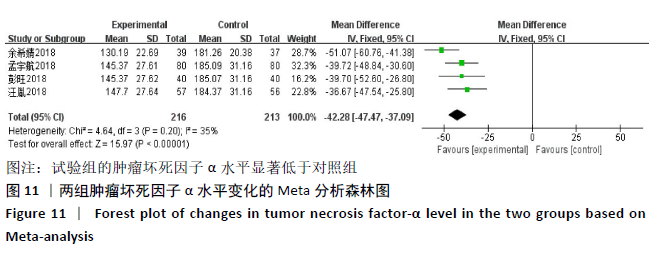
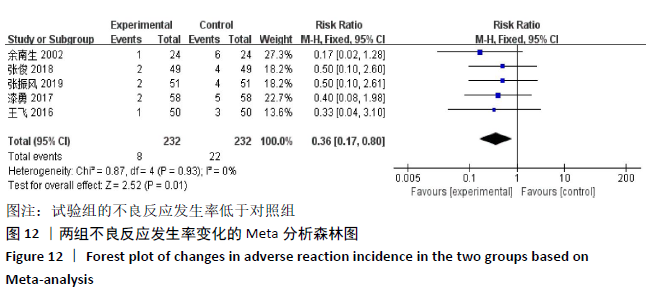
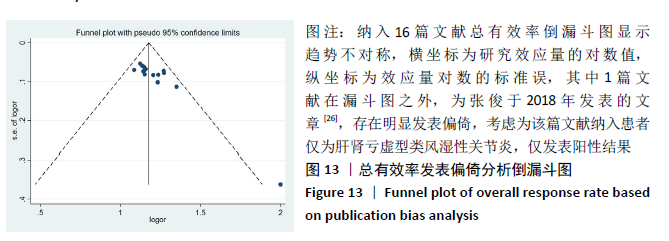
[1] SPARKS JA. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170(1):C1-C16.
[2] LITTLEJOHN EA, MONRAD SU. Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Prim Care. 2018;45(2):237-255.
[3] 2018中国类风湿关节炎诊疗指南[J].中华内科杂志,2018,57(4):242-251.
[4] 朱丽芳,俸一然,许东云.类风湿关节炎患者生存质量的研究进展[J].风湿病与关节炎,2018,7(4):76-80.
[5] 欧敏,朱艳.针灸治疗类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J].中医药临床杂志,2018, 30(10):1934-1936.
[6] 张鸿婷,杜旭,郭丹丹,等.独活寄生汤治疗类风湿关节炎药效学及作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中医药学报,2020,48(9):77-80.
[7] 周铭芳,范伏元.独活寄生汤治疗类风湿关节炎的Meta分析[J].中医药临床杂志,2019,31(10):1871-1874.
[8] 张星华,朱博雯,赵彬元,等.针灸治疗类风湿关节炎随机对照临床研究Meta分析[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2015,22(2):42-46.
[9] 王燕,陈思思,李泽光.浅谈针药结合治疗类风湿性关节炎的临床应用及作用机制[J].针灸临床杂志,2019,35(6):92-95.
[10] SILMAN AJ. The 1987 revised American Rheumatism Association criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1988; 27(5):315-324.
[11] 中华医学会风湿病学分会.类风湿关节炎诊断及治疗指南[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2010,14(4):265-270.
[12] 杜俊生.独活寄生汤加减、针灸联合治疗类风湿性关节炎的临床价值分析[J].心理月刊,2019,14(18):222.
[13] 韩志敏.针刺结合独活寄生汤加减治疗类风湿性关节炎临床观察[J].实用中医药杂志,2020,6(4):431-432.
[14] 李爱平.独活寄生汤加减等治疗类风湿性关节炎40例临床观察[J].现代养生, 2015(2):236.
[15] 孟宇航,杨卫彬,董宝强.独活寄生汤加减联合针灸治疗类风湿性关节炎的临床疗效分析[J].中医药信息,2018,35(1):58-62.
[16] 彭旺,曾令伟.独活寄生汤方加减配合针灸疗法对肝肾亏虚患者类风湿性关节炎的疗效及其对血清TNF-α、CRP水平的影响[J].抗感染药学,2018,15(7):1285-1287.
[17] 宋新安.针刺配合独活寄生汤治疗类风湿性关节炎临床观察[J]. 实用中医药杂志,2018,34(2):149-150.
[18] 王飞.针刺配合独活寄生汤治疗老年类风湿性关节炎临床疗效观察[J].新中医,2016,48(6):97-99.
[19] 王澎澎.独活寄生汤加减联合针灸治疗类风湿性关节炎的临床疗效[J].中国保健营养,2017,27(35):109.
[20] 魏淑凤,李秀兰,梁利娜,等.独活寄生汤加减联合针灸治疗类风湿性关节炎40例临床观察[J].中医药导报,2012,18(9): 67-69.
[21] 汪胤.独活寄生汤加减联合针灸治疗类风湿关节炎的临床疗效及对炎症因子的影响[J].江西医药,2018,53(4):325-328.
[22] 王颖诗.独活寄生汤加减联合针灸治疗类风湿性关节炎48例[J].中医外治杂志, 2017,26(2):18-19.
[23] 漆勇,漆良,夏会敏,等.独活寄生汤联合针灸治疗肝肾亏虚型类风湿关节炎效果观察[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2017, 26(7):742-744.
[24] 余南生,詹可顺.独活寄生汤加艾灸治疗类风湿性关节炎疗效观察及免疫学指标分析[J].安徽医药,2002,6(4):18-20.
[25] 余希婧,华水生.独活寄生汤方加减与针灸疗法对类风湿关节炎患者的疗效及其对血清CRP、ESR和氧化应激指标水平的影响[J].抗感染药学,2018,15(10): 1784-1786.
[26] 张俊.针灸联合独活寄生汤治疗肝肾亏虚型类风湿关节炎49例疗效观察[J].云南中医中药杂志,2018,39(1):64-66.
[27] 张振风.针药结合治疗类风湿性关节炎疗效观察[J].湖北中医杂志,2019,41(3): 53-55.
[28] SEOANE-MATO D, SANCHEZ-PIEDRA C, SILVA-FERNANDEZ L, et al. Prevalence of rheumatic diseases in adult population in Spain (EPISER 2016 study): aims and methodology. Reumatol Clin. 2019;15(2): 90-96.
[29] WEINBLATT ME. Methotrexate: who would have predicted its importance in rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):103.
[30] CUTOLO M. Glucocorticoids and chronotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open. 2016;2(1):e203.
[31] GILANI ST, KHAN DA, KHAN FA, et al. Adverse effects of low dose methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2012;22(2):101-104.
[32] 袁娟,胡玲,宋小鸽,等.艾灸对类风湿性关节炎大鼠关节滑膜组织Toll样受体4-骨髓样分化因子88-核转录因子-κB信号通路的影响[J].针刺研究,2015, 40(3):199-204.
[33] 李佳,李静,唐宏图,等.电针对类风湿性关节炎大鼠膝关节滑膜组织肿瘤坏死因子-α转换酶/核转录因子-κB信号通路的影响[J].针刺研究,2016,41(3):215-219.
[34] 张传英,胡玲,蔡荣林,等.艾灸对类风湿性关节炎大鼠踝关节滑膜组织Toll样受体4/核因子-κB信号通路的影响[J].针刺研究,2018,43(11):687-691.
[35] 高晓鹏,鲁贵生.独活寄生汤含药血清对佐剂性关节炎大鼠滑膜成纤维细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J].新中医,2018,50(4):1-5.
[36] 农贤刚,程卫萍,曾麟杰,等.艾灸加独活寄生汤对中老年膝关节炎患者hs-CRP、IL-1β和TNF-α的影响[J]. 针灸推拿医学(英文版), 2017,15(4):277-280.
[37] HAZLEWOOD GS, BARNABE C, TOMLINSON G, et al. Methotrexate monotherapy and methotrexate combination therapy with traditional and biologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis: abridged Cochrane systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2016;353:i1777.
[38] 周铭芳,范伏元.独活寄生汤治疗类风湿关节炎的Meta分析[J].中医药临床杂志,2019,31(10):1871-1874.
[39] 王海瑜,宋陈惠,刘小平,等.针灸联合甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎的Meta分析[J].中华中医药学刊,2019,37(6):1399-1403.
[40] 张星华,朱博雯,赵彬元,等.针灸治疗类风湿关节炎随机对照临床研究Meta分析[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2015,22(2): 42-46.
|