中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (26): 4175-4179.doi: 10.12307/2021.117
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
脂氧素A4对脊髓缺血再灌注损伤模型大鼠的神经保护
路 坦1,常耀辉2,尉 娜3
- 1新乡医学院第一附属医院骨外二科,河南省卫辉市 453100;2修武县人民医院骨外科,河南省焦作市 454350;3新乡医学院第三附属医院神经内二科,河南省新乡市 453003
Lipoxanthin A4 plays a neuroprotective role against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats
Lu Tan1, Chang Yaohui2, Wei Na3
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical University, Weihui 453100, Henan Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Xiuwu County People’s Hospital, Jiaozuo 454350, Henan Province, China; 3Department of Neurology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang 453003, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
脊髓缺血再灌注损伤:在脊髓损伤长期受压后,当脊髓受压解除血液再通后继而出现神经损伤症状,其本质是当脊髓血液再通后多种因素造成不可逆性神经元死亡,包括二次打击。
脂氧素:是一类由花生四烯酸代谢而来的内源性脂类介质,主要作用是促进炎症反应的及时消退,被称为炎症反应的“刹车信号”,可以明显抑制白细胞的驱化和激活,是体内重要的抗炎递质。
背景:前期研究已证明脂氧素A4对大鼠脊髓损伤具有神经保护作用,但其在脊髓缺血再灌注损伤中的作用机制仍不明确。
目的:探讨脂氧素A4在大鼠脊髓缺血再灌注损伤中的保护作用。
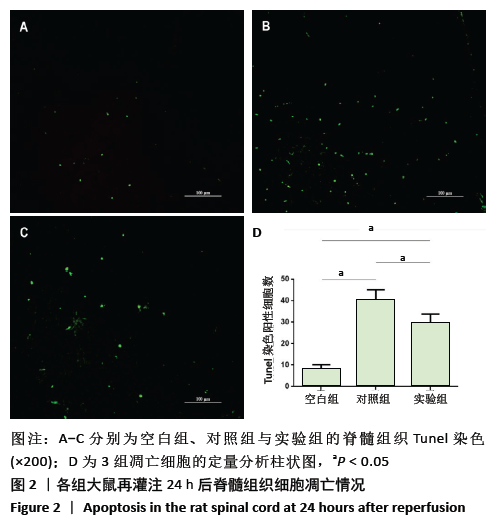
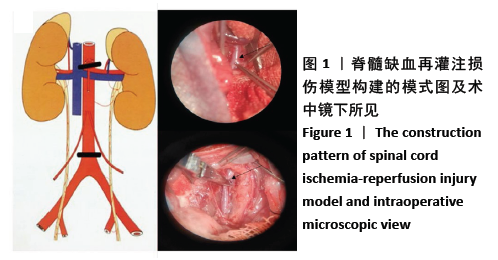
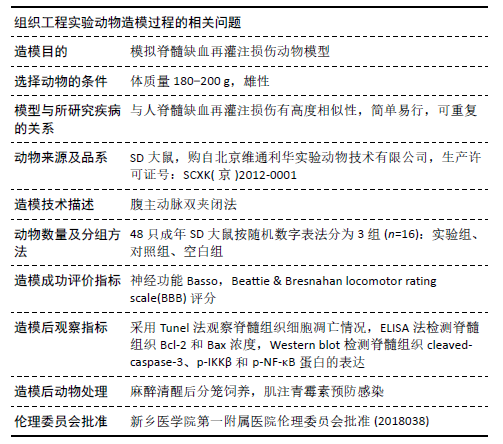
方法:将48只SD大鼠随机分为3组,每组16只:对照组、实验组制作脊髓缺血再灌注损伤模型,实验组脊髓鞘内注射脂氧素A4,对照组脊髓鞘内注射生理盐水;空白组不造模。造模后6,12,24,48 h,利用BBB评分评估大鼠运动神经功能;再灌注后24 h,采用Tunel法观察脊髓组织细胞凋亡情况,ELISA法检测脊髓组织Bcl-2和Bax浓度,Western blot检测脊髓组织cleaved-caspase-3、p-IKKβ和p-NF-κB蛋白的表达。实验通过新乡医学院第一附属医院伦理委员会批准(2018038)。
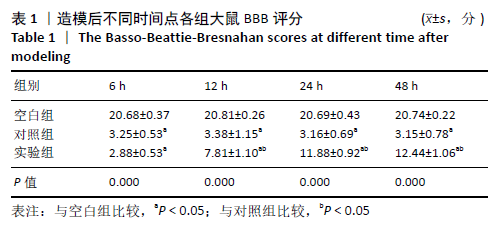
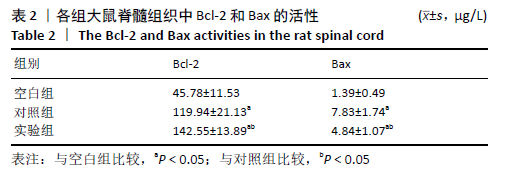
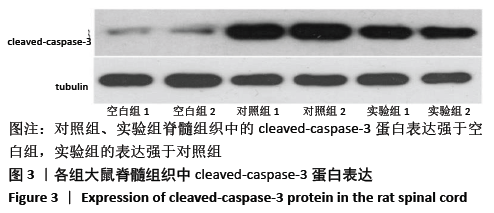
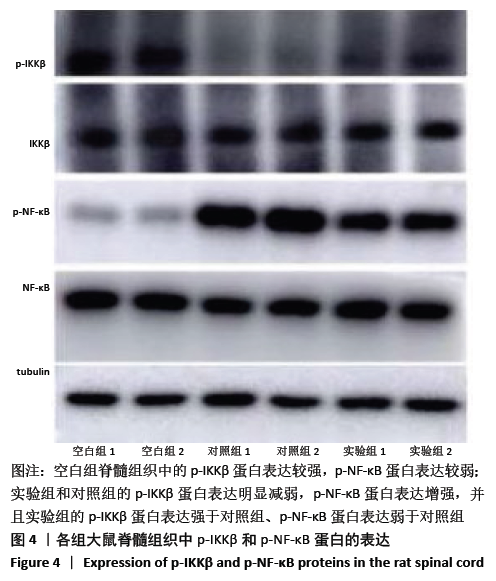
结果与结论:①对照组不同时间点的BBB评分低于空白组(P < 0.05),实验组造模后12,24,48 h的BBB评分高于对照组(P < 0.05);②对照组细胞凋亡多于空白组(P < 0.05),实验组少于对照组(P < 0.05);③对照组脊髓组织内的Bcl-2、Bax水平均高于空白组(P < 0.05);实验组的Bcl-2水平高于对照组(P < 0.05),Bax水平低于对照组(P < 0.05);④对照组cleaved-caspase-3、p-NF-κB蛋白表达强于空白组,p-IKKβ蛋白表达弱于空白组;实验组cleaved-caspase-3、p-NF-κB蛋白表达弱于对照组,p-IKKβ蛋白表达强于对照组;⑤结果表明,脂氧素A4可激活细胞质中caspase-3/IKKβ/NF-κB通道的活化,抑制细胞凋亡,起到治疗脊髓缺血再灌注损伤的作用。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5493-814X (路坦)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: