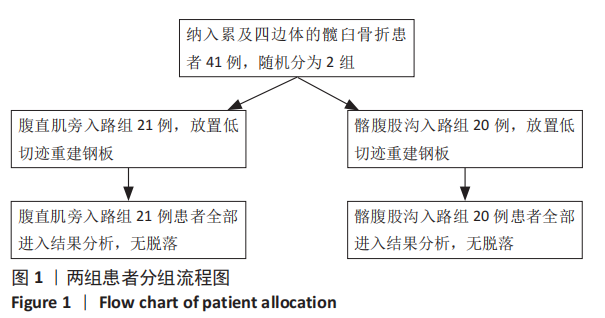
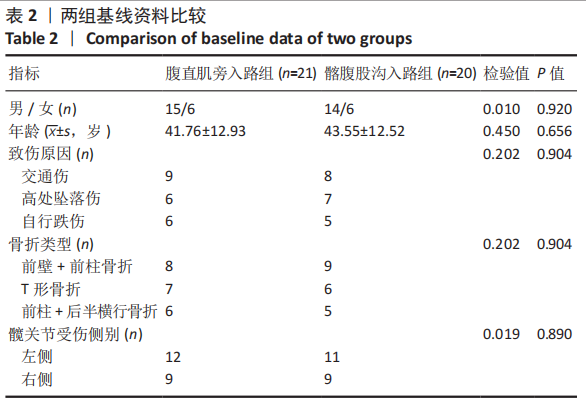
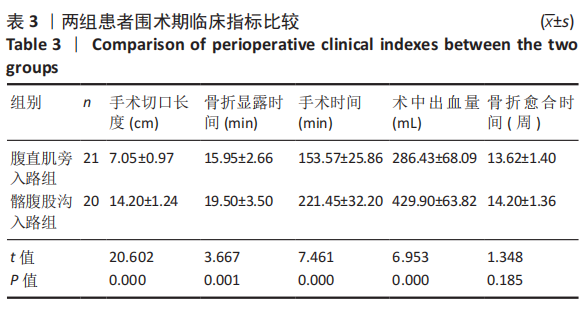
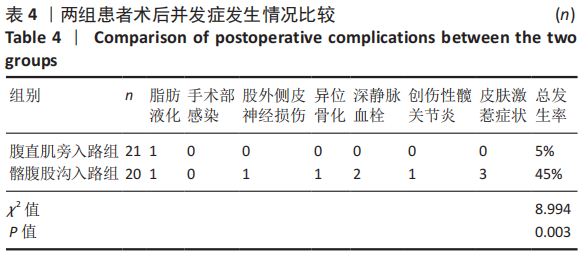
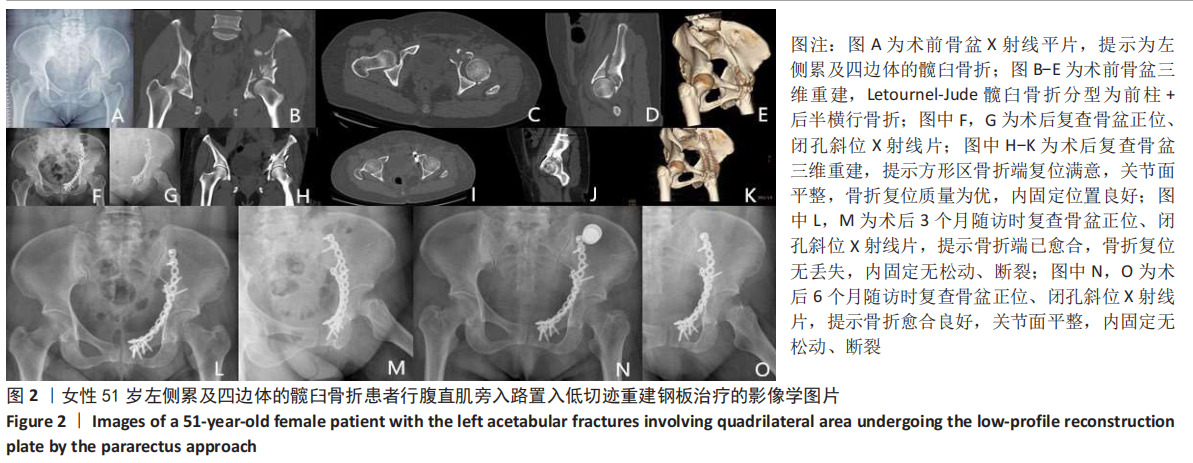
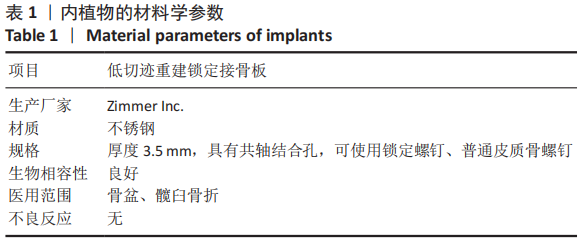
[1] KELLY ME, LEONARD M, GREEN C. Should money follow the patient: financial implication for being the national centre for the treatment and management of pelvic and acetabular fractures in Ireland. Injury. 2013; 44(12):1816-1819.
[2] 杨晓东, 刘涵, 谷城, 等. 髂坐钢板经腹直肌外侧入路治疗涉及方形区的髋臼骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(20):1836-1840.
[3] 尚冉冉, 宋成璟, 吴海洋, 等. 前路动力化方形区钛板螺钉系统钢板轨迹长度测量的解剖学研究[J]. 中华解剖与临床杂志,2020,25(1):31-36.
[4] 周东生. 髋臼骨折的治疗进展及思考[J]. 中国骨伤,2016,29(4):293-297.
[5] XIAO X, CHEN J, WANG C, et al. Central dislocation of femoral head without involvement of acetabular anterior and posterior columns. J Int Med Res. 2018;46(8):3388-3393.
[6] 李明, 庞清江, 郑琦. 髋臼四方区骨折内固定的研究进展[J].中华创伤杂志,2017,33(5):470-474.
[7] MÄRDIAN S, SCHASER KD, HINZ P, et al. Fixation of acetabular fractures via the ilioinguinal versus pararectus approach: a direct comparison. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(9):1271-1278.
[8] MATTA JM. Operative treatment of acetabular fractures through the ilioinguinal approach: a 10-year perspective. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(1Suppl):S20-S29.
[9] MERLE D’AUBIGNÉ RM, POSTEL M. Functional results of hip arthroplasty with acrylic prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1954;36(3):451-475.
[10] SEPEHRI A, SCIADINI MF, NASCONE JW, et al. Initial experience with the T-Clamp for temporary fixation of mechanically and hemodynamically unstable pelvic ring injuries. Injury. 2020;51(3):699-704.
[11] GIORDANO V, PECEGUEIRO DO AMARAL N, FRANKLIN CE, et al. Functional outcome after operative treatment of displaced fractures of the acetabulum: A 12-month to 5-year follow-up investigation. Eur J Trauma Emerg S. 2007;33(5):520-527.
[12] 陈开放, 姚升, 万意州, 等. 跨弓状缘髋臼四方区阻挡钢板治疗复杂髋臼骨折[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2020, 40(5): 294-301.
[13] FLINT L, CRYER HG. Pelvic fracture: the last 50 years. J Trauma. 2010;69(3): 483-488.
[14] May C, Egloff M, Butscher A, et al. Comparison of fixation techniques for acetabular fractures involving the anterior column with disruption of the quadrilateral plate: a biomechanical study. JBJS. 2018; 100(12): 1047-1054.
[15] 兰贺军, 赵振伟, 贾春, 等. 三种内固定方式治疗髋臼横行后壁骨折后髋臼接触特性的生物力学比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(27): 4375-4379.
[16] 殷建新, 李连欣. 髂腹股沟与Stoppa入路手术治疗骨盆及髋臼骨折疗效对比观察[J]. 山东医药,2016,56(42):57-58.
[17] 杨洪武, 郑祖根, 徐杰, 等. 手术复位治疗髋臼骨折移位259例[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2007,23(3):193-197.
[18] MAINI L, VERMA T, SHARMA A, et al. Evaluation of accuracy of virtual surgical planning for patient-specific pre-contoured plate in acetabular fracture fixation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138(4):495-504.
[19] 蔡贤华, 刘曦明, 汪国栋, 等. 涉及髋臼方形区骨折髂腹股沟人路显露与开放复位策略分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(16):1443-1447.
[20] 余洋, 陈龙, 仇道迪,等. Kocher-Langenbeck入路联合部分近端 Watson-Jones切口治疗涉及臼顶负重区的髋臼骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科志,2018, 20(3):210-216.
[21] Gänsslen A, Grechenig ST, Nerlich M, et al. Standard Approaches to the Acetabulum Part 2: Ilioinguinal Approach. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2016;83(4):217-222.
[22] 徐应明, 蔡贤华, 陈岩召, 等. 动力化前路方形区肽板螺钉系统内固定治疗涉及方形区的复杂髋臼骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(6):464-470.
[23] ELMADAG M, GUZEL Y, AKSOY Y, et al. Surgical Treatment of Displaced Acetabular Fractures Using a Modified Stoppa Approach. Orthopedics. 2016;39(2):e340-345.
[24] VERBEEK DO, PONSEN KJ, VAN HEIJL M, et al. Modified Stoppa approach for operative treatment of acetabular fractures: 1O-year experience and mid-term follow-up. Injury. 2018;49(6):1137-1140.
[25] 张潇, 熊然, 李涛, 等. 经腹直肌外侧切口入路治疗髋臼骨折的解剖学研究[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2015,33(1):17-20.
[26] 刘家国, 尚峰, 罗斌, 等. 腹直肌外侧入路钢板结合后柱拉力螺钉固定治疗涉及后柱的髋臼骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(6):490-497.
[27] 邹如意,吴敏,官建中,等.经腹直肌旁手术入路治疗髋臼骨折的研究进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(4):332-335.
[28] KEEL MJ, ECKER TM, CULLMANN JL, et al. The Pararectusaproach for anterior intrapelvic management of acetabular fractures: an anatomical study and clinical evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(3):405-411.
[29] 吴华川, 倪卫东. 腹直肌旁入路治疗髋臼骨折的研究进展[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,34(3):274-278.
[30] GOSWAMI T, MARKERT RJ, ANDERSON CG, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of a pre-contoured clavical plate. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17:815-818.
[31] 钟晓, 贾叙锋, 黄光平, 等. 锁定加压重建钢板不同途径内固定置入治疗髋臼横行骨折的生物力学比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018;22(27): 4305-4310.
[32] LIU M, NAKASAKI M, SHIH YV, et al. Effect of age on biomaterial-mediated in situ bone tissue regeneration. Acta Biomaterialia.2018;78:329-340.
|