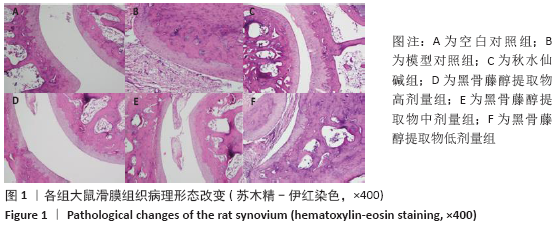
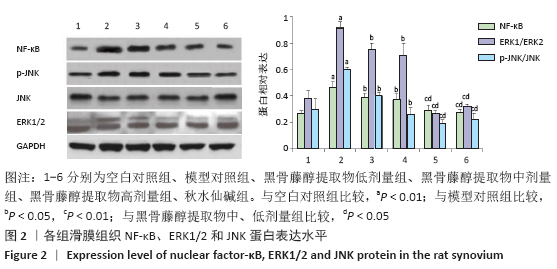
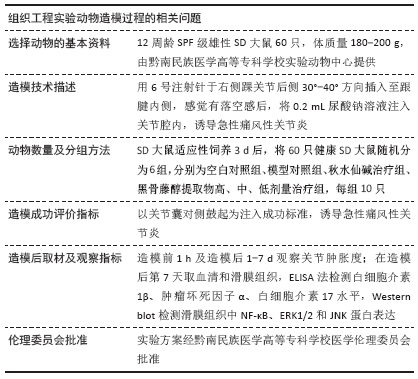
[1] MIRMIRAN R, BUSH T, CERRA MM, et al. Joint Clinical Consensus Statement of the American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons® and the American Association of Nurse Practitioners®: Etiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Consensus for Gouty Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2018;57(6):1207-1217.
[2] 曹波,唐庆昆,李海歌,等.痛风尿酸盐结晶在膝关节分布特征的观察与分析:——项基于双源CT双能量成像的初步研究[J].临床放射学杂志,2019,38(12):2396-2401.
[3] 沈嘉艳,许飞,周文强,等.痛风石的非药物疗法及其研究进展[J].风湿病与关节炎,2018,7(10):77-80.
[4] CRONSTEIN BN, SUNKUREDDI P. Mechanistic aspects of inflammation and clinical management of inflammation in acute gouty arthritis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2013;19(1):19-29.
[5] BLANDIN C, FORIEN M, GARDETTE A, et al.Tophus size is associated with hallux valgus deformity in gout. Eur J Clin Invest. 2018;48(1):12862.
[6] VARUGHESE GI, VARGHESE AI. Colchicine in acute gouty arthritis: the optimum dose? Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(5):405.
[7] ZAVODOVSKY BV, SIVORDOVA LE. Cardiovascular safety of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Ter Arkh. 2018;90(8):101-106.
[8] TANAKA C, MATSUDA T, KANEKO M. Neurological side-effects of antiallergic drug, colchicine and glucocorticoids. Ryoikibetsu Shokogun Shirizu. 1999;(27 Pt 2):606-609.
[9] ZHOU Q, SU J, ZHOU T, et al. A study comparing the safety and efficacy of febuxostat, allopurinol, and benzbromarone in Chinese gout patients: a retrospective cohort study.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017; 55(2):163-168.
[10] YUAN X, FAN YS, XU L, et al. Jia-Wei-Si-Miao-Wan alleviates acute gouty arthritis by targeting NLRP3 inflammasome.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2019;33(1):63-71.
[11] MA TH, SHENG T, TIAN CM, et al. Effect of ethanolic extract of Polygonum cuspidatum on acute gouty arthritis in mice through NLRP3/ASC/caspase-1 axis. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019;44(3):546-552.
[12] WANG Y, WANG L, LI E, et al. Chuanhu anti-gout mixture versus colchicine for acute gouty arthritis: a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, non-inferiority trial. Int J Med Sci. 2014;11(9):880-885.
[13] LEE YM, SHON EJ, KIM OS, et al. Effects of Mollugo pentaphylla extract on monosodium urate crystal-induced gouty arthritis in mice. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017;17(1):447.
[14] 骆镜妃,胡宗科,邓康,等.黑骨藤追风活络胶囊抗类风湿性关节炎的药理作用及机制[J].中南医学科学杂志,2016,44(2):140-142, 146.
[15] 党荣敏,龚莉莉.苗药黑骨藤种子幼芽与黑骨藤不同部位对PC12细胞氧化损伤的影响[J].深圳中西医结合杂志,2016,26(3):16-17.
[16] 张鹰,赵芡,李轩豪,等.基于网络药理学的苗药黑骨藤防治肺癌分子机制研究[J].中药材,2019,42(2):399-404.
[17] 党荣敏,刘元忠,谢洪书,等.黑骨藤抗急性痛风性关节炎的实验研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2016,32(9):1295-1298.
[18] 陈庆,靳凤云,陈华国,等.苗族黑骨藤有效部位的筛选研究[J].中国民族民间医药杂志,2005(3):163-165.
[19] KHANNA D, KHANNA PP, FITZGERALD JD, et al. 2012 American College of Rheumatology guidelines for management of gout. Part 2: therapy and antiinflammatory prophylaxis of acute gouty arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64(10):1447-1461.
[20] CLEOPHAS MC, CRIŞAN TO, JOOSTEN LA. Factors modulating the inflammatory response in acute gouty arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017;29(2):163-170.
[21] LU X, ZENG R, LIN J, et al. Pharmacological basis for use of madecassoside in gouty arthritis: anti-inflammatory, anti-hyperuricemic, and NLRP3 inhibition. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2019;41(2): 277-284.
[22] DUMUSC A, SO A. Interleukin-1 as a therapeutic target in gout. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27(2):156-163.
[23] 江丹,熊金河,尚华.洛索洛芬钠对急性痛风性关节炎大鼠血清IL-1β和滑膜组织中NF-κB蛋白表达的影响[J].郑州大学学报(医学版), 2019,54(3):446-449.
[24] 周琦,张宁,卢芳,等.穿山龙总皂苷对痛风性关节炎大鼠关节炎滑膜IL-1β及其信号转导通路的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2013, 29(6):52-57.
[25] 胡亚彬,杨青,张传玉,等.中性粒细胞胞外诱捕网和氧化应激在痛风发病机制中的作用[J].国际免疫学杂志,2018,41(6):690-694.
[26] LIU Y, ZHAO Q, YIN Y, et al. Serum levels of IL-17 are elevated in patients with acute gouty arthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;497(3):897-902.
[27] 李雪峰,刘育辰,刘刚.苗药黑骨藤化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J].中成药,2018,40(4): 904-912.
[28] 梁江,王乾宇,黄维琛,等.黑骨藤追风活络胶囊抑制CIA大鼠滑膜组织NF-κB表达并减轻关节炎症反应[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2019, 35(3):193-198.
[29] 黄明进,罗春丽,郭刚,等.黑骨藤抗类风湿性关节炎作用及其分子机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2011,17(12):174-177.
[30] VIATOUR P, MERVILLE MP, BOURS V, et al. Phosphorylation of NF-kappaB and IkappaB proteins: implication in cancer and inflammation. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30(1):43-52.
[31] ZHAO Z, TANG X, ZHAO X, et al. Tylvalosin exhibits anti-inflammatory property and attenuates acute lung injury in different models, possibly through suppression of NF-κB activation. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014; 90(1):73-87.
[32] DHANASEKAR C, KALAISELVAN S, RASOOL M. Morin, a Bioflavonoid Suppresses Monosodium Urate Crystal-Induced Inflammatory Immune Response in RAW 264.7 Macrophages through the Inhibition of Inflammatory Mediators, Intracellular ROS Levels and NF-κB Activation. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0145093.
[33] LIN TH, PAJARINEN J, LU L, et al. NF-κB as a Therapeutic Target in Inflammatory-Associated Bone Diseases. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2017;107:117-154.
[34] HAYDEN MS, GHOSH S. NF-κB in immunobiology. Cell Res. 2011;21(2): 223-244.
[35] WARD C, WALKER A, DRANSFIELD I,et al. Regulation of granulocyte apoptosis by NF-kappaB. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004;32(Pt3):465-467.
[36] PIOTROWSKA A, IZYKOWSKA I, PODHORSKA-OKOŁÓW M, et al. The structure of NF- kappaB family proteins and their role in apoptosis.Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2008;62:64-74.
[37] ESPÍN-PALAZÓN R, TRAVER D. The NF-κB family: Key players during embryonic development and HSC emergence. Exp Hematol. 2016; 44(7):519-527.
[38] 陈刚,殷钟意,郑旭煦,等.丹皮酚改善大鼠痛风性关节炎与调节核因子κB活化的关系研究[J].中国药理学通报,2018,34(12):1730-1735.
[39] SENFTLEBEN U, CAO Y, XIAO G, et al. Activation by IKKalpha of a second, evolutionary conserved, NF-kappa B signaling pathway. Science. 2001; 293(5534):1495-1499.
[40] HAYDEN MS, GHOSH S. Regulation of NF-κB by TNF family cytokines. Semin Immunol. 2014;26(3):253-266.
[41] MELOCHE S, POUYSSÉGUR J. The ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway as a master regulator of the G1- to S-phase transition. Oncogene. 2007;26(22):3227-3239.
[42] 徐轶尔,于雪峰,陈水林,等.基于JNK信号通路探讨豨莶草对痛风性关节炎影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(10):1340-1345. |