中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 1423-1427.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.4011
• 骨与关节图像与影像Bone and joint imaging • 上一篇 下一篇
影像学评估高选择性神经根封闭辅助退行性脊柱侧凸短节段固定融合的效果
梁 彦1,赵永飞2,徐 帅1,朱震奇1,王凯丰1,刘海鹰1,毛克亚2
- 1北京大学人民医院脊柱外科,北京市 100853;2中国人民解放军总医院骨科,北京市 100042
Imaging evaluation of short-segment fixation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis assisted by highly selective nerve root block
Liang Yan1, Zhao Yongfei2, Xu Shuai1, Zhu Zhenqi1, Wang Kaifeng1, Liu Haiying1, Mao Keya2
- 1Department of Spine Surgery, People’s Hospital of Peking University, Beijing 100853, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100042, China
摘要:

文题释义:
成人退行性腰椎侧凸:因腰椎小关节突和椎间盘退变导致的腰椎侧凸大于10°,其临床特征主要是退行性改变导致的脊柱序列改变,常表现为腰椎滑脱、旋转半脱位,通常伴有腰痛,伴或不伴有下肢神经痛。
高选择性神经根封闭:是一种在C臂引导下的微创神经根阻滞剂术,临床上可作为诊断和治疗方法,有助于临床医生明确责任间隙,制定准确的手术方案。
背景:关于成人退行性腰椎侧凸的治疗选择中,采用短节段固定或长节段固定仍存在较大的争议。
目的:探讨高选择性神经根封闭辅助下对成人退行性腰椎侧凸行短节段固定精准治疗的有效性和可行性。
方法:选择2014年5月至2017年9月301医院和北大人民医院收治的35例退行性腰椎侧凸患者,其中男14例,女21例,年龄(64.2±8.1)岁,所有患者均在高选择性神经根封闭下确定固定节段,进行经椎间孔腰椎间融合治疗。术后随访评估腰腿部目测类比评分与Oswestry残疾指数,通过影像学检查获得Cobb角、腰椎前凸角、骶骨倾斜角和骨盆倾斜角数据与椎间融合情况,记录并发症。试验获得301医院和北大人民医院伦理委员会批准。
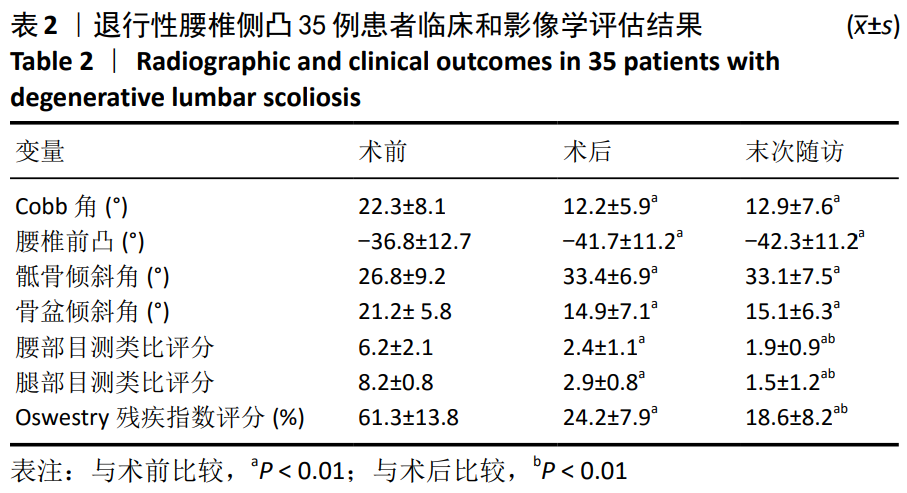
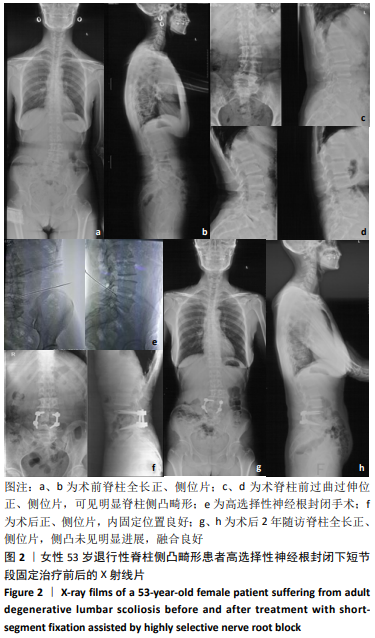
结果与结论:①35例患者中27例行单节段微创经椎间孔腰椎融合,5例行双节段微创经椎间孔腰椎融合,3例行三节段微创经椎间孔腰椎融合;②35例患者获得平均(25.6±1.5)个月随访,均获Ⅰ级融合,3个月内出现硬膜撕裂脑脊液漏3例,下肢肌间静脉血栓1例,肺炎1例,伤口脂肪液化1例;3个月后出现邻近节段退变1例;无神经损伤或不愈合,无螺钉或钛棒断裂;③35例患者末次随访的腰腿部目测类比评分、Oswestry残疾指数、Cobb角、腰椎前凸角、骶骨倾斜角和骨盆倾斜角均较术前明显改善(P < 0.01);④结果表明,高选择性神经根封闭辅助下对退行性腰椎侧凸患者行短节段固定精准治疗可取得较好的临床疗效。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1723-4930 (梁彦)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: