中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (8): 1243-1248.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2348
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
成骨细胞特异因子2基因家族的全基因组鉴定、分类及进化分析
谭婧玉,刘海文
- 锦州医科大学附属第一医院,辽宁省锦州市 121001
Genome-wide identification, classification and phylogenetic analysis of Fasciclin gene family for osteoblast specific factor 2
Tan Jingyu, Liu Haiwen#br#
- The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
成骨细胞特异性因子2:即Periostin,是由成骨细胞及其前体细胞分泌产生的一种细胞外基质蛋白,参与细胞外基质的重建,对基质蓄积、细胞基质相互作用及纤维化进行调节,具有促进细胞黏附及细胞迁移等功能。
保守结构域:是指在生物进化中一个蛋白家族中具有不变或相同的结构域,具有重要的功能,不能被改变。结构域是蛋白质中由不同二级结构和超二级结构组合而成的独立的稳定结构区域,是蛋白质功能单元。
背景:目前,Fasciclin基因家族的保守结构、蛋白特性、系统发育关系尚无系统的研究。
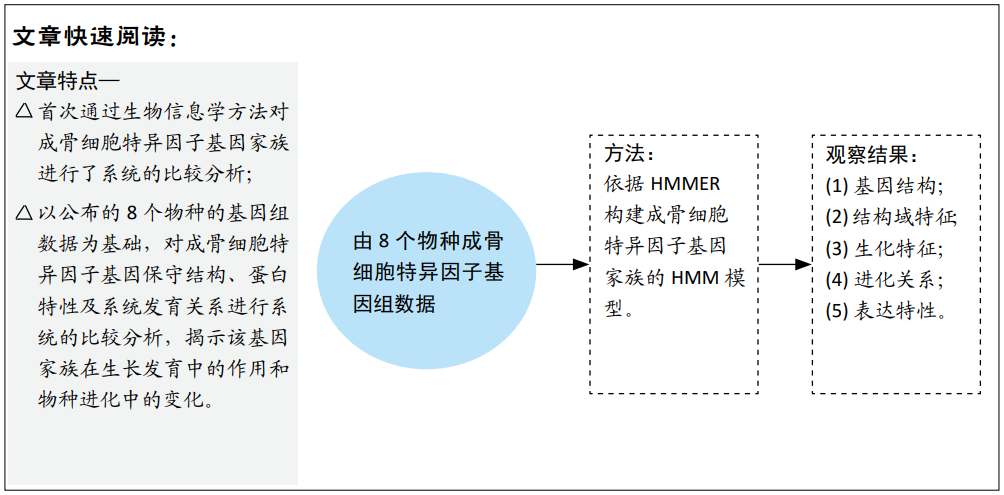
目的:探讨成骨细胞特异因子基因家族的进化历史,对成骨细胞特异因子基因家族的保守结构、蛋白特性、系统发育关系进行系统的比较分析。
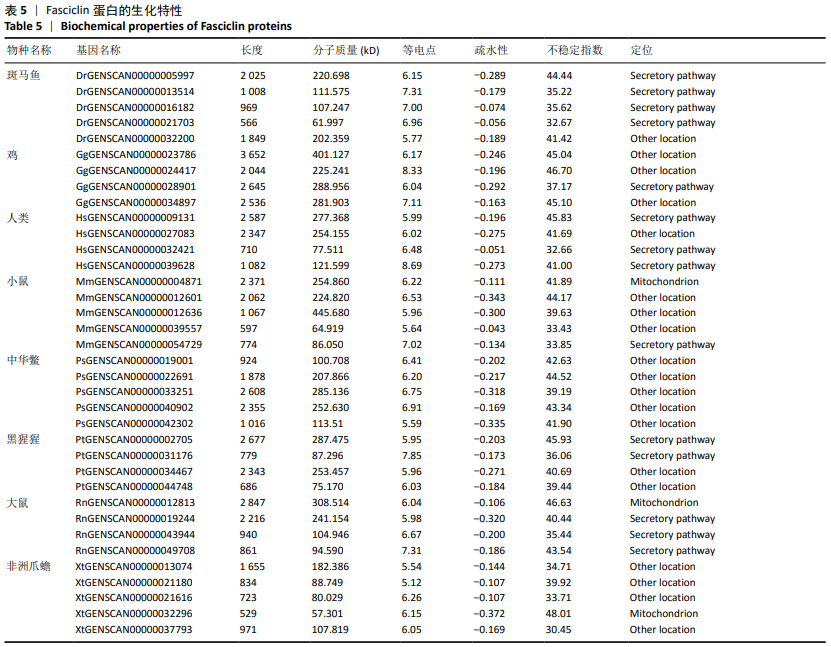
方法:实验基于已公布的人、黑猩猩、斑马鱼等8个物种的基因组数据,依据HMMER软件构建成骨细胞特异因子基因家族的HMM模型,分析了其基因结构、结构域特征、生化特征、进化关系和表达特性。
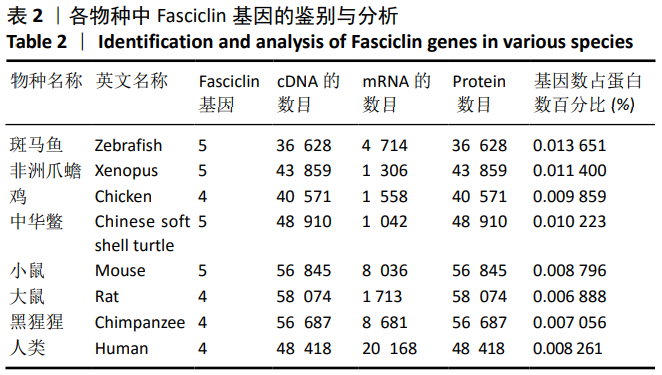
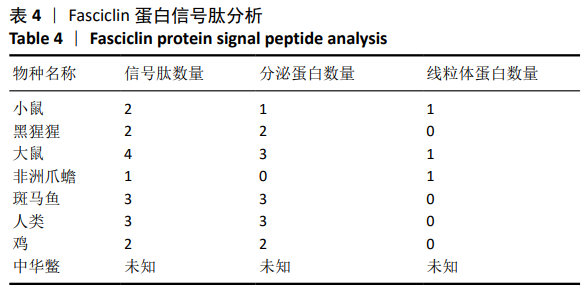
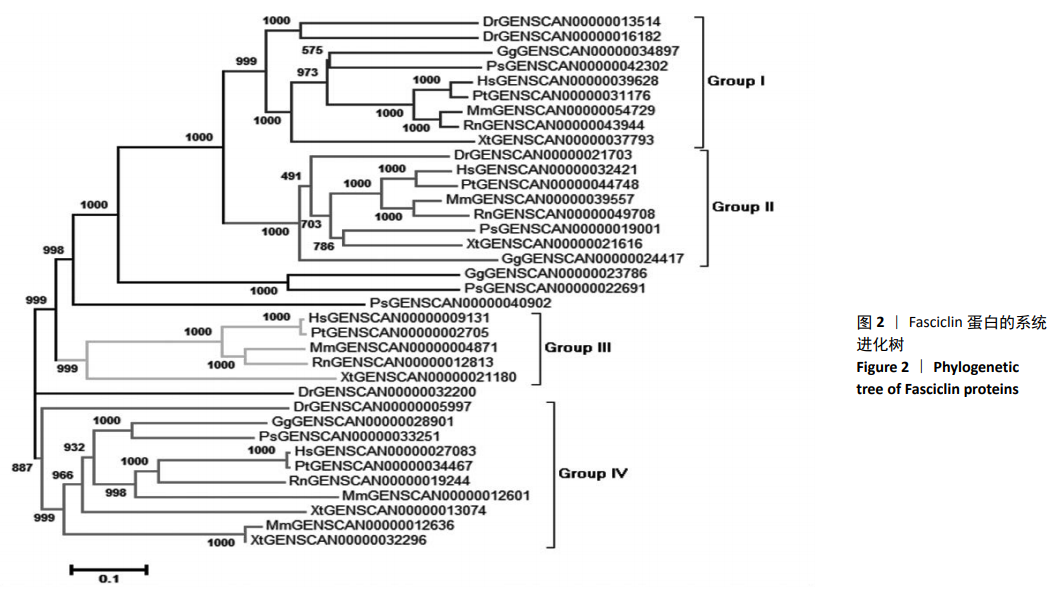
结果与结论:①在鱼类(斑马鱼)、两栖类(非洲爪蟾)、鸟类(鸡)、爬行类(中华鳖)、哺乳类(大鼠和小鼠)和灵长类(黑猩猩和人)等8个物种中,各检索出5,5,4,5,5,4,4,4个成骨细胞特异因子候选基因;②通过对成骨细胞特异因子基因在8个物种中的系统发育分析,发现成骨细胞特异因子基因家族整个进化树可以分为4个进化分支,其中2个进化分支的基因具有更强的保守性,可能是主要的成骨细胞特异因子;其中一个分支则可能是两栖类、哺乳类和灵长类特有的成骨细胞特异因子;另外一个分支也具有较好的保守性,但是非洲爪蟾和小鼠在该进化分支中有2个拷贝基因,这个进化分支可能对这两类物种起着重要的作用;③上述数据说明,在物种进化过程中,该家族基因并没有发生较大变化,这类基因可能是重要的生长发育相关基因,推测这类基因的缺失可能会导致个体的死亡或导致物种的灭绝。
中图分类号: