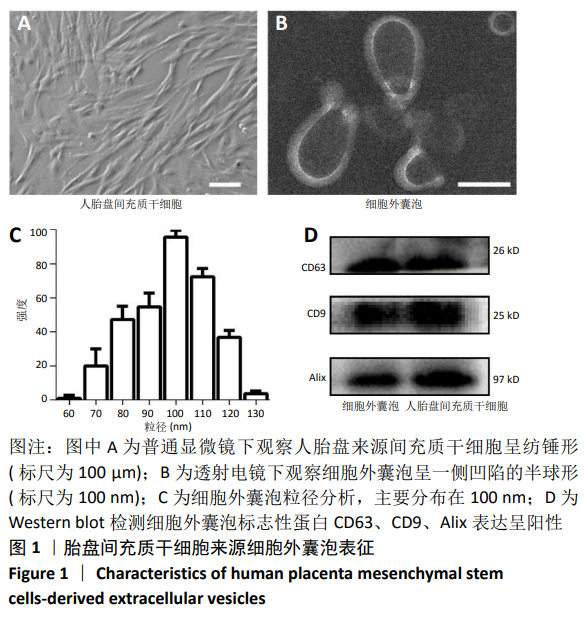
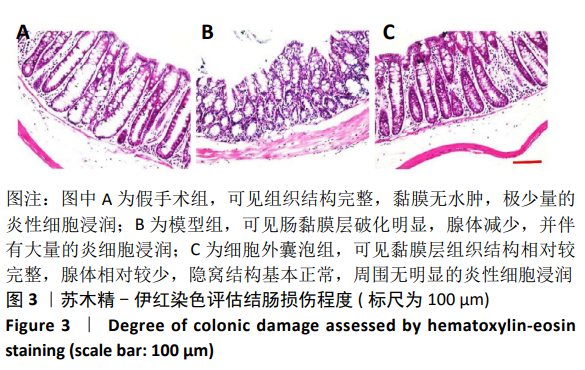
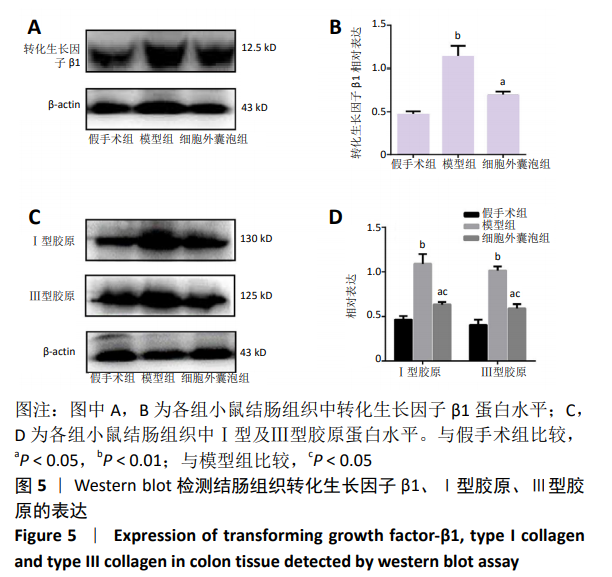
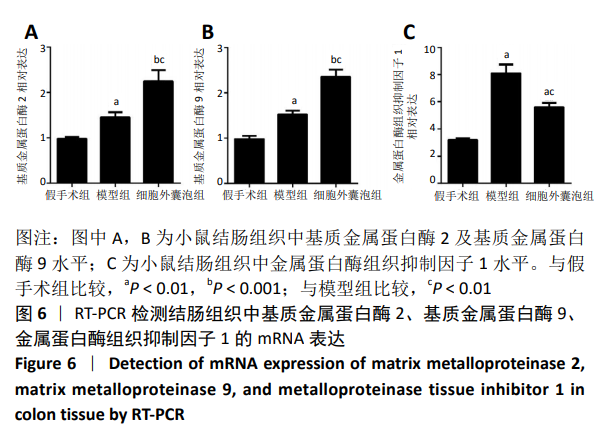
[1] WEIMERS P, MUNKHOLM P. The Natural History of IBD: Lessons Learned. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2018;16(1):101-111.
[2] FIOCCHI C, LUND PK. Themes in fibrosis and gastrointestinal inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011;300(5):G677-683.
[3] PALLONE F, MONTELEONE G. Mechanisms of tissue damage in inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2001;17(4):307-312.
[4] ZORZI F, CALABRESE E, MONTELEONE G. Pathogenic aspects and therapeutic avenues of intestinal fibrosis in Crohn’s disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015;129(12):1107-1113.
[5] LATELLA G, DI GREGORIO J, FLATI V, et al. Mechanisms of initiation and progression of intestinal fibrosis in IBD. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015;50(1): 53-65.
[6] LI J, MAO R, KURADA S, et al. Pathogenesis of fibrostenosing Crohn’s disease. Transl Res. 2019;209:39-54.
[7] RIEDER F, FIOCCHI C, ROGLER G. Mechanisms, Management, and Treatment of Fibrosis in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(2): 340-350.e6.
[8] LOEUILLARD E, BERTRAND J, HERRANEN A, et al. 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced chronic colitis with fibrosis and modulation of TGF-β1 signaling. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(48):18207-18215.
[9] DI SABATINO A, JACKSON CL, PICKARD KM, et al. Transforming growth factor beta signalling and matrix metalloproteinases in the mucosa overlying Crohn’s disease strictures. Gut. 2009;58(6):777-789.
[10] BETTENWORTH D, RIEDER F. Pathogenesis of Intestinal Fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Perspectives for Therapeutic Implication. Dig Dis. 2017;35(1-2):25-31.
[11] MEIJER MJ, MIEREMET-OOMS MA, VAN DER ZON AM, et al. Increased mucosal matrix metalloproteinase-1, -2, -3 and -9 activity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and the relation with Crohn’s disease phenotype. Dig Liver Dis. 2007;39(8):733-739.
[12] EL AGHA E, KRAMANN R, SCHNEIDER RK, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Fibrotic Disease. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;21(2):166-177.
[13] VOSWINKEL J, FRANCOIS S, SIMON JM, et al. Use of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in chronic inflammatory fistulizing and fibrotic diseases: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013;45(2):180-192.
[14] CAMUSSI G, DEREGIBUS MC, CANTALUPPI V. Role of stem-cell-derived microvesicles in the paracrine action of stem cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013; 41(1):283-287.
[15] VAN NIEL G, D’ANGELO G, RAPOSO G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(4):213-228.
[16] SHOJAATI G, KHANDAKER I, FUNDERBURGH ML, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reduce Corneal Fibrosis and Inflammation via Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Delivery of miRNA. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(11):1192-1201.
[17] LAWRANCE IC, WU F, LEITE AZ, et al. A murine model of chronic inflammation-induced intestinal fibrosis down-regulated by antisense NF-kappa B. Gastroenterology. 2003;125(6):1750-1761.
[18] MURTHY SN, COOPER HS, SHIM H, et al. Treatment of dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine colitis by intracolonic cyclosporin. Dig Dis Sci. 1993; 38(9):1722-1734.
[19] CHOI YJ, KOO JB, KIM HY, et al. Umbilical cord/placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit fibrogenic activation in human intestinal myofibroblasts via inhibition of myocardin-related transcription factor A. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):291.
[20] LI T, YAN Y, WANG B, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(6): 845-854.
[21] BIANCONE L, BRUNO S, DEREGIBUS MC, et al. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(8): 3037-3042.
[22] BURRELLO J, MONTICONE S, GAI C, et al. Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Immune-Modulation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016;4:83.
[23] WANG B, YAO K, HUUSKES BM, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Deliver Exogenous MicroRNA-let7c via Exosomes to Attenuate Renal Fibrosis. Mol Ther. 2016;24(7):1290-1301.
[24] LOU G, CHEN Z, ZHENG M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(6):e346.
[25] MARDPOUR S, GHANIAN MH, SADEGHI-ABANDANSARI H, et al. Hydrogel-Mediated Sustained Systemic Delivery of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Improves Hepatic Regeneration in Chronic Liver Failure. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(41):37421-37433.
[26] FANG S, XU C, ZHANG Y, et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Suppress Myofibroblast Differentiation by Inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor-β/SMAD2 Pathway During Wound Healing. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(10): 1425-1439.
[27] BIER A, BERENSTEIN P, KRONFELD N, et al. Placenta-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and their exosomes exert therapeutic effects in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Biomaterials. 2018;174:67-78.
[28] DOEPPNER TR, HERZ J, GÖRGENS A, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Improve Post-Stroke Neuroregeneration and Prevent Postischemic Immunosuppression. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(10):1131-1143.
[29] QI X, ZHANG J, YUAN H, et al. Exosomes Secreted by Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Repair Critical-Sized Bone Defects through Enhanced Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis in Osteoporotic Rats. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12(7):836-849.
[30] GARCÍA-OLMO D, GARCÍA-ARRANZ M, GARCÍA LG, et al. Autologous stem cell transplantation for treatment of rectovaginal fistula in perianal Crohn’s disease: a new cell-based therapy. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2003;18(5):451-454.
[31] CARVELLO M, LIGHTNER A, YAMAMOTO T, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Perianal Crohn’s Disease. Cells. 2019;8(7). pii: E764.
[32] PHINNEY DG, PITTENGER MF. Concise Review: MSC-Derived Exosomes for Cell-Free Therapy. Stem Cells. 2017;35(4):851-858.
[33] QIU G, ZHENG G, GE M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles affect disease outcomes via transfer of microRNAs. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):320.
[34] KESHTKAR S, AZARPIRA N, GHAHREMANI MH. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: novel frontiers in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):63.
[35] HONG P, YANG H, WU Y, et al. The functions and clinical application potential of exosomes derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells: a comprehensive review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):242.
[36] TKACH M, THÉRY C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell. 2016;164(6):1226-1232.
[37] RIEDER F, FIOCCHI C. Mechanisms of tissue remodeling in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis. 2013;31(2):186-193.
|