[1] ROSAL MC, AYERS D, LI W, et al. A randomized clinical trial of a peri-operative behavioral intervention to improve physical activity adherence and functional outcomes following total knee replacement. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:226.
[2] Maradit KH, Larson DR, Crowson CS, et al. Prevalence of total hip and knee replacement in the united states. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(17):1386-1397.
[3] 雷光华, 王坤正. 骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)解读[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2018, 38 (12):716-717.
[4] ZHU NN, XU PP, LEI TT, et al. Postoperative pain self-management behavior in patients who underwent total knee or hip arthroplasty. AORN J. 2017;105(4):355-364.
[5] BESWICK AD, WYLDE V, GOOBERMAN-HILL R, et al. What proportion of patients report long-term pain after total hip or knee replacement for osteoarthritis? A systematic review of prospective studies in unselected patients. BMJ Open. 2012;2(1):e435.
[6] 沈彬,翁习生,廖刃,等. 中国髋、膝关节置换术加速康复——围术期疼痛与睡眠管理专家共识[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2016,9(2):91-97.
[7] 朱诗白,翟洁,蒋超,等.膝关节置换围手术期的快速康复措施[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(3):456-463.
[8] 郑博,许冠华,夏超,等. 塞来昔布联合汉防己甲素对膝关节置换术围术期镇痛效果的评价[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志, 2019,25(10):765-769.
[9] 廖红,郑曼,朱娟,等. 针刺治疗全膝关节置换术后疼痛研究进展[J]. 河南中医, 2020,40(2):321-324.
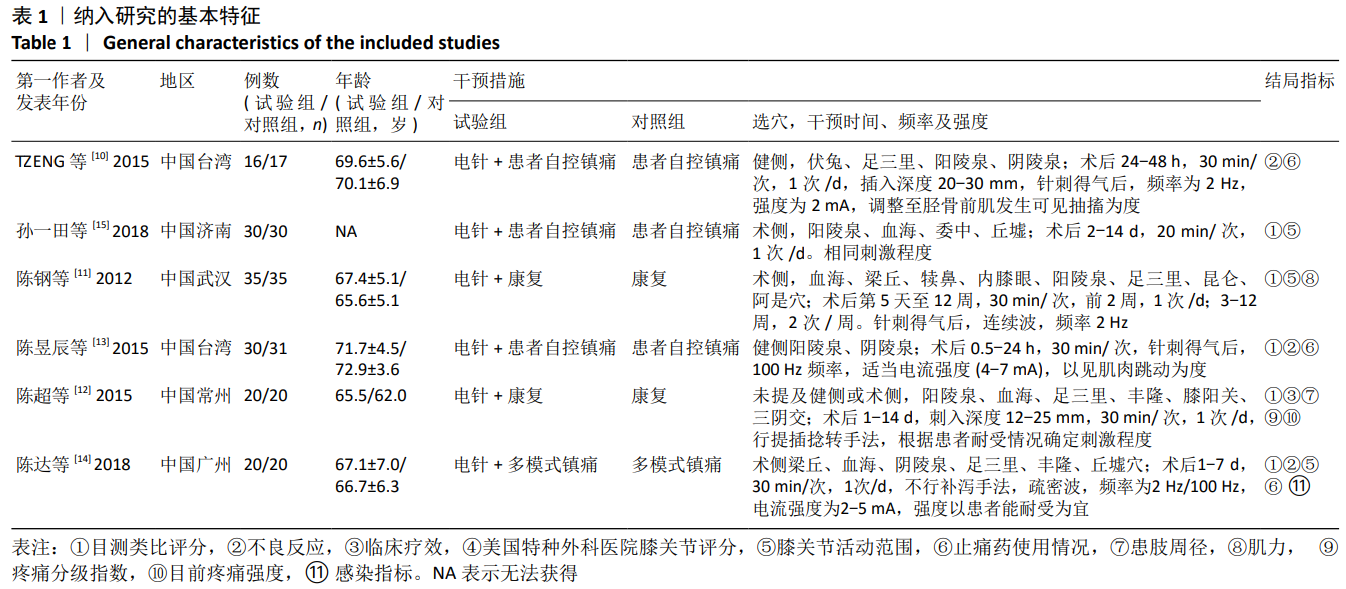
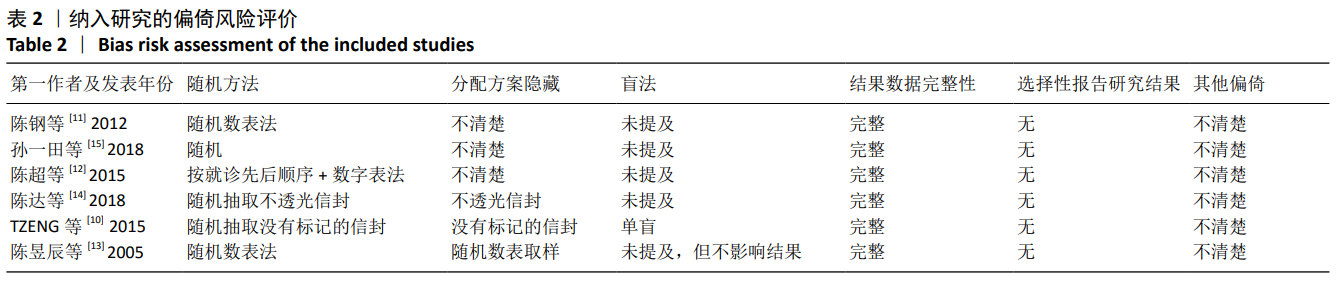
10] TZENG CY, CHANG SL, WU CC, et al. Single-blinded, randomised preliminary study evaluating the effects of 2 Hz electroacupuncture for postoperative pain in patients with total knee arthroplasty. Acupunct Med. 2015;33(4):284-288.
[11] 陈钢,辜锐鑫,徐丹丹.电针疗法在全膝关节置换术后康复中的应用[J]. 中国针灸, 2012,32(4):309-312.
[12] 陈超, 张一, 郭海英, 等. 电针结合康复训练治疗全膝关节置换术后下肢肿胀疗效观察[J]. 山东中医药大学学报, 2015, 39(2):139-141.
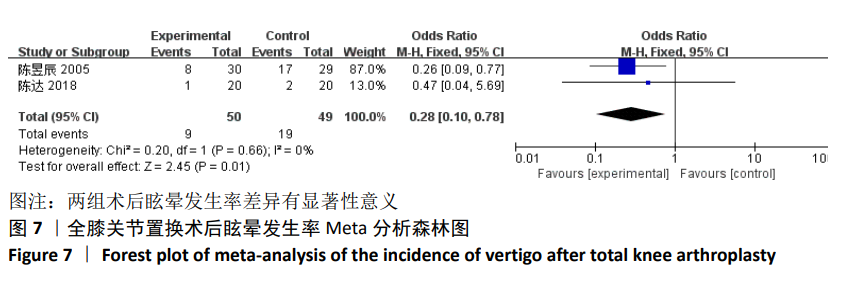
[13] 陈昱辰, 刘旭然, 林昭庚. 术後电针对膝关节腔手术後疼痛缓解效应的评估[J]. 台湾中医医学杂志, 2005,4(1):5-23.
[14] 陈达, 盛东, 徐景利, 等. 电针在全膝关节置换术后镇痛的临床疗效分析[J]. 针刺研究, 2018,43(10):616-621.
[15] 孙一田, 阎伟, 刘晓晨. 电针疗法用于全膝关节置换术后疼痛的临床研究[J]. 中医外治杂志, 2018,27(5):15-16.
[16] SKOU ST, ROOS EM, LAURSEN MB, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of total knee replacement. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373(17):1597-1606.
[17] 谢小伟, 岳辰, 康鹏德, 等. 加速康复模式下初次全膝关节置换术后急性疼痛的相关因素分析[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2016,9(6):489-492.
[18] 沈松坡, 翁习生, 冯宾. 全膝关节置换术后疼痛原因分析及疼痛预测模型的研究进展[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2018,38(17): 1082-1088.
[19] 高彩霞, 高丽. 人工全膝关节置换术后影响关节长期疼痛的原因分析[J]. 中国药物与临床, 2020,20(2):233-234.
[20] 高强, 姚运峰. 全膝关节表面置换术后膝前疼痛的原因与治疗方法[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2019,34(12):1340-1343.
[21] 杜宁, 李娴, 樊碧发, 等. MAPK和NO相关信号通路在电针镇痛作用机理的研究进展[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志, 2019, 25(11):854-858.
[22] 韩济生. 针麻镇痛研究[J]. 针刺研究, 2016,41(5):377-387.
[23] 周杰, 陈贞羽, 龚杰, 等. 不同参数组合电针对炎性痛模型大鼠镇痛效应及中枢内啡肽的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34(3):939-943.
[24] 陈达, 盛东, 徐景利, 等. 电针对全膝关节置换术后患者的辅助镇痛效应及对血清β-内啡肽及前列腺素E-2水平的影响[J]. 中国针灸, 2019,39(3):247-250.
[25] 阎丽娟, 付宏伟, 赵悦, 等. 基于电针频率的针刺镇痛机理研究进展[J]. 上海针灸杂志, 2016,35(1):121-124.
[26] 穆蕊, 余剑波, 吴丽丽. 脊髓ERK信号通路在电针足三里穴减轻瑞芬太尼诱发切口痛大鼠痛觉过敏中的作用[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2015,35(10):1241-1244.
[27] 王鑫, 朱忠强, 王珂, 等. 电针对切口痛大鼠的镇痛效应和背根神经节瞬时受体电位香草酸亚型1表达的影响[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2016,33(11):2493-2495.
[28] 周晟, 曹红霞, 俞连春, 等. 电针针刺委中穴和大肠俞穴fMRI下任务态脑疼痛中枢和默认网络的改变[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2016,96(7):531-534.
[29] 潘卫星. 针灸的神经生物学机理[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2018,33(10):4281-4297.
[30] 肖亮, 彭海东, 蔡清萍. 电针参数对针麻镇痛效果的影响[J]. 针刺研究, 2006, 31(6):372-374.
[31] 朱丹, 白洁静, 张晓庆, 等. 电针参数定量化的研究进展[J]. 中国针灸, 2015, 35(5):525-528.
[32] 庄晟坚, 龚杰, 周杰, 等. 不同电针刺激参数对镇痛效应的实验研究进展[J]. 浙江中医药大学学报, 2015,39(12):913-917.
[33] 付宏伟, 阎丽娟, 刘阳阳, 等. 不同电针刺激参数对镇痛效应影响的研究概述[J]. 上海针灸杂志, 2018,37(11):1331-1335.
[34] 周杰, 陈贞羽, 龚杰, 等. 不同参数组合电针对炎性痛模型大鼠镇痛效应及中枢内啡肽的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34(3):939-943.
[35] 赵天易, 席强, 郭义. 电针治疗手术后疼痛刺激参数的研究现状和分析[J]. 上海针灸杂志, 2015,34(5):464-467.
[36] YUE C, ZHANG X, ZHU Y, et al. Systematic review of three electrical stimulation techniques for rehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018; 33(7):2330-2337.
[37] ALWARDAT M, ETOOM M, SINIBALDI SP. Letter to the editor on “systematic review of three electrical stimulation techniques for rehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty”. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(8):2696-2697.
[38] 付慕勇, 张智龙. 辨证取穴针刺治疗膝关节骨性关节炎:随机对照研究(英文)[J]. 世界针灸杂志(英文版), 2012,22(3): 11-17.
[39] 张玉森, 王子轩. 温针配合玻璃酸钠关节内注射治疗膝关节骨性关节炎随机对照观察[J]. 针刺研究, 2011,36(5):373-376.
[40] 张银娟, 杨志新. “相对穴”阴陵泉与阳陵泉治疗关节疾病特异性研究概况[J]. 河南中医, 2016,36(7):1263-1265. |