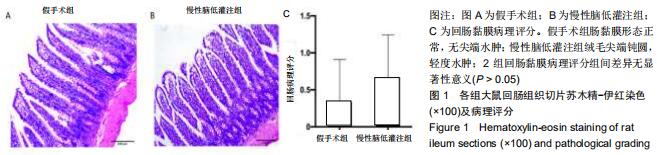
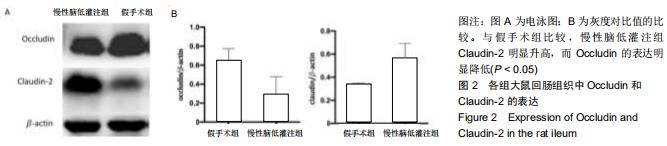
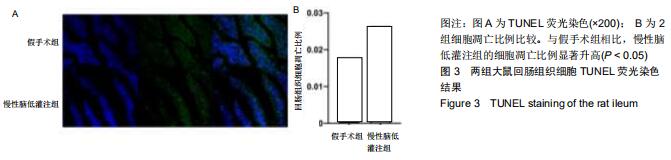
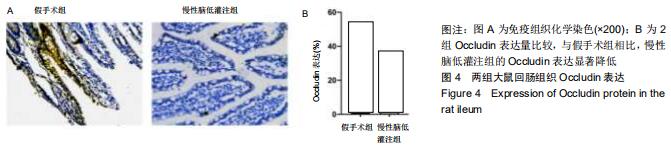
|
[1] 王陇德,刘建民,杨弋,等. 我国脑卒中防治仍面临巨大挑战——《中国脑卒中防治报告2018》概要[J].中国循环杂志,2019, 34(2):105-19.
[2] 王陇德,刘建民,杨弋,等.《中国脑卒中防治报告2017》概要[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志,2018,15(11):611-7.
[3] 孙海欣,王文志.中国60万人群脑血管病流行病学抽样调查报告[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志,2018,18(2):83-8.
[4] 吴林.缺血性脑卒中临床治疗研究现状与进展[J].医学理论与实践,2019,32(19):3065-6+47.
[5] HAN E, KIM TH, KOO H, et al. Heterogeneity in costs and prognosis for acute ischemic stroke treatment by comorbidities. J Neurol. 2019;266(6):1429-1438.
[6] PAN JW, YU XR, ZHOU SY, et al. Computed tomography perfusion and computed tomography angiography for prediction of clinical outcomes in ischemic stroke patients after thrombolysis. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(1):103-108.
[7] CAMARA-LEMARROY CR, IBARRA-YRUEGAS BE, GONGORA-RIVERA F. Gastrointestinal complications after ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci. 2014;346(1-2):20-25.
[8] STANLEY D, MASON LJ, MACKIN KE, et al. Translocation and dissemination of commensal bacteria in post-stroke infection. Nat Med. 2016;22(11):1277-1284.
[9] YAMASHIRO K, TANAKA R, URABE T, et al. Gut dysbiosis is associated with metabolism and systemic inflammation in patients with ischemic stroke. PloS one. 2017;12(2): e0171521.
[10] STANLEY D, MOORE RJ, WONG CHY. An insight into intestinal mucosal microbiota disruption after stroke. Scientific reports. 2018;8(1):568.
[11] VUONG HE, YANO JM, FUNG TC, et al. The Microbiome and Host Behavior.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2017;25;40:21-49.
[12] MALKKI H. Stroke: Gut microbiota influence stroke recovery in mice. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12(5):252.
[13] WINEK K, MEISEL A, DIRNAGL U. Gut microbiota impact on stroke outcome: Fad or fact?. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016;36(5):891-898.
[14] BENAKIS C, BREA D,CABALLERO S,et al. Commensal microbiota affects ischemic stroke outcome by regulating intestinal gammadelta T cells. Nat Med. 2016;22(5):516-23.
[15] AM M, WV G, JR T. Epithelial barriers in homeostasis and disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2010;5:119-144.
[16] 王尊松.尿毒症患者肠黏膜屏障功能的研究[D].济南:山东大学, 2011.
[17] NAGPAL R, YADAV H. Bacterial Translocation from the Gut to the Distant Organs: An Overview. Ann Nutr Metab. 2017;71 Suppl 1:11-16.
[18] HU CA, HOU Y, YI D,et al. Autophagy and tight junction proteins in the intestine and intestinal diseases. Anim Nutr. 2015,1(3):123-127.
[19] WANG Z, FAN J, WANG J, et al. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induces long-lasting cognitive deficits accompanied by long-term hippocampal silent synapses increase in rats. Behav Brain Res. 2016;301:243-252.
[20] 张棋,舒佳惠,欧阳梦琪,等.慢性脑低灌注致大鼠肠黏膜损伤及claudin-3表达变化的研究[J]. 西南国防医药, 2018,28(12): 1136-1138.
[21] JING Z, SHI C, ZHU L, et al. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induces vascular plasticity and hemodynamics but also neuronal degeneration and cognitive impairment. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015;35(8):1249-59.
[22] 王庆松,何婧.关注线粒体老化在缺血性脑损害中的作用[J].西部医学,2017,29(6):741-4+8.
[23] 欧阳梦琪,舒佳慧,张棋,等.辣椒素对慢性脑低灌注大鼠认知行为受损及海马线粒体-内质网结构偶联表达的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2019,35(8):1393-402.
[24] ZHU JD, WANG JJ, ZHANG XH, et al. Panax ginseng extract attenuates neuronal injury and cognitive deficits in rats with vascular dementia induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(4):664-672.
[25] 杜果,王建,王庆松,等.丝切蛋白棒状结构致慢性脑低灌注大鼠海马突触丢失[J].西部医学, 2017,29(6):758-62.
[26] 黄燕,何婧,向阳,等.慢性脑低灌注致大鼠持续性学习记忆受损及海马神经血管单元改变研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2018,40(17): 1-7.
[27] FOSTER JA, LYTE M, MEYER E,et al. Gut Microbiota and Brain Function: An Evolving Field in Neuroscience. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016;19(5). pii: pyv114.
[28] WEKERLE H. Brain Autoimmunity and Intestinal Microbiota: 100 Trillion Game Changers.Trends Immunol. 2017;38(7): 483-497.
[29] CASO JR, HURTADO O, PEREIRA MP,et al. Colonic bacterial translocation as a possible factor in stress-worsening experimental stroke outcome.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009;296(4):R979-85.
[30] AWAD WA, HESS C, HESS M. Enteric Pathogens and Their Toxin-Induced Disruption of the Intestinal Barrier through Alteration of Tight Junctions in Chickens.Toxins (Basel). 2017; 9(2). pii: E60.
[31] TASCILAR N, IRKORUCU O, TASCILAR O, et al. Bacterial translocation in experimental stroke: what happens to the gut barrier?. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2010;111(4):194-199.
[32] CHAMORRO A, MEISEL A, PLANAS AM, et al. The immunology of acute stroke. Nat Rev Neurol. 2012;8(7): 401-410.
[33] SHIM R, WONG CHY. Complex interplay of multiple biological systems that contribute to post-stroke infections. Brain Behav Immun. 2018;70:10-20.
[34] CAMARA-LEMARROY CR, ESCOBEDO-ZUNIGA N, GUZMAN-DE LA GARZA FJ, et al. D-Lactate and intestinal fatty acid-binding protein are elevated in serum in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Acta Neurol Belg. 2018. doi: 10.1007/s13760-018-0940-x.
[35] ROSENTHAL R, GUNZEL D, THEUNE D, et al. Water channels and barriers formed by claudins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017;1397(1):100-109.
[36] ROSENTHAL R, GUNZEL D, KRUG SM, et al. Claudin-2-mediated cation and water transport share a common pore. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2017;219(2):521-536.
[37] ISHIMOTO H, OSHIMA T, SEI H, et al. Claudin-2 expression is upregulated in the ileum of diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome patients. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2017;60(2): 146-50.
[38] LUETTIG J,ROSENTHAL R,BARMEYER C,et al.Claudin-2 as a mediator of leaky gut barrier during intestinal inflammation. Tissue Barriers. 2015;3(1-2):e977176.
[39] WANG Y, MUMM JB, HERBST R, et al. IL-22 Increases Permeability of Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junctions by Enhancing Claudin-2 Expression. J Immunol. 2017;199(9): 3316-3325.
[40] NIGHOT PK, HU CA, MA TY. Autophagy enhances intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier function by targeting claudin-2 protein degradation. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(11):7234-7246.
[41] 娄文静,刘冬妍.肠道紧密连接跨膜蛋白研究进展[J]. 实用药物与临床,2019,22(11):1214-9.
[42] 王庆治,张帮杰,王素娟,等.谷氨酰胺对大鼠急性全脑缺血再灌注损伤后小肠黏膜Occludin蛋白表达的影响[J].郑州大学学报(医学版). 2011,46(6):878-81.
[43] ZHANG QY, WANG ZJ, SUN DM,et al. Novel Therapeutic Effects of Leonurine On Ischemic Stroke: New Mechanisms of BBB Integrity. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:7150376.
[44] 张芯. 肠道菌群移位继发的单核细胞活化在实验性脑缺血/再灌注损伤中的作用及其干预研究[D].天津:天津医科大学; 2016.
[45] BISCHOFF SC, BARBARA G, BUURMAN W, et al. Intestinal permeability--a new target for disease prevention and therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014;14:189.
[46] RAHMAN MT, GHOSH C, HOSSAIN M,et al. IFN-gamma, IL-17A, or zonulin rapidly increase the permeability of the blood-brain and small intestinal epithelial barriers: Relevance for neuro-inflammatory diseases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;507(1-4):274-279.
|