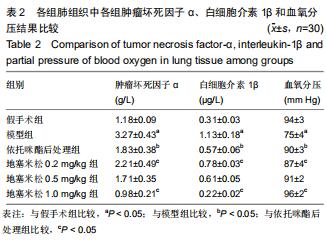
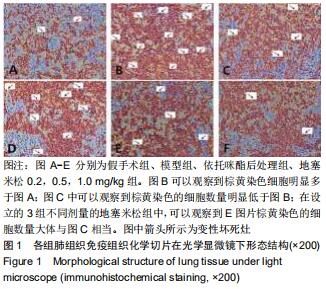
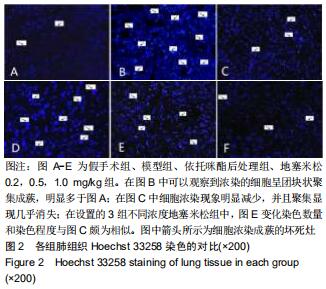
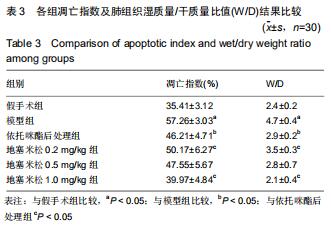
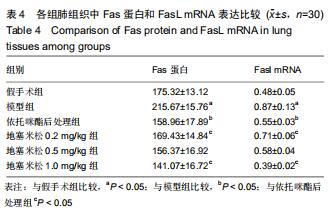
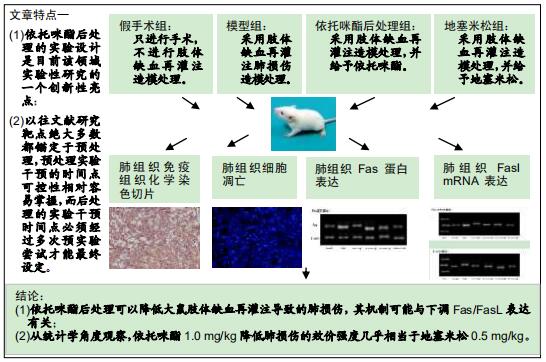
|
[1] 邹海波,孙晓峰.姜黄素后处理肢体缺血再灌注肾损伤模型大鼠基质金属蛋白酶9及基质金属蛋白酶组织抑制因子1平衡的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(23):3643-3648.
[2] 邹海波,孙晓峰.姜黄素后处理对大鼠肢体缺血再灌注肺损伤的影响[J].沈阳药科大学学报.2019.
[3] TSAROUCHA AK, VALSAMI G, KOSTOMITSOPOULOS N, et al. Silibinin Effect on Fas/FasL, HMGB1, and CD45 Expressions in a Rat Model Subjected to Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. J INVEST SURG. 2018;31(6):491-502.
[4] ZHU Y, YIN X. Overexpression of microRNA-204-5p alleviates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice through blockage of Fas/FasL pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2019;381(2):208-214.
[5] 邹海波,孙晓峰.姜黄素后处理对缺血再灌注肾损伤大鼠Notch2/Hes-1通路的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志,2019,29(19):17-22.
[6] 李丽萌,郑晓春,郑艇,等.肢体缺血预处理对大鼠肝缺血再灌注诱发肠损伤和脑损伤的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2018,38(1):105-109.
[7] ZOU HB, SUN XF. Post-treatment curcumin reduced ischemia- reperfusion-induced pulmonary injury via the Notch2/Hes-1 pathway. J Int Med Res. 2019.DOI: 10.1177/0300060519892432.
[8] ZHENG MX, SONG D, LUO ZY. Effect of puerarin on expression of Fas/FasL mRNA in pulmonary injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rabbits. Nat Prod Commun. 2015;10(2):252-256.
[9] 陈靖宜,柯昌斌,谢华.依托咪酯预处理对肺缺血再灌注损伤的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2016,25(12):1285-1287.
[10] 王建军,刘亚楠,王建辉,等.二乙酰胺三氮脒对肢体缺血再灌注模型小鼠肾损伤的保护作用及其机制[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2020,1:14-19.
[11] 武莉,曹定睿,刘臻.依托咪酯后处理对大鼠肝缺血再灌注肾细胞凋亡及Bcl-2和Bax表达的影响[J].中国药物与临床,2015,15(4):480-482.
[12] MCGRATH M, HOFMANN A, RAINES DE. Behavioral and steroidogenic pharmacology of phenyl ring substituted etomidate analogs in rats. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019;20:48.
[13] LIU X, SONG H, YANG J, et al. The etomidate analog ET-26 HCl retains superior myocardial performance: comparisons with etomidate in vivo and in vitro. PLoS One. 2018;13(1):1-13.
[14] NIIKAWA H, OKAMOTO T, AYYAT KS, et al. The protective effect of prone lung position on ischemia-reperfusion injury and lung function in an ex vivo porcine lung model. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019;157(1): 425-433.
[15] 邓红,高静,刘金碧,等.依托咪酯对大鼠肺缺血再灌注损伤时NF-kB活性的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2017,37(4):498-500.
[16] LEE B, LEE DG. Reactive oxygen species depletion by silibinin stimulates apoptosis-like death in escherichia coli. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017;27(12):12.
[17] 邓红,丁永永,彭捷.依托咪酯对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用及机制[J].华西药学杂志,2017,32(4):381-384.
[18] RATHORE VS, GUPTA S. A Comparative study of propofol, etomidate and 50% admixture of etomidate and propofol for induction in general anaesthesia. J Dent Med Sci. 2018. DOI: 10.9790/0853-1707124145.
[19] 李睿,张立民,罗星,等.依托咪酯后处理对大鼠缺氧缺糖一复糖复氧皮质神经元线粒体通透性转换孔的影响:与Robo受体的关系[J].中华麻醉学杂志, 2016,36(2):253-256.
[20] ZHAO XR, ZHANG Z, GAO M, et al. MicroRNA-27a-3p aggravates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by promoting oxidative stress via targeting growth factor receptor-bound protein 2. Pharmacol Res. 2020;18:104718.
[21] BISHT M, POKHRIYAL AS, KHURANA G, et al. Effect of Fentanyl and Nalbuphine for Prevention of Etomidate-Induced Myoclonus. Anesth Essays Res. 2019;13(1):119-125.
[22] MCGRATH M, MA C, RAINES DE. Dimethoxy-etomidate: a nonhypnotic etomidate analog that potently inhibits steroidogenesis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018;364(2):229-237.
[23] 张效云,宋桂芹,辇晓峰.阻断白介素-17对博来霉素诱导小鼠肺纤维化及肺组织Fas/FasL表达的影响[J].南京医科大学学报,2017,37(5):584-587.
[24] 杨迎春,王瑞芳,陈新骥,等.高血脂大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤后Bcl-2和Bax的表达变化及灯盏乙素的影响[J].解剖学报,2019,50(4):431-437.
[25] 张红健,宋杨,杨明.pEGFP-N1-IL-17通过调控Fas/FasL信号通路影响喉癌Hep-2细胞的凋亡[J].安徽医科大学学报,2019,54(11):1683-1687.
[26] ALCOVERRO-FORTUNY Ò, ALARCÓN BG, USAN FV, et al. Etomidate improves seizure adequacy during electroconvulsive therapy. Psychiatry Res. 2019;273:350-354.
[27] JANYOU A, WICHA P, SEECHAMNANTURAKIT V, et al. Dihydrocapsaicin-induced angiogenesis and improved functional recovery after cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in a rat model. J Pharmacol Sci. 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.jphs.2020.02.001.
[28] LEE JM, MIN G, LEE JM, et al. Efficacy and safety of etomidate– midazolam for screening colonoscopy in the elderly. Medicine. 2018; 97(20):e10635.
[29] 王振宇,彭红军,陈思,等.依托咪酯对老年冠心病患者非心脏手术中血流动力学及肌钙蛋白I和超敏C反应蛋白的影响[J].广东医学,2016,37(z1): 216-218.
[30] 李卫星,叶西就,韩海华.依托咪酯靶控输注复合瑞芬太尼诱导对中老年高血压患者血流动力学的影响及临床麻醉效果[J].北方药学,2016,13(9): 52.
[31] 张霖,耿庆,范涛,等.香草乙酮静注对大鼠肺缺血再灌注损伤的预防作用观察[J].山东医药,2020,3:30-33.
[32] 王继武,陈小珍,徐志强,等.核因子E2相关因子2信号通路对肺缺血再灌注损伤的保护机制[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019,36(8):1430-1432.
|