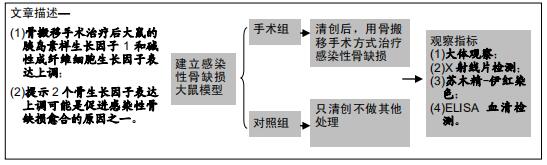
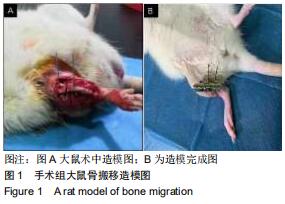
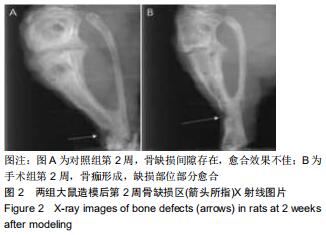
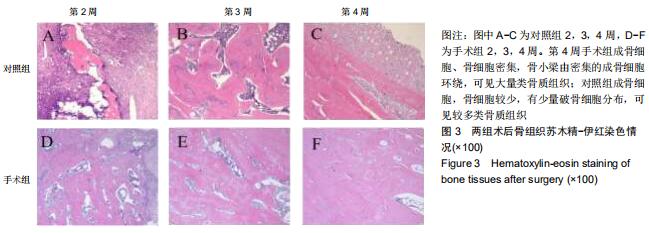
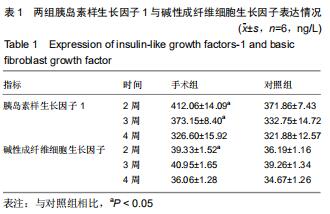
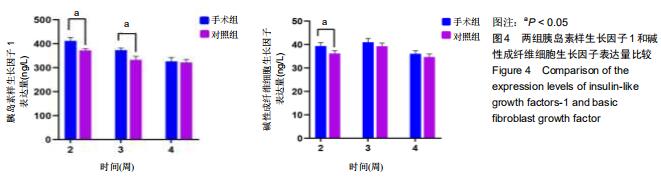
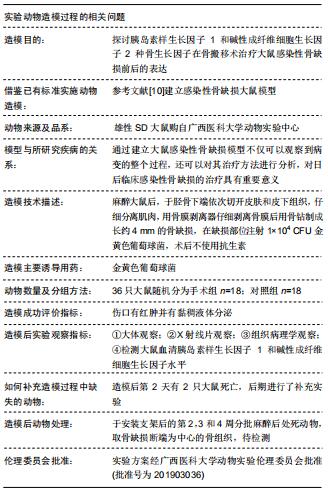
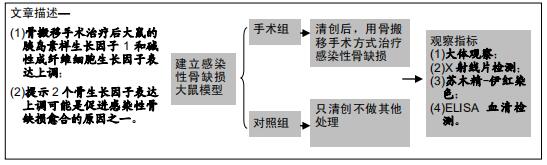
|
[1] PEARSON JJ, GERKEN N, BAE C, et al. In vivo hydroxyapatite scaffold performance in infected bone defects. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(3): 1157-1166.
[2] 叶焕竞.Ilizarov骨搬移术治疗胫骨骨髓炎伴长段缺损的疗效分析[J].双足与保健,2018,27(20):97-99.
[3] 张晨阳,贾桂,张广峰,等.骨搬移术治疗胫骨骨折术后大段骨缺损20例疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(4):372-374.
[4] IL'IN DA, ARKHIPOV SA, SHKURUPY VA. Analysis of IL-1α, bFGF, TGF-β1, IFNγ, MMP-1, and CatD Expression in Multinuclea Macrophages In Vitro.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2018; 164(4):456-458.
[5] YANG YH, FU XB, SUN TZ, et al. bFGF and TGFbeta expression in rat kidneys after ischemic/ reperfusional gut injury and its relationship with tissue repair. World J Gastroenterol. 2000;6(1):147-149.
[6] XUE P, WU X, ZHOU L, et al. IGF1 promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells derived from rat bone marrow by increasing TAZ expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;433(2):226-231.
[7] ZHANG Y, WANG Z, WANG Y, et al. A Novel Approach via Surface Modification of Degradable Polymers With Adhesive DOPA-IGF-1 for Neural Tissue Engineering. J Pharm Sci. 2019;108(1):551-562.
[8] 王晓波,郑欣,陈一心.感染性骨缺损动物模型的研究进展[J].医学综述,2015,21(7):1158-1161.
[9] PARK KH, CHO OH, JUNG M, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of hematogenous vertebral osteomyelitis caused by gram-negative bacteria.J Infect. 2014;69(1):42-50.
[10] CHEN X, TSUKAYAMA DT, KIDDER LS, et al. Characterization of a chronic infection in an internally-stabilized segmental defect in the rat femur. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(4):816-823.
[11] LINDSEY BA., CLOVIS NB, SMITH ES, et al. An animal model for open femur fracture and osteomyelitis: Part I. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(1):38-42.
[12] MASQUELET A, KANAKARIS NK, OBERT L, et al. Bone Repair Using the Masquelet Technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(11):1024-1036.
[13] LIU T, ZHANG X, LI Z, et al. Management of combined bone defect and limb-length discrepancy after tibial chronic osteomyelitis .Orthopedics. 2011;34(8):e363-367.
[14] 张松,张涛,童超,等.骨搬移技术治疗胫骨骨缺损及血清炎症因子的变化:X射线影像学评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(31): 5003-5008.
[15] KLIUSHIN NM, STEPANENKO P, MEKKI WA. Treatment of forearm diaphyseal defect by distraction compression bone transport and continued distraction for radial head reduction: A case study.Chin J Traumatol. 2019;22(5):304-307.
[16] CHEN X, ZHANG W, YU Z, et al. Application of bone transport with unilateral external fixator combined with locked plate internal fixation in treatment of infected tibial nonunion. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019;33(3): 328-331.
[17] GKIATAS I, LYKISSAS M, KOSTAS-AGNANTIS I,et al. Factors affecting bone growth.Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2015;44(2):61-67.
[18] 蔡立雄,骨延长临床应用与淫羊藿苷促进牵拉新骨形成的实验研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2014.
[19] 李沛,李钊伟,唐保明,等.富血小板血浆对促进骨折愈合的最新研究[J].青海医药杂志,2017,47(4):93-96.
[20] 王荣,贾爱华,刘新艳,等. IGF-1及其相关性因素对2型糖尿病并发骨质疏松的影响研究[J].陕西医学杂志,2019,48(9): 1163-1166.
[21] 朱勇,唐成芳,王峰,等.胰岛素样生长因子-1对骨质疏松大鼠种植体周围骨组织的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2017,37(1):44-46.
[22] 林洪明, 胰岛素样生长因子1对糖尿病大鼠伴骨折模型骨折愈合的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2017,37(18):4491-4493.
[23] LI JA, ZHAO CF, LI SJ, et al. Modified insulin-like growth factor 1 containing collagen-binding domain for nerve regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(2):298-303.
[24] MEINEL L, ZOIDIS E, ZAPF J, et al. Localized insulin-like growth factor I delivery to enhance new bone formation.Bone. 2003;33(4):660-672.
[25] ZHANG F, PENG WX, WANG L,et al. Role of FGF-2 Transfected Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Engineered Bone Tissue for Repair of Avascular Necrosis of Femoral Head in Rabbits.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(2): 773-784.
[26] 朱清,陈艳,龙大宏,等. NGF联合b-FGF对胚胎大鼠隔区来源神经干细胞分化为神经元的诱导作用[J].广东医学,2019,40(5): 636-641.
[27] 王远锏.bFGF:碱性成纤维细胞生长因子的研究现状与应用[J].科技创新与应用,2019(26):165-166.
[28] VALIZADEH A, MAJIDINIA M, SAMADI-KAFIL H, et al. The roles of signaling pathways in liver repair and regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2019 Feb 15.
[29] CANALIS E, CENTRELLA M, MCCARTHY T. Effects of basic fibroblast growth factor on bone formation in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1988;81(5):1572-1572.
[30] 李辉,刘汉辉,刘鹄,等. FGF生物蛋白海绵治疗骨缺损的临床研究[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2011,20(16):1978-1979.
[31] 方幸.运动介导肌肉因子IGF-1、FGF-2对小鼠骨的影响[D].上海:华东师范大学,2018.
[32] FENG R, MA X, MA J, et al. Positive effect of IGF-1 injection on gastrocnemius of rat during distraction osteogenesis. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(10):1424-1432.
[33] SCHUMACHER B, ALBRECHTSEN J, KELLER J, et al. Periosteal insulin-like growth factor I and bone formation. Changes during tibial lengthening in rabbits. Acta Orthop Scand. 1996;67(3):237-241.
|