中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (32): 5108-5113.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2856
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
人甲壳质酶蛋白40通过PI3K/Akt信号通路调控膝骨性关节炎兔软骨细胞的凋亡
田胜兰1,王国延1,杨 扬2
- 1武汉科技大学医院,湖北省武汉市 430065;2武汉科技大学临床学院,湖北省武汉市 430064
Mechanism of YKL-40 regulating apoptosis of rabbit osteoarthritis chondrocytes via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
Tian Shenglan1, Wang Guoyan1, Yang Yang2
- 1Wuhan University of Science and Technology Hospital, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China; 2School of Clinical Medicine, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430064, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
膝骨关节炎(knee osteoarthritis,KOA):常发生在中老年人群,其病理过程涉及软骨基质退行性病变、软骨细胞性状显著性改变和数量明显减少。在外力及内部环境改变等因素影响下,软骨细胞外基质、软骨细胞及软骨下骨的合成和降解动态平衡出现紊乱,软骨细胞大量凋亡使得软骨修复、重塑等稳定状态出现异常,上述情况均可诱导膝骨关节炎的发生。
人甲壳质酶蛋白40(YKL-40):是一种广泛存在于关节滑膜细胞、软骨细胞中的软骨糖蛋白,具有多种生物学功能作用:①促进软骨细胞、成骨细胞的增殖生长及分化;②促进新生血管组织的形成;③调控细胞外基质的重构过程;④协助细胞适应生长环境的显著性改变及缺氧等病理损伤,此外在软骨细胞凋亡方面也发挥一定作用。
背景:由于PI3K/Akt信号通路与骨组织生理代谢之间存在着密切的联系,而人甲壳质酶蛋白40(YKL-40)对乳腺癌发病机制中的PI3K/Akt信号通路具有一定调控作用,由此推测YKL-40可能通过PI3K/Akt信号通路对膝骨性关节炎软骨细胞凋亡进行调控。
目的:研究YKL-40通过PI3K/Akt信号通路调控膝骨性关节炎兔软骨细胞凋亡的作用机制。
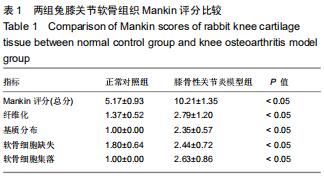
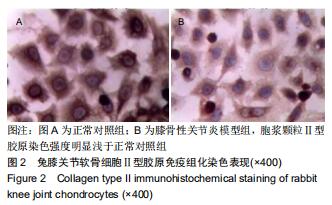
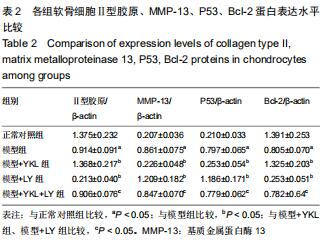
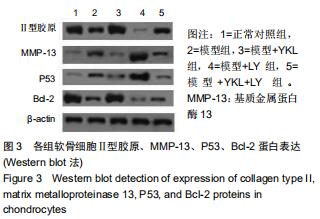
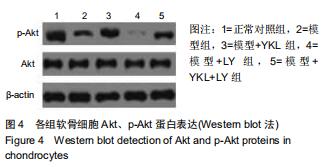
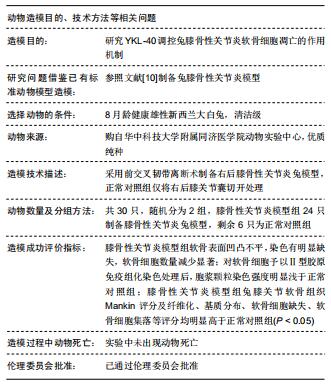
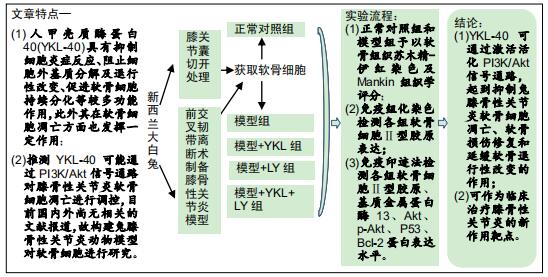
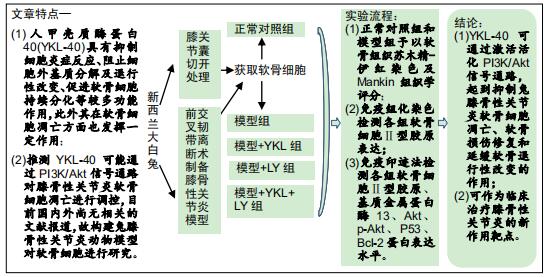
方法:①将新西兰大白兔随机分为2组,膝骨性关节炎模型组采用前交叉韧带离断术制作右后膝骨性关节炎动物模型,正常对照组仅切开右后膝关节囊,造模后第6周取材并分离软骨细胞,予以软骨组织苏木精-伊红染色及Mankin组织学评分,同时免疫组化染色检测软骨细胞Ⅱ型胶原表达;②正常对照组兔第2代软骨细胞为正常对照组;将膝骨性关节炎模型组兔第2代软骨细胞分为4组,模型组仅予以含体积分数10%胎牛血清的高糖DMEM培养基培养,模型+YKL组培养基中加入100 μg/L YKL-40干预,模型+LY组培养基中加入50 µmol/L PI3K通路抑制剂LY294002干预,模型+YKL+LY组:培养基中加入100 μg/L YKL-40和50 µmol/L LY294002干预,采用免疫印迹法检测各组软骨细胞Ⅱ型胶原、基质金属蛋白酶13、Akt、p-Akt、P53、Bcl-2蛋白表达水平。
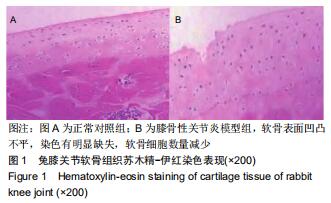
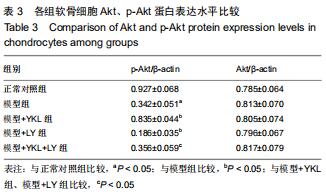
结果与结论:①经软骨组织苏木精-伊红染色、Mankin组织学评分及软骨细胞Ⅱ型胶原免疫组化染色证实,膝骨性关节炎动物模型构建和软骨细胞培养均获得成功;②模型组Ⅱ型胶原、Bcl-2、p-Akt蛋白表达明显低于正常对照组(P < 0.05),基质金属蛋白酶13、P53蛋白表达明显高于正常对照组(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,模型+YKL组上述指标得到明显改善(P < 0.05),而模型+LY组上述指标则进一步恶化(P < 0.05),模型+YKL+LY组上述指标与模型组比较无显著性差异(P > 0.05),但与模型+YKL组和模型+LY组比较有显著性差异(P < 0.05);各组Akt蛋白表达水平比较无显著性差异(P > 0.05)。提示:YKL-40可通过激活活化PI3K/Akt信号通路,起到抑制兔膝骨性关节炎软骨细胞凋亡,加快软骨损伤修复和延缓软骨退行性改变的作用,可作为临床治疗膝骨性关节炎的新作用靶点。
ORCID: 0000-0002-7889-445X(田胜兰)中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: