中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (32): 5085-5091.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2853
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 下一篇
髋部骨折2 342例流行病学分布特点的单中心分析
刘泽民,吕 欣,刘晋元,王小虎
- 山西医科大学第二医院骨科,山西省太原市 030001
Epidemiological distribution characteristics of 2 342 cases of hip fracture: a single center analysis
Liu Zemin, Lü Xin, Liu Jinyuan, Wang Xiaohu
- Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
髋部骨折:髋部骨折指发生在股骨近端的骨折,包括股骨颈骨折和股骨转子间骨折。髋部骨折占全身骨折的6.73%、股骨骨折的52.77%。股骨颈骨折约占全身骨折总数的3.58%,股骨转子间骨折约占全身骨折总数的3.4%。髋部骨折是最严重的骨质疏松性骨折。
回顾性研究:是以现在为结果,回溯过去的研究方法。这一研究方式由于条件限制较少,具有耗时短、成本低、较少引起伦理争议等优点,同时也具有资料有限、易产生选择偏倚和回忆偏倚等缺点。
背景:加强对髋部骨折危险人群的早期预防,可有效降低髋部骨折的发生风险。流行病学研究可为此类患者临床防治工作提供指导。
目的:回顾性分析山西医科大学第二医院2016-01-01/2018-12-31入院的髋部骨折患者流行病学分布特点。
方法:收集2 342例患者的年龄、性别、骨折类型、患者属地、受伤季节、致伤原因、手术方式、术中情况、血栓情况、住院时间、费用及入院至手术时间、体质量指数、合并症等信息,采用SPSS 26.0软件进行数据处理,分析髋部骨折的流行病学分布特点。
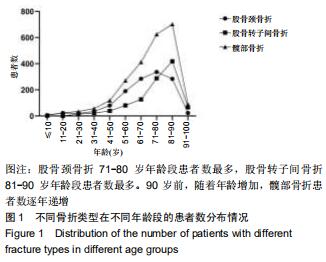
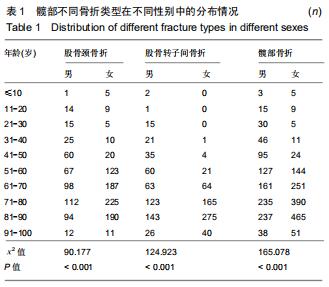
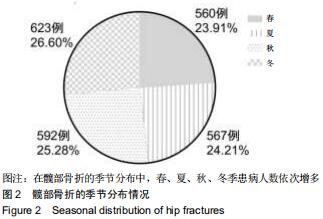
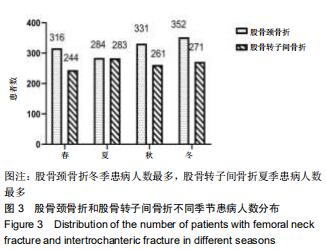
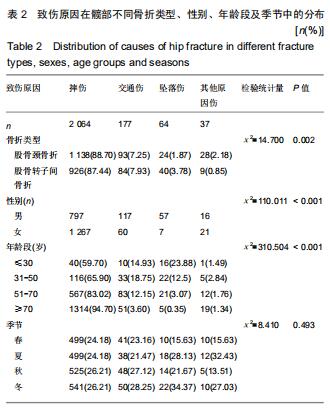
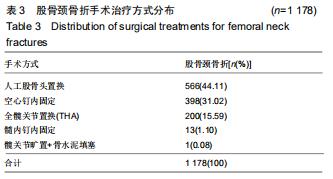
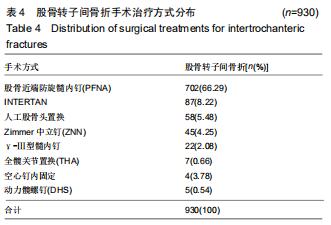
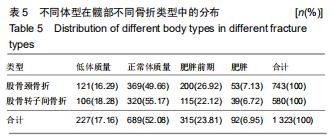
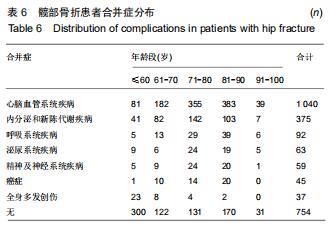
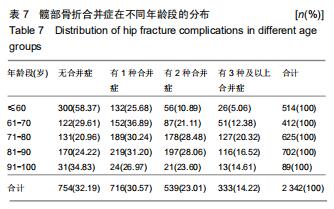
结果与结论:①髋部骨折患者平均年龄(73.90±13.43)岁,80-90岁组患者最多,占29.97%;②髋部骨折冬季多见,股骨颈和股骨转子间骨折季节分布差异具有统计学意义;③摔伤导致髋部骨折最多,占88.13%;④2 108例行手术治疗的髋部骨折患者中,股骨颈骨折主要选择髋关节置换术,占60.03%;股骨转子间骨折主要选择髓内固定,占92.04%;⑤2 097例行血管彩超检查的髋部骨折患者中,32.38%(679/2 097)的患者检查出下肢动静脉血栓,其中28.71%(195/679)的患者行下腔静脉滤器置入术;⑥髋部骨折患者平均住院时间(10.49±7.06)d,平均住院费用(4.63±3.14)万元;⑦股骨颈骨折平均平均住院费用,平均失血量、平均手术时长均比股骨转子间骨折少,差异有统计学意义;⑧股骨转子间骨折的患者比股骨颈骨折的患者整体偏瘦;⑨有44.41%髋部骨折患者合并心脑血管系统疾病;⑩结果提示,髋部骨折患者以老年人群为主,尤其是老年女性,随着年龄增加,股骨转子间骨折所占比例逐渐升高;摔倒是老年人髋部骨折的主要致伤原因。髋部骨折主要选择手术治疗,术前备血及围术期预防血栓形成可提高患者预后。
ORCID: 0000-0003-4810-9200(刘泽民)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: