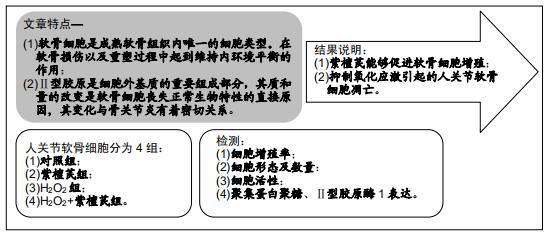
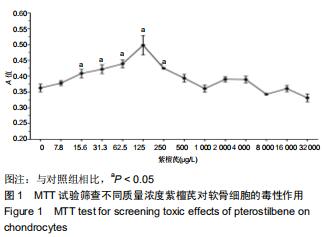
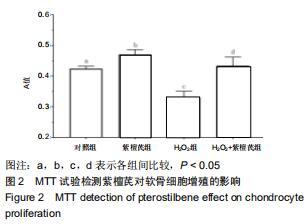
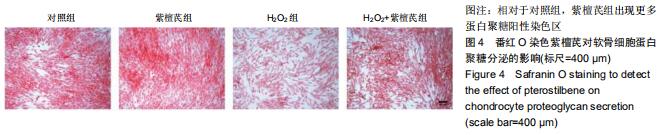
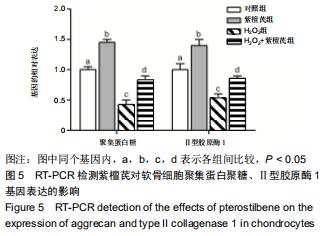
|
[1] SCHAAP LA, PEETERS GM, DENNISON EM, et al. European Project on OSteoArthritis (EPOSA): methodological challenges in harmonization of existing data from five European population-based cohorts on aging.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:272.
[2] MARTÍNEZ-PÉREZ B, DE LA TORRE-DÍEZ I, LÓPEZ-CORONADO M. Mobile health applications for the most prevalent conditions by the World Health Organization: review and analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2013;15(6):e120.
[3] AL FAQEH H, NOR HAMDAN BM, CHEN HC, et al. The potential of intra-articular injection of chondrogenic-induced bone marrow stem cells to retard the progression of osteoarthritis in a sheep model.Exp Gerontol. 2012;47(6):458-464.
[4] FENG K, CHEN Z, PENGCHENG L, et al. Quercetin attenuates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via SIRT1/AMPK-mediated inhibition of ER stress in rat chondrocytes and prevents the progression of osteoarthritis in a rat model.J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):18192-18205.
[5] CHARLIER E, RELIC B, DEROYER C, et al. Insights on Molecular Mechanisms of Chondrocytes Death in Osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12). pii: E2146.
[6] LEPETSOS P, PAPAVASSILIOU AG.ROS/oxidative stress signaling in osteoarthritis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1862(4):576-591.
[7] ZHAI Y, BEHERA J, TYAGI SC. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates homocysteine-induced osteoblast dysfunction by inhibiting mitochondrial toxicity.J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):18602-18614.
[8] YE W, ZHU S, LIAO C, et al. Advanced oxidation protein products induce apoptosis of human chondrocyte through reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2017;31(1):64-74.
[9] LI B, JIANG T, LIU H, et al. Andrographolide protects chondrocytes from oxidative stress injury by activation of the Keap1-Nrf2-Are signaling pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2018;234(1):561-571.
[10] BURGOS RA, HANCKE JL, BERTOGLIO JC, et al. Efficacy of an Andrographis paniculata composition for the relief of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms: a prospective randomized placebo-controlled trial. Clin Rheumatol. 2009;28(8):931-946.
[11] LAZZARONI M. Gastrointestinal side-effects of traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and new formulations.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004;20 Suppl 2:48-58.
[12] SCHNITZER TJ, BURMESTER GR, MYSLER E, et al. Comparison of lumiracoxib with naproxen and ibuprofen in the Therapeutic Arthritis Research and Gastrointestinal Event Trial (TARGET), reduction in ulcer complications: randomised controlled trial. Lancet.2004; 364(9435):665-674.
[13] SELLAM J. The role of synovitis in pathophysiology and clinical symptoms of osteoarthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6(11):625-635.
[14] ZENG L, WANG W, RONG XF, et al. Chondroprotective effects and multi-target mechanisms of Icariin in IL-1 beta-induced human SW 1353 chondrosarcoma cells and a rat osteoarthritis model.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014;18(1):175-181.
[15] 姚顺晗,廖亮,覃家港,等.罗汉果皂苷V刺激成骨细胞增殖与分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(29):4701-4706.
[16] MCCORMACK D, MCFADDEN D. Pterostilbene and cancer: current review.J Surg Res. 2012;173(2):e53-61.
[17] RUIZ MJ, FERNÁNDEZ M, PICÓ Y, et al. Dietary administration of high doses of pterostilbene and quercetin to mice is not toxic.J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57(8):3180-3186.
[18] MCCORMACK D, MCFADDEN D. A review of pterostilbene antioxidant activity and disease modification.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:575482.
[19] MAGILL P, BYRNE DP, BAKER JF. Review article: Osteochondral reconstruction and grafting.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2011;19(1):93-98.
[20] STEADMAN JR, BRIGGS KK, RODRIGO JJ, et al. Outcomes of microfracture for traumatic chondral defects of the knee: average 11-year follow-up.Arthroscopy. 2003;19(5):477-484.
[21] HASHIMOTO S, OCHS RL, KOMIYA S. Linkage of chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degradation in human osteoarthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41(9):1632-1638.
[22] ASADA S, FUKUDA K, NISHISAKA F, et al. Hydrogen peroxide induces apoptosis of chondrocytes; involvement of calcium ion and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase.Inflamm Res. 2001;50(1):19-23.
[23] MATSUSHITA T, FUKUDA K, YAMAZAKI K, et al. Hypoxia-induced nitric oxide protects chondrocytes from damage by hydrogen peroxide. Inflamm Res. 2004;53(8):344-350.
[24] SHIM JH, KIM KH, CHO YS, et al. Protective effect of oxidative stress in HaCaT keratinocytes expressing E7 oncogene. Amino Acids. 2008; 34(1):135-141.
[25] MOON D, MCCORMACK D, MCDONALD D. Pterostilbene induces mitochondrially derived apoptosis in breast cancer cells in vitro.J Surg Res. 2013;180(2):208-215.
[26] ZHANG L, ZHOU G, SONG W, et al. Pterostilbene protects vascular endothelial cells against oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo.Apoptosis. 2012;17(1):25-36.
[27] CHIOU YS, TSAI ML, NAGABHUSHANAM K, et al. Pterostilbene is more potent than resveratrol in preventing azoxymethane (AOM)-induced colon tumorigenesis via activation of the NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)-mediated antioxidant signaling pathwayJ Agric Food Chem. 2011;59(6):2725-2733.
[28] XUE EX, LIN JP, ZHANG Y, et al. Pterostilbene inhibits inflammation and ROS production in chondrocytes by activating Nrf2 pathway. Oncotarget.2017;8(26):41988-42000.
|