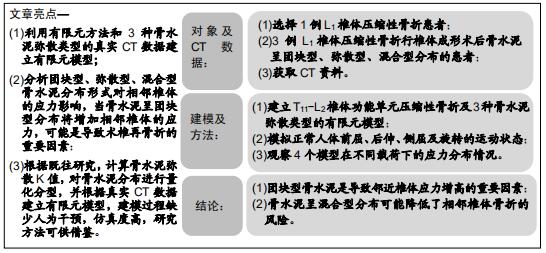
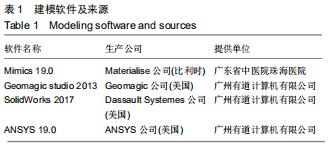
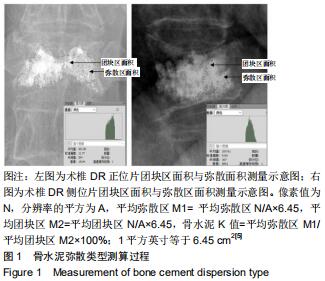
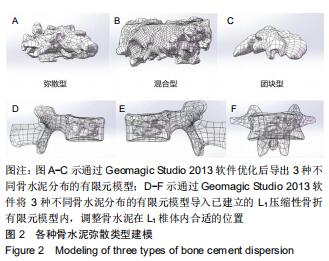
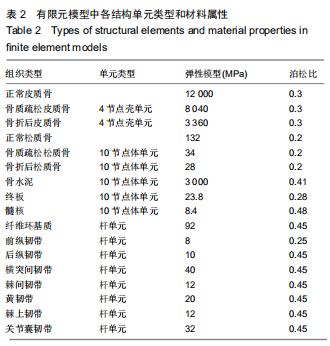
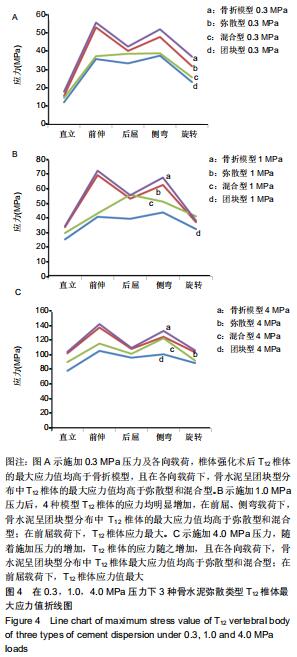
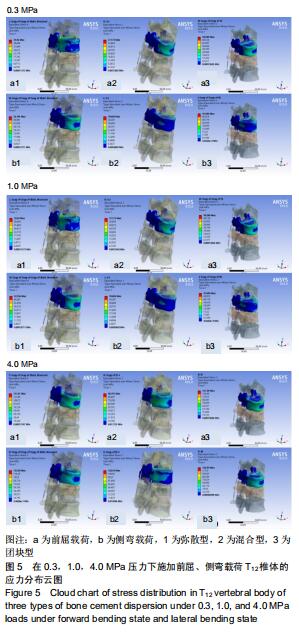
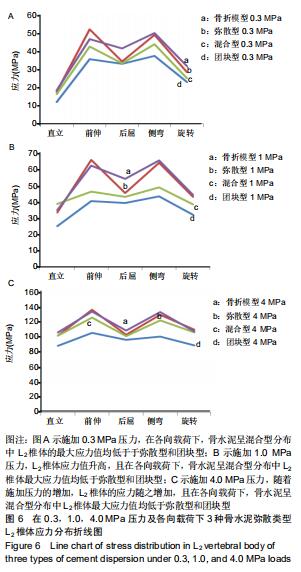
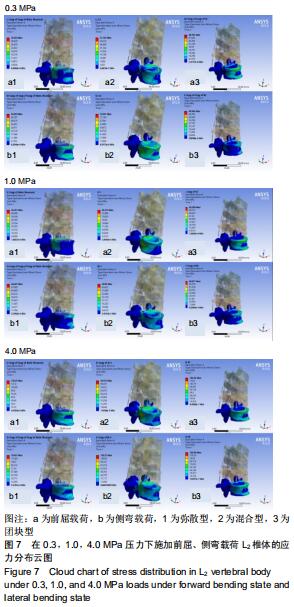
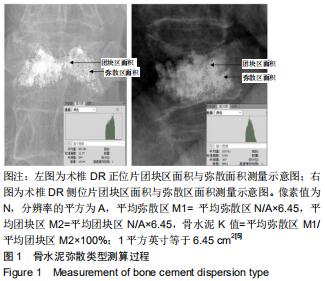
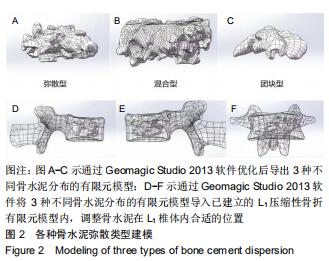
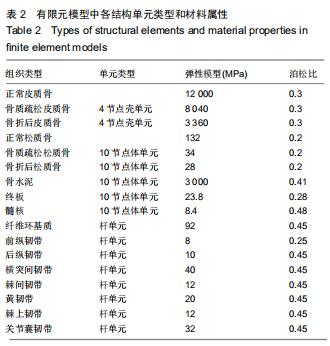
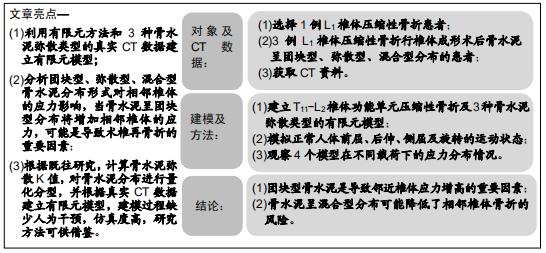
|
[1] STEVENSON M, GOMERSALLT, LLOYD JONES M, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: A systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol Assess. 2014;18(17):1-290.
[2] TSOUMAKIDOU G, TOO CW, KOCH G, et al. CIRSE guidelines on percutaneous vertebral augmentation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol.2017;40(3): 331-342.
[3] SEO DH, OH SH, YOON KW, et al. Risk factors of new adjacent compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty: effectiveness of bisphosphonate in osteoporotic or osteopenic elderly patients. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2014;10(2):86-91.
[4] ZHAI W, JIA Y, WANG J, et al. The clinical effect of percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of multiple osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures and the prevention of new vertebral fractures. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(8):13473-13481.
[5] SUN YC, TENG MM, YUAN WS, et al. Risk of post-vertebroplasty fracture in adjacent vertebral bodies appears correlated with the morphologic extent of bone cement. J Chin Med Assoc. 2011; 74(8):357-362.
[6] YI X, LU H, TIAN F, et al. Recompression in new levels after percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty compared with conservative treatment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(1): 21-30.
[7] HE X, LI H, MENG Y, et al. Percutaneousky- phoplasty evaluated by cement volume and distribution:an analysis of clinical data. Pain Physician. 2016;19(7):495- 506.
[8] CHO AR,CHO SB,LEE JH. Effect of augmentation material stiffness on adjacent vertebrae after osteoporotic vertebroplasty using finite element analysis with different loading methods. Pain Physician. 2015;18:E1101-1110.
[9] SCHULTE TL, KEILER A, RIECHELMANN F, et al. Biomechanical comparison of vertebral augmentation with silicone and PMMA cement and two filling grades. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(12): 2695-2701.
[10] LIEBSCHNER MAK, ROSENBERG WS, KEAVENY TM. Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness af- ter vertebroplasty. Spine. 2001;26(14): 1547-1554.
[11] 李飞虎,谢恩,郝定均,等.PVP术后相邻节段椎体应力分布的有限元分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(11):1135-1137.
[12] LIANG D, YE LQ, JIANG XB, et al. Biomechanical effects of cement distribution in the fractured area on osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Surg Res. 2015; 195(1):246-256.
[13] 谢亮.Photoshop像素法在计算地图面积中的应用[J].电脑知识与技术,2010,6(15):4021-4022.
[14] 赵永生,李强,历强,等.骨水泥弥散类型对治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的影响[J].中国骨伤,2017,30(5):446-452.
[15] 陈伟健,谢炜星等.胸腰段骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折有限元模型的建立[J].山东医药,2018,58(32):55-58.
[16] 费琦,李秋军,李东,等.椎体后凸成形术后骨水泥椎间盘渗漏对邻近节段力学影响的有限元分析[J].中华医学杂志, 2011,91(1):51-55.
[17] 徐建彪,张伟学,王鸿晨,等.骨水泥注入量对经皮椎体后凸成形术后相邻椎体应力影响的有限元分析[J].脊柱外科杂志,2017,15(3): 177-181.
[18] 刘仕友,路青林,郑伟,等.椎体后凸成形椎间盘骨水泥渗漏时行相邻椎体预防性强化的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(22): 4001-4005.
[19] BLIEMEL C, OBERKIRCHER L, BUECKING B, et al. Higher incidence of new vertebral fractures following percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty—fact or fiction? Acta Orthop Belg. 2012;78(2):220-229.
[20] BERLEMANN U, FERGUSON SJ, NOLTE LP, et al. Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty. A biomechanical investigation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(5): 748-752.
[21] BAROUD G, BOHNER M. Biomechanicalimpactof vertebroplasty. Postoperative biomechanics of vertebroplasty. Joint Bon Spine. 2006;73(2):144-150.
[22] HUANG TJ, KOU YH, YIN XF, et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of newly developed vertebral fractures after vertebral augmentation. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 2015;47(2): 237-241.
[23] QIN DA, SONG JF, WEI J, et al. Analysis of the reason of secondary fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteo- porotic vertebral compression fractures. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014;27(9): 730-733.
[24] NAGARAJA S, AWADA HK, DREHER ML, et al. Effects of verte- broplasty on endplate subsidence in elderly female spines. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;22(3): 273-282.
[25] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyze the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Ortho Scand. 1972;43: 301.
[26] 王吉博.有限元法评估经皮椎体成形和后凸成形治疗脊柱三明治骨折的生物力学变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(35):5703-5708.
[27] SHAMAMI DZ, KARIMI A, BEIGZADEH B, et al. A 3D finite element study for stress analysis in bone tissue around single implants with different materials and various bone qualities. J Biom Tissue Eng. 2014;4(8):632-637.
[28] 林娟颖,刘晓颖,邢立杰,等.基于有限元法的跟骨生物力学分析[J].医用生物力学,2018,33(1):37-41.
[29] 周伟,刘贵省,周丽萍,等.不同方式灌注骨水泥治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(14):2147-2152.
[30] 方驰华,周五一,黄立伟,等.虚拟中国人女性一号肝脏图像三维重建和虚拟手术的切割[J].中华外科杂志,2005,43(11):748-752.
[31] 刘文军,钟世镇.虚拟中国人女性一号松质骨图像数据的配准与三维重建[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2004,22(4):380-383.
[32] 张建国,芦俊鹏,阮世捷,等.以头部为例的人体有限元几何重建的方法初步探讨[J].微机计算机信息(管控一体化), 2006,22(22):249-252.
[33] 李家琼,王冬梅,孙璟川,等.骨水泥对椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松压缩性骨折的生物力学影响[J].医用生物力学,2018,33(1):6-12.
[34] BERLEMANN U, FERGUSON SJ, NOLTE LP, et al. Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty. A biomechanical investigation. J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 2002;84(5):748-752.
[35] 韦竑宇,谭明生,梁立.单侧多穿刺通道注射骨水泥法在骨质疏松椎体压缩骨折经皮椎体成形术中的应用[J].中国骨伤,2013,26(12):1010-1014.
[36] 吴钊钿,陈荣彬,李勇,等.骨水泥弥散类型与椎体成形术后再发术椎塌陷的相关性分析[J].中国医药导报,2018,15(27):6.
[37] 何奇龙,陈荣彬,李勇.骨水泥的弥散情况对经皮椎体成形的疗效影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2018,26(6):51-55.
[38] LIEBSCHNER MA, ROSENBERG WS, KEAVENY TM. Effects of bone ce- ment volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebro-plasty. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1547-1554.
|