中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (29): 4599-4604.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2785
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
基于网络药理学分析牛膝-桑寄生药对治疗骨关节炎的作用机制
黄泽灵1,何俊君1,2,施珊妮1,高弘建1,洪振强1,2
- 1福建中医药大学中医学院,福建省福州市 350122;2中医骨伤及运动康复教育部重点实验室,福建省福州市 350122
Mechanism of Achyranthes bidentata Bl.-Taxillus chinensis Danser in the treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology
Huang Zeling1, He Junjun1, 2, Shi Shanni1, Gao Hongjian1, Hong Zhenqiang1, 2
1School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China; 2Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Bone Trauma and Sports Rehabilitation, Ministry of Education, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
网络药理学:基于系统生物学的理论,对生物系统网络进行分析,从成分-靶点-通路进行整体预测及阐明药物在体内的作用机制。
骨关节炎:是以中年后可动关节的关节软骨退行性变和继发性骨质增生为特征的慢性关节疾病,以关节疼痛、活动受限和关节畸形为主要表现,又称退行性关节炎。
背景:牛膝-桑寄生是临床治疗骨关节炎最常用的药物组合,但其药理机制尚不明确。
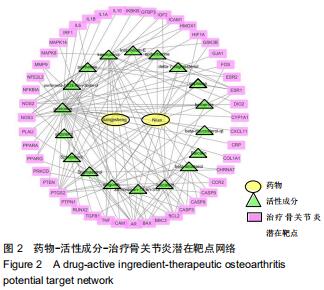
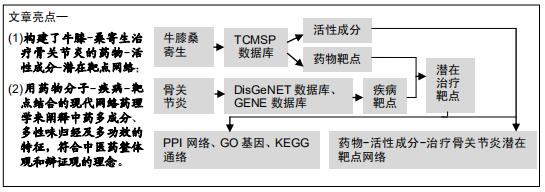
目的:基于网络药理学的方法,对牛膝-桑寄生的主要活性化学成分进行筛选,并收集化合物对应的靶点,构建药物-活性成分-治疗骨关节炎潜在靶点网络,对其治疗骨关节炎的药理作用机制进行系统阐述。
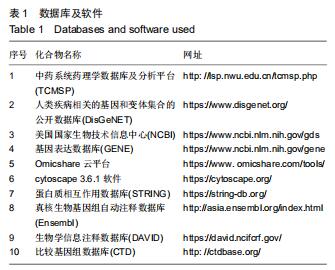
方法:利用TCMSP数据库获取牛膝-桑寄生药物活性成分及靶点,与DisGeNET和GENE数据库获取的骨关节炎疾病靶点映射,筛选出牛膝-桑寄生治疗骨关节炎的潜在靶点;利用String数据库和Cytoscape 3.6.1软件构建药物-活性成分-治疗骨关节炎潜在靶点网络及潜在靶点间的蛋白互作网络,同时通过Omicshare云平台和DAVID数据库分析潜在靶点的GO生物学功能和KEGG通路富集分析。
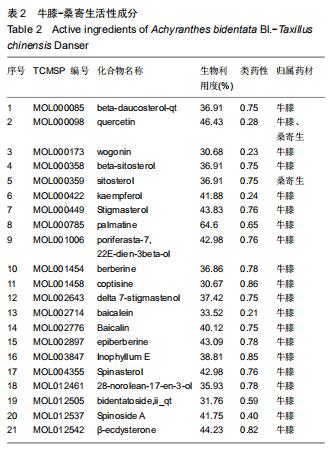
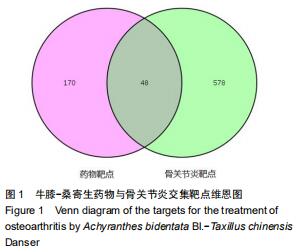
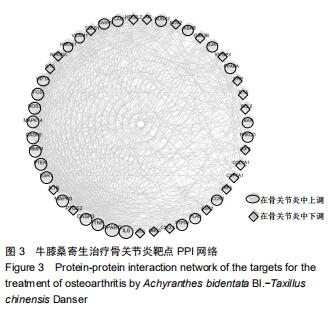
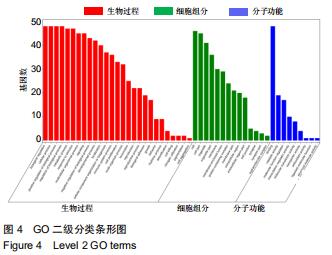
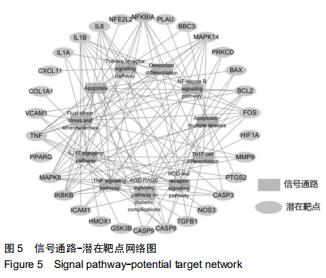
结果与结论:①从牛膝-桑寄生中共筛选出了21个活性成分及48个防治骨关节炎的潜在靶点;②GO富集分析共获取1 970个GO条目,其中生物过程1 862个,细胞组分占29个,分子功能79个(P < 0.01);③KEGG通路富集分析筛选出了76条牛膝-桑寄生防治骨关节炎的潜在信号通路(P < 0.01);④表明牛膝-桑寄生通过作用于多个靶点,影响不同的代谢通路,相互作用、相互协调,从而起到对骨关节炎的防治作用;⑤初步阐述了牛膝-桑寄生通过多成分-多靶点-多通路防治骨关节炎的作用机制,为骨关节炎的防治提供了新的思路与线索。
ORCID: 0000-0002-2014-9844(黄泽灵)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: