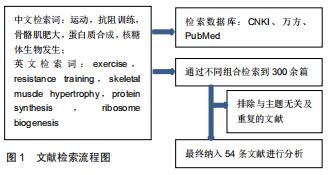
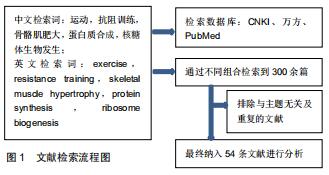
|
[1] 刘晓光,陈佩杰,肖卫华.骨骼肌肥大的生物学机制与诱导策略研究进展[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2018,37(10):869-878
[2] KIM HG, GUO B, NADER GA. Regulation of Ribosome Biogenesis During Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2019;47(2): 91-97.
[3] CHAILLOU T. Ribosome specialization and its potential role in the control of protein translation and skeletal muscle size. J Appl Physiol. 1985;2019; 127(2):599-607.
[4] FIGUEIREDO VC, MCCARTHY JJ. Regulation of ribosome biogenesis in skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Physiology (Bethesda). 2019; 34(1):30-42.
[5] FIGUEIREDO VC. Revisiting the roles of protein synthesis during skeletal muscle hypertrophy induced by exercise. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2019;317(5):R709-R718.
[6] WEN Y, ALIMOV AP, MCCARTHY JJ. Ribosome biogenesis is necessary for skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2016; 44(3):110-115.
[7] VON WALDEN F. Ribosome biogenesis in skeletal muscle: coordination of transcription and translation. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;127(2):591-598.
[8] VON WALDEN F, LIU C, AURIGEMMA N, et al. mTOR signaling regulates myotube hypertrophy by modulating protein synthesis, rDNA transcription, and chromatin remodeling. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016; 311(4):C663-672.
[9] NADER GA, MCLOUGHLIN TJ, ESSER KA, et al. mTOR function in skeletal muscle hypertrophy: increased ribosomal RNA via cell cycle regulators. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2005; 289(6):C1457-1465.
[10] STEC MJ, KELLY NA, MANY GM, et al. Ribosome biogenesis may augment resistance training-induced myofiber hypertrophy and is required for myotube growth in vitro. Am. J. Physiol.Endocrinol. Metab. 2016; 310(8):E652-661.
[11] VON WALDEN F, CASAGRANDE V, OSTLUND FARRANTS AK, et al. Mechanical loading induces the expression of a Pol I regulon at the onset of skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2012; 302(10):C1523-1530.
[12] MIYAZAKI M, MCCARTHY JJ, FEDELE MJ, et al. Early activation of mTORC1 signalling in response to mechanical overload is independent of phosphoinositide 3--kinase/Akt signalling. J Physiol 2011; 589(Pt 7):1831-1846.
[13] NADER GA, VON WALDEN F, LIU C, et al. Resistance exercise training modulates acute gene expression during human skeletal muscle hypertrophy. J Appl Physiol. 2014; 116(6):693-702.
[14] REIDY PT, BORACK MS, MARKOFSKI MM, et al. Post-absorptive muscle proteinturnover affects resistance training hypertrophy. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2017;117(5):853-866.
[15] NAKADA S, OGASAWARA R, KAWADA S, et al. Correlation between ribosome biogenesis and the magnitude of hypertrophy in overloadedskeletal muscle. PLoS One. 2016; 11(1):e0147284.
[16] MOBLEY CB, MUMFORD PW, KEPHART WC, et al. Aging in rats differentially affects markers of transcriptional and translational capacity in soleus and plantaris muscle. Front Physiol. 2017; 8:518.
[17] STEC MJ, MAYHEW DL, BAMMAN MM. The effects of age and resistance loading on skeletal muscle ribosome biogenesis. J Appl Physiol. 2015; 119(8):851-857.
[18] BROOK MS, WILKINSON DJ, MITCHELL WK, et al. Skeletal muscle hypertrophy adaptations predominate in the early stages of resistance exercise training, matching deuterium oxide-derived measures of muscle protein synthesis and mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 signaling. FASEB J. 2015; 29(11):4485-4496.
[19] 关尚一,张少生,卢健. mTOR/p70s6k通路与运动诱导的肌肉蛋白质合成[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(24):4738-4741.
[20] IADEVAIA V, HUO Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Roles of the mammalian target of rapamycin, mTOR, in controlling ribosome biogenesis and protein synthesis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012;40:168-172.
[21] MAYER C, ZHAO J, YUAN X, et al. MTOR-dependent activation of the transcription factor TIF-IA links rRNA synthesis to nutrient availability. Genes Dev. 2004; 18:423-434.
[22] TSANG CK, LIU H, ZHENG XF. MTOR binds to the promoters of RNA polymerase I- and III-transcribed genes. Cell Cycle. 2010;9:953-957.
[23] HANNAN KM, BRANDENBURGER Y, JENKINS A, et al. MTOR-dependent regulation of ribosomal gene transcription requires S6K1 and is mediated by phosphorylation of the carboxy-terminal activation domain of the nucleolar transcription factor UBF. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:8862-8877.
[24] KANTIDAKIS T, RAMSBOTTOM BA, BIRCH JL, et al. MTOR associates with TFIIIC, is found at tRNA and 5S rRNA genes, and targets their repressor Maf1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107: 11823-11828.
[25] STEFANOVSKY VY, LANGLOIS F, BAZETT-JONES D, et al. ERK modulates DNA bending and enhancesome structure by phosphorylating HMG1-boxes 1 and 2 of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor UBF. Biochemistry. 2006;45:3626-3634.
[26] ZHAO J, YUAN X, FRÖDIN M, et al. ERK-dependent phosphorylation of the transcription initiation factor TIF-IA is required for RNA polymerase I transcription and cell growth. Mol Cell. 2003; 11:405-413.
[27] VOIT R, GRUMMT I. Phosphorylation of UBF at serine 388 is required for interaction with RNA polymerase I and activation of rDNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98: 13631-13636.
[28] VOIT R, HOFFMANN M, GRUMMT I. Phosphorylation by G1-specific cdk-cyclin complexes activates the nucleolar transcription factor UBF. EMBO J. 1999; 18:1891-1899.
[29] ARABI A, WU S, RIDDERSTRÅLE K, et al. c-Myc associates with ribosomal DNA and activates RNA polymerase I transcription. Nat Cell Biol. 2005; 7:303-310.
[30] ZELLER KI, ZHAO X, LEE CW, et al. Global mapping of c-Myc binding sites and target gene networks in human B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:17834-17839.
[31] VAN RIGGELEN J, YETIL A, FELSHER DW. MYC as a regulator of ribosome biogenesis and protein synthesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010; 10:301-309.
[32] KIM S, LI Q, DANG CV, et al. Induction of ribosomal genes and hepatocytehypertrophy by adenovirus-mediated expression of c-Myc in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000,97:11198-11202.
[33] WU CH, SAHOO D, ARVANITIS C, et al. Combined analysis of murine and human microarrays and ChIP analysis reveals genes associated with the abilityof MYC to maintain tumorigenesis. PLoS Genet. 2008;4: e1000090.
[34] CHAILLOU T, KIRBY TJ, MCCARTHY J, et al. Ribosome Biogenesis: Emerging Evidence for a Central Role in the Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Mass. J Cell Physiol. 2014;229(11):1584-1594.
[35] KIRBY TJ, LEE JD, ENGLAND JH, et al. Blunted hypertrophic response in aged skeletal muscle is associated with decreased ribosome biogenesis. J Appl Physiol. 2015;119: 321-327.
[36] KIRBY TJ, PATEL RM, MCCLINTOCK TS, et al. Myonuclear transcription is responsive to mechanical load and DNA content but uncoupled from cell size during hypertrophy. Mol Biol Cell. 2016; 27: 788-798.
[37] FYFE JJ, BISHOP DJ, BARTLETT JD, et al. Enhanced skeletal muscle ribosome biogenesis, yet attenuated mTORC1 and ribosome biogenesisrelated signalling, following shortterm concurrent versus single mode resistance training. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):560.
[38] FIGUEIREDO VC, CALDOW MK, MASSIE V, et al. Ribosome biogenesis adaptation in resistance training-induced human skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015;309: E72-E83.
[39] FIGUEIREDO VC, ROBERTS LA, MARKWORTH JF, et al. Impact of resistance exercise on ribosome biogenesis is acutely regulated by post-exercise recovery strategies. Physiol Rep. 2016; 4: e12670.
[40] MOBLEY CB, HAUN CT, ROBERSON PA, et al. Biomarkers associated with low, moderate, and high vastus lateralis muscle hypertrophy following 12 weeks of resistance training. PLoS One. 2018;13: e0195203.
[41] OGASAWARA R, FUJITA S, HORNBERGER TA, et al. The role of mTOR signalling in the regulation of skeletal muscle mass in a rodent model of resistance exercise. Sci Rep. 2016; 6: 31142.
[42] BROOK MS, WILKINSON DJ, MITCHELL WK, et al. Synchronous deficits in cumulative muscle protein synthesis and ribosomal biogenesis underlie age-related anabolic resistance to exercise in humans. J Physiol. 2016; 594: 7399-7417.
[43] REIDY PT, BORACK MS, MARKOFSKI MM, et al. Post-absorptive muscle protein turnover affects resistance training hypertrophy. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2017; 117: 853-866.
[44] WEST DWD, BAEHR LM, MARCOTTE GR, et al. Acute resistance exercise activates rapamycin-sensitive and -insensitive mechanisms that control translational activity and capacity in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 2016; 594:453-468.
[45] SIELJACKS P, WANG J, GROENNEBAEK T, et al. Six Weeks of Low-Load Blood Flow Restricted and High-Load Resistance Exercise Training Produce Similar Increases in Cumulative Myofibrillar Protein Synthesis and Ribosomal Biogenesis in Healthy Males. Front Physiol. 2019;10:649.
[46] BROOK MS, WILKINSON DJ, MITCHELL WK, et al. A novel D 2 O tracer method to quantify RNA turnover as a biomarker of de novo ribosomal biogenesis, in vitro, in animal models, and in human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Metab. 2017;313: E681-E689.
[47] MORO T, BRIGHTWELL CR, DEER RR, et al. Muscle protein anabolic resistance to essential amino acids does not occur in healthy older adults before or after resistance exercise training. J Nutr. 2018;148: 900-909.
[48] KIM PL, STARON RS, PHILLIPS SM. Fasted-state skeletal muscle protein synthesis after resistance exercise is altered with training. J Physiol. 2005;568: 283-293.
[49] PHILLIPS SM, PARISE G, ROY BD, et al. Resistance training-induced adaptations in skeletal muscle protein turnover in the fed state. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2002; 80: 1045-1053.
[50] WILKINSON SB, PHILLIPS SM, ATHERTON PJ, et al. Differential effects of resistance and endurance exercise in the fed state on signalling molecule phosphorylation and protein synthesis in human muscle. J Physiol. 2008;586: 3701-3717.
[51] HAUN CT, VANN CG, MOBLEY CB, et al. Pre-training skeletal muscle fiber size and predominant fiber type best predict hypertrophic responses to 6 weeks of resistance training in previously trained young men. Front Physiol. 2019;10:297.
[52] 赵燕,尚画雨. 肌肉肥大与萎缩的基础科学研究进展———基于第 65 届美国运动医学会年会报告综述[J]. 北京体育大学学报, 2018,41(8): 66-71.
[53] ROMERO MA, MOBLEY CB, LINDEN MA, et al. Endurance training lowers ribosome density despite increasing ribosome biogenesis markers in rodent skeletal muscle. BMC Res Notes. 2019;10(1):399
[54] HAMMARSTRÖM D, ØFSTENG S, KOLL L, et al. Benefits of higher resistance-training volume are related to ribosome biogenesis. J Physiol. 2020;598(3):543-565.
|