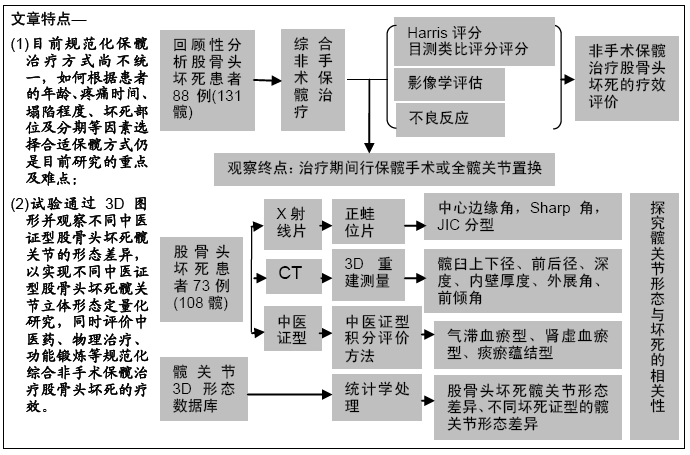
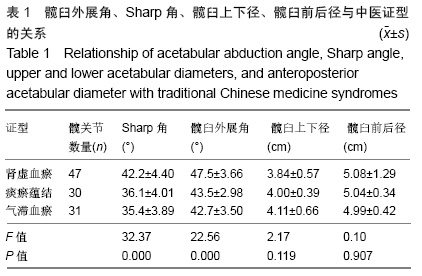
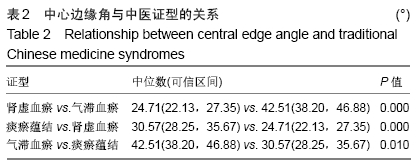
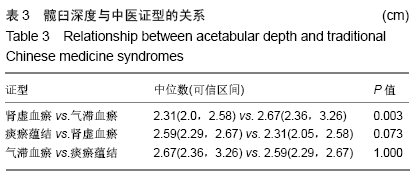
[1] WANG XS, ZHUANG QY, WENG XS, et al. Etiological and clinical analysis of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Chinese patients.Chin Med J (Engl).2013;126(2):290-295.
[2] MONT MA, ZYWIEL MG, MARKER DR, et al. The natural history of untreated asymptomatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a systematic literature review.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(12): 2165-2170.
[3] FUKUSHIMA W, FUJIOKA M, KUBO T, et al. Nationwide epidemiologic survey of idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2010;468(10):2715-2724.
[4] KANG JS, PARK S, SONG JH, et al. Prevalence of osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a nationwide epidemiologic analysis in Korea.J Arthroplasty.2009;24(8):1178-1183.
[5] CHOI HR, STEINBERG ME, CHENG E. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: diagnosis and classification systems.Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med.2015;8(3):210-220.
[6] 王炳德.高位股骨头颈开窗植骨支撑术治疗早期股骨头坏死患者的疗效观察[J].中国民康医学,2015,27(18):54-55.
[7] SUN W, LI ZR, WANG BL, et al. Relationship between preservation of the lateral pillar and collapse of the femoral head in patients with osteonecrosis.Orthopedics.2014;37(1):e24-e28.
[8] 李锐博,黄强,杨静,等.成人非创伤性股骨头坏死与髋关节发育不良相关性的影像学研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2016,5(7):511-515.
[9] 曾子全.不同证型非创伤性股骨头坏死新月征与疼痛相关性研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2014.
[10] MONT MA, CHERIAN JJ, SIERRA RJ, et al. Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today? A Ten-Year Update.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2015;97(19):1604-1627.
[11] 刘晓琳,盛加根,张长青,等.单侧供体吻合血管游离腓骨移植治疗双侧股骨头缺血性坏死[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(6):641-645.
[12] IIDA S, HARADA Y, SHIMIZU K, et al. Correlation between bone marrow edema and collapse of the femoral head in steroid-induced osteonecrosis.AJR Am J Roentgenol.2000;174(3):735-743.
[13] 魏秋实,何伟,邓伟民,等.股骨头坏死中医证型与影像学特点的关联性研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(4):304-306.
[14] 于潼,谢利民,吴飚,等.股骨头坏死不同中医证型MRI信号分布差异研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2013,33(12):1617-1620.
[15] 李黔春,江中潮.发育性髋关节发育不良早期诊断的研究进展[J].岭南现代临床外科,2017,17(4):494-497.
[16] 唐涛,苟远涛,唐俊,等.成都地区成人股骨头坏死流行病学研究[J].中国康复理论与实践,2018,24(8):970-974.
[17] CUI L, ZHUANG Q, LIN J, et al. Multicentric epidemiologic study on six thousand three hundred and ninety five cases of femoral head osteonecrosis in China.Int Orthop. 2016;40(2):267-276.
[18] HIRAHARA K, KANO Y, ASANO Y, et al. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head in a patient with Henoch-Schonlein purpura and drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome treated with corticosteroids.Acta Derm Venereol.2013;93(1):85-86.
[19] YEH CH, CHANG JK, WANG YH, et al. Ethanol may suppress Wnt/beta-catenin signaling on human bone marrow stroma cells: a preliminary study.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2008;466(5):1047-1053.
[20] WEINSTEIN RS, CHEN JR, POWERS CC, et al. Promotion of osteoclast survival and antagonism of bisphosphonate-induced osteoclast apoptosis by glucocorticoids.J Clin Invest.2002;109(8):1041-1048.
[21] BEJAR J, PELED E, BOSS JH. Vasculature deprivation--induced osteonecrosis of the rat femoral head as a model for therapeutic trials. Theor Biol Med Model.2005;2:24.
[22] TAKETA M, FUJII T, KUBOTA H, et al. Correlation between centeredge angle and acetabulum-head index in developmental dysplasia of the hip with avascular necrosis of the femoral head.Pediatr Orthop B. 2003; 12(3):215-218.
[23] 李锐博,黄强,杨静,等.成人非创伤性股骨头坏死与髋关节发育不良相关性的影像学研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2016,5(7):511-515.
[24] TAKETA M, FUJII T, KUBOTA H, et al. Correlation between center-edge angle and acetabulum-head index in developmental dysplasia of the hip with avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Pediatr Orthop B.2003;12(3):215-218.
[25] RUSSELL ME, SHIVANNA KH, GROSLAND NM, et al. Cartilage contact pressure elevations in dysplastic hips: a chronic overload model.J Orthop Surg Res.2006;1:6.
[26] 何伟,李勇,张庆文,等.股骨头坏死保髋手术的疗效评估[C].中华中医药学会骨伤分会第四届第三次学术年会暨国家中医药管理局“十一五”重点专科(专病)建设骨伤协作组经验交流会,中国浙江富阳,2008.
[27] WINGSTRAND H, WINGSTRAND A. Biomechanics of the hip joint capsule-a mathematical model and clinical implications.Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon).1997;12(5):273-280.
[28] 魏秋实,何伟,张庆文,等.股骨头坏死中医证型分布规律的文献研究和系统评价[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2013,7(3):369-372.
[29] 刘少军,王海彬,袁浩.生脉成骨胶囊对骨髓微循环损害的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2002,10(2):36-39.
[30] MASSARI L, FINI M, CADOSSI R, et al. Biophysical stimulation with pulsed electromagnetic fields in osteonecrosis of the femoral head.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2006;88 Suppl 3:56-60.
[31] ZHANG Q, LIU L, SUN W, et al. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in osteonecrosis of femoral head: A systematic review of now available clinical evidences.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(4):e5897.
[32] 陈思凯,邢金明,张蕾蕾.中药熏洗配合理筋手法治疗髋关节滑膜炎临床观察[J].风湿病与关节炎,2016,5(5):18-20.
[33] 梅全喜.中药熏蒸疗法的养生保健作用[J].中华养生保健, 2012(5):46-47.
[34] 姜淑云,褚立希,查建林,等.理筋手法结合功能训练治疗膝骨关节炎的步态特征研究[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2011,26(11):1056-1059.
|