[1] 曹谊林.组织工程学理论与实践[M].上海:上海科技出版社,2004.
[2] VIJAYAVENKATARAMAN S, LU WF, FUH JY. 3D bioprinting of skin: a state-of-the-art review on modelling, materials, and processes. Biofabrication.2016;8(3):032001.
[3] 刘多静,刘长勇,徐圆圆,等.胶原支架在组织工程角膜中的研究进展[J].生物医学工程与临床,2014,18(3):291-295.
[4] O'CONNELL G, GARCIA J, AMIR J. 3D Bioprinting: New directions in articular cartilage tissue engineering.Acs Biomater-Sci Eng. 2017; 3(11):550-587.
[5] LEE A, HUDSON AR, SHIWARSKI DJ, et al. 3D bioprinting of collagen to rebuild components of the human heart.Science. 2019;365(6452): 482-487.
[6] MALDA J, KLEIN TJ, UPTON Z. The roles of hypoxia in the in vitro engineering of tissues.Tissue Eng.2007;13(9):2153-2162.
[7] MOON JJ, WEST JL. Vascularization of engineered tissues: approaches to promote angio-genesis in biomaterials.Curr Top Med Chem.2008;8(4):300-310.
[8] BAE H, PURANIK AS, GAUVIN R, et al. Building vascular networks. Sci Transl Med.2012;4(160):123-160.
[9] KOLESKY DB, TRUBY RL, GLADMAN AS, et al. 3D bioprinting of vascularized, heterogeneous cell-laden tissue constructs.Adv Mater. 2014;26(19):3124-3130.
[10] MATTHYS OB, HOOKWAY TA, MCDEVITT TC. Design principles for engineering of tissues from human pluripotent stem cells.Stem Cell Rep.2016;2(1):43-51.
[11] KOLESKY DB, HOMAN KA, SKYLAR-SCOTT MA, et al. Three-dimensional bioprinting of thick vascularized tissues.P Natl Acad Sci USA.2016;113(12):3179-3184.
[12] LEE J, LEE S, LEE B, et al. Fabrication of Microchannels and Evaluation of Guided Vascularization in Biomimetic Hydrogels.J Tissue Eng Regen M.2018;15(4):403-413.
[13] ZHANG Y, YU Y, CHEN H, et al. Characterization of printable cellular micro-fluidic channels for tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2013; 5(2):25004-25015.
[14] WANG X, LI X, DAI X, et al. Coaxial extrusion bioprinted shell-core hydrogel microfibers mimic glioma microenvironment and enhance the drug resistance of cancer cells.Colloid Surface B. 2018;171(1):291-299.
[15] GAO Q, HE Y, FU JZ, et al. Coaxial nozzle-assisted 3D bioprinting with built-in microchannels for nutrients delivery. Biomaterials. 2015;61(1): 203-215.
[16] KIM G, AHN S, KIM Y, et al. Coaxial structured collagen-alginate scaffolds: fabrication, physical properties, and biomedical application for skin tissue regeneration.J Mater Chem A.2011;21(17):6165-6172.
[17] DAI X, LIU L, OUYANG J, et al. Coaxial 3D bioprinting of self-assembled multicellular heterogeneous tumor fibers.Sci Rep-UK. 2017;7(1):1457-1468.
[18] ROWLEY J, MADLAMBAYAN GD. Alginate hydrogels as synthetic extracellular matrix materials. Biomaterials.1999;20(1):45-53.
[19] MOON JJ, SAIK JE, POCHÉ RA, et al. Biomimetic hydrogels with pro-angiogenic properties. Biomaterials.2010;31(14):3840-3847.
[20] COLOSI C, SHIN SR, MANOHARAN V, et al. Microfluidic bioprinting of heterogeneous 3d tissue constructs using low‐viscosity bioink.Adv Mater.2016;28(4):677-684.
[21] JIA W, GUNGOR-OZKERIM PS, ZHANG YS, et al. Direct 3D bioprinting of perfusable vascular constructs using a blend bioink. Biomaterials. 2016;106(1):58-68.
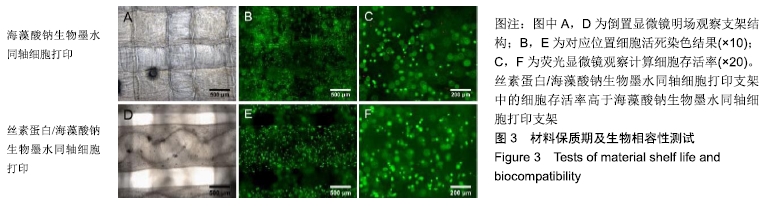
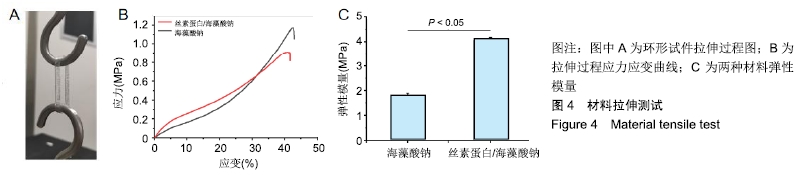
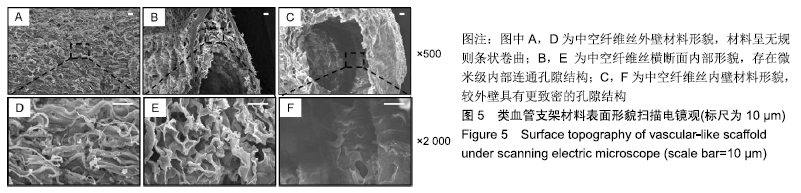
[22] 李宁宁,徐铭恩,索海瑞,等.同轴打印双交联海藻酸钠/丝素蛋白血管网络支架[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(18):2865-2870.
[23] ROCKWOOD DN, PREDA RC, YÜCEL T, et al. Materials fabrication from Bombyx mori silk fibroin.Nat Protoc.2011;6(10):1612-1631.
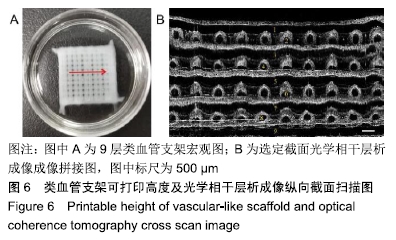
[24] DREXLER W. Optical coherence tomography// Drexler,Wolfgang, James G,eds.Technology and Applications.Switzerland:Spring International,2008.
[25] 黄孟杰,罗莉,王玲,等.生物三维打印细胞负载水凝胶类组织的精准优化[J].中国生物医学工程学报, 2018,37(4):468-480.
[26] GAO Q, LIU Z, LIN Z, et al. 3D bioprinting of vessel-like structures with multilevel fluidic channels.ACS Biomater-Sci Eng.2017;3(3):399-408.
[27] 杜显彬,徐铭恩,王玲,等.基于同轴流技术的肝组织生物3D打印研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报, 2018,37(6):731-738.
[28] 邓春闽,钟天翼,许亚娟,等.泊洛沙姆对再生丝素蛋白凝胶化结构及形态的影响[J].丝绸,2013, 50(1):4-9.
[29] KWEON HY, YEO J H, LEE KG, et al. Effects of poloxamer on the gelation of silk sericin. Macromol Rapid Comm. 2000;21(18): 1302-1305.
[30] 朱良均,胡国梁.丝素蛋白在胶凝时的分子结构,结晶性的探讨[J].蚕业科学,1998,4(4):226-230.
[31] YANG MY. Silk-based biomaterials. Microsc Res Techniq. 2017;80(3): 321-300.
[32] RODRIGUEZ MJ, BROWN J, GIORDANO J, et al. Silk based bioinks for soft tissue reconstruction using 3-dimensional (3D) printing with in vitro and in vivo assessments.Biomaterials.2017;117:105-115.
[33] 罗会涛,赵婧,范兴平,等.不同类型多孔结构生物材料支架制备及其性能优化[J].中国材料进展, 2012;31(5):30-39.
[34] ARMSTRONG JP, BURKE M, CARTER BM, et al. 3D bioprinting using a templated porous bioink.Adv Healthc Mater.2016;5(14):1724-1730.
[35] LOVETT M, LEE K, EDWARDS A. Vascularization strategies for tissue engineering.Tissue Eng.2009;15(3):353-370.
[36] SKARDAL A, ZHANG J, PRESTWICH GD. Bioprinting vessel-like constructs using hyaluronan hydrogels crosslinked with tetrahedral polyethylene glycol tetracrylates.Biomaterials.2010;31(24):6173-6181.
|