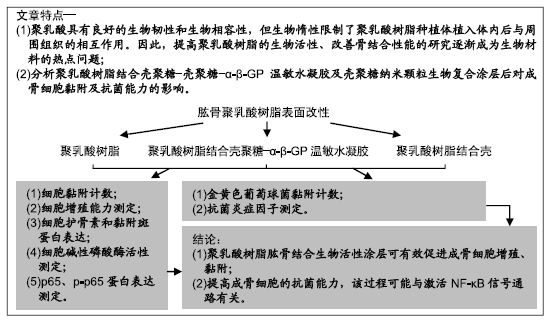
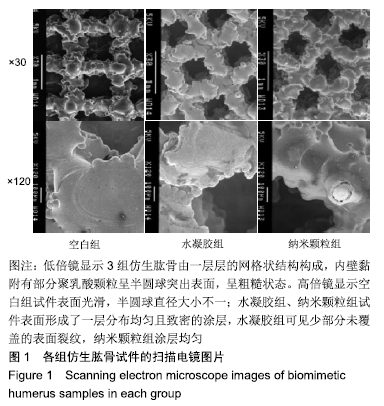
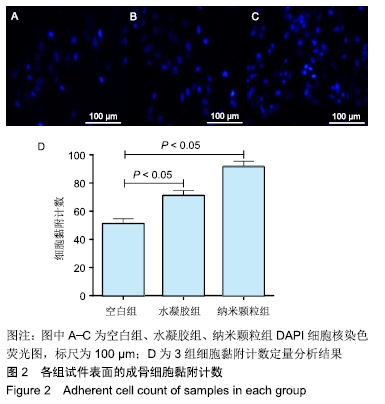
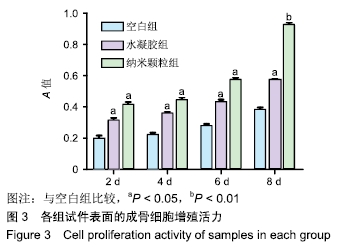
[1] 施庆锋.基于聚乳酸的生物可降解复合材料的制备和研究[D].上海:华东理工大学,2011.
[2] 邹俊.聚乳酸及其纳米复合材料的研究[D].上海:华东理工大学, 2011.
[3] 桂宗彦.聚乳酸材料的改性研究[D].上海:华东理工大学,2012.
[4] 王鑫众.PLA/MSM缓释微球的制备及骨关节炎治疗[D].长春:吉林大学,2013.
[5] 张薷文,周延民,赵静辉.种植体骨结合相关检测手段研究现状[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2013,29(5):730-734.
[6] 周弘.种植体表面不同形貌对骨质疏松症骨结合的影响[D].西安:第四军医大学,2011.
[7] 石磊.种植体表面改性—光诱导超亲水性表面骨结合机制研究[D].西安:第四军医大学, 2013.
[8] 唐刚.聚乳酸/次磷酸盐复合材料的制备、阻燃机理以及烟气毒性研究[D].合肥:中国科学技术大学,2013.
[9] 宋亚男.聚乳酸基复合材料的性能与结构研究[D].大连:大连理工大学,2013.
[10] 张绍清,蔡洪桢,王飞翔,等.钛基钽涂层人工种植体植入不同部位的骨结合对比研究[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志, 2018,19(2): 106-112.
[11] 王方辉,张姗姗,舒静媛,等.纯钛种植体表面改性对骨结合的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(52):8491-8497.
[12] 叶川,马敏先,张弢,等.Ⅰ型胶原修饰纯钛片促进人脂肪间充质干细胞增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(25):4032-4037.
[13] RICARD-BLUM S, RUGGIERO F.The collagen superfamily: From the extracellular matrix to the cell membrane.Pathol Biol(Paris).2005;53(7):430-442.
[14] MORRA M, CASSINELLI C, MEDA L, et al.Surface analysis and effects on interfacial bone microhardness of collagen-coated titanium implants: A rabbit model.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2005;20(1):23-30.
[15] ZHANG H, SUN ZQ, ZHOU LY, et al.Polylactic acid / polycaprolactone / poly (ε-caprolactone-L-lactide) copolymerstructure and performance of ternary blend system.Chin J Appl Chem.2016;32(9):1027-1031.
[16] GUO XJ, ZHANG JW, HUANG JJ, et al.Poly(lactic acid)/polyoxymethylene blends:Morphology,crystallization, rheology, and thermal mechanical properties.Polymer. 2015; 69:103-109.
[17] SHAHMORADI S, YAZDIAN F, TABANDEH F, et al.Controlled surface morphology and hydrophilicity of polycaprolactone toward human retinal pigment epithelium cells.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;73:300-309.
[18] YANG FW, LIN YL, TIAN XM, et al.Preparation of PLA/PCL Blend and Its Application on Medical Materials.Eng Plastic Appl.2014;2(42):1-5.
[19] WU A, CHEN L, XIONG ZC, et al.Preparation and Characterization Study of Poly (ε-caprolactone-co-L-lactide)/ Poly L-lactic Acid Composites.China Plastic Industry. 2014; 42(2):47-51.
[20] LI B, LI Y, LI J, et al.Influence of nanostructures on the biologicalproperties of ti implants after anodic oxidation.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2014;25(1):199-205.
[21] 李赛娜,康跻耀,高建萍,等.胶原涂层对3d 打印种植体表面生物相容性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(10): 1558-1564.
[22] TAKAYAMA T, TODO M, ARAKAWA K, et al.Characterization of Impact Fracture Behavior of BiodegradablePLA/PCL Polymer Blend.Key Eng Mater.2006;328:1569-1572.
[23] GAAL G, MENDES M, DE ALMEIDA TP, et al.Simplified fabrication of integrated microfluidic devices using fused deposition modeling 3D printing.Sensor Actuat B-Chem. 2017;242:35-40.
[24] 王素军.基于聚乳酸的靶向药物释放载体材料的研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2012.
[25] JIN Y, WAN Y, ZHANG B, et al.Modeling of the chemical finishing process for polylactic acid parts infused deposition modeling and investigation of its tensile properties.J Mater Proc Technol.2017;240:233-239.
[26] CARRICO1 JD, TRAEDEN NW, AURELI M, et al.Fused filament 3D printing of ionic polymer-metal composites (IPMCs).Smart Mater Struct.2015;24(12):1-12.
[27] 田玲玲.聚乳酸—己内酯乳液静电纺组织工程支架的制备及性能评价[D].上海:东华大学, 2014.
[28] 邵俊东.聚乳酸纳米纤维支架的构建与改性及其纳米力学性能研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2013.
[29] 赵永青.生物降解聚乳酸基复合材料的制备与性能研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2009.
[30] ROCHA CR, TORRADO PEREZ AR, ROBERSON DA. Novel ABS-based binary and ternary polymer blends for materialextrusion 3D printing.J Mater Res.2014;29(17): 1859-1866.
[31] SHIN BY, HAN DH. Compatibilization of immisciblepoly(lactic acid)/poly(e-caprolactone)blend through electron-beam irradiation with the addition of acompatibilizing agent.Radiat Phys Chem.2013;83:98-104.
[32] ZHAN X, ZHANG C, DISSANAYAKA WL, et al.Storage media enhance osteoclastogenic potential of human periodontal ligament cells via rankl-independent signaling. Dent Traumatol. 2013;29(1):59-65.
[33] DOUGLAS P, ALBADARIN AB, AL-MUHTASEB AH, et al. Al-Muhtase.Thermo-mechanical properties of polyε-caprolactone/poly L-lactic acidblends: Addition of nalidixic acidand polyethylene glycol additives.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2015;45:154-165.
[34] 刘鹏.抗结核药物缓释微球在兔椎体中释放及分布规律的研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2013.
[35] 向琳,陈晖璐,袁影,等.降钙素基因相关肽对种植体周围神经、血管再生及骨结合的作用[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2018,45(5): 509-515.
[36] 吴倩,李德超,张慧明,等.钛合金微弧氧化载抗菌肽涂层的动物体内骨结合行为[J]. 中国体视学与图像分析,2018,23(1):1-8.
[37] 陈江,陈旭晞,周麟.骨免疫调节机制对种植体骨结合及骨生物材料引导骨再生的影响[J].口腔疾病防治,2018,26(10):613-620.
[38] VON WILMOWSKY C, BAUER S, ROEDL S, et al.The diameter of anodic tio2 nanotubes affects bone formation and correlates with the bone morphogenetic protein-2 expression in vivo.Clin Oral Implants Res.2012;23(3):359-366.
[39] 李养军.ILK在糖尿病视网膜病变中作用的研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2007.
[40] 刘佩,彭晓燕,逄明杰,等.Ghrelin,内脂素和护骨素在Ⅱ型糖尿病发病机制中的作用研究[J].现代生物医学进展, 2016,16(18): 3423-3426.
[41] KOWALCZYK M, PIORKOWSKA E, DUTKIEWICZ S, et al. Toughening of polylactide by blending with a novel randomaliphatic–aromatic copolyester.Eur Polym J.2014;59: 59-68.
[42] 鲍启忠,朱康,马明.护骨素和κB-受体激活因子水平变化对缺血性股骨头坏死保护作用效果及作用机制分析[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2018,17(13):1410-1412.
[43] 邓云龙,李德超,李慕勤,等.纯钛表面GRGDSP多肽对骨结合能力的影响[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2018,16(3):199-204.
[44] SUL YT.Electrochemical growth behavior, surface properties, and enhanced in vivo bone response of tio2 nanotubes on microstructured surfaces of blasted, screw-shaped titanium implants.Int J Nanomedicine.2010;5:87-100.
[45] WANG Y, WEI Z, LI Y. Highlytoughened polylactide/epoxidized poly(styrene-bbutadiene-b-styrene) blends with excellent tensile performance. Eur Polym J.2016;85:92104.
|