1.1 设计 细胞学体外实验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2010年7月至2013年4月在华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院实验室完成。
1.3 材料
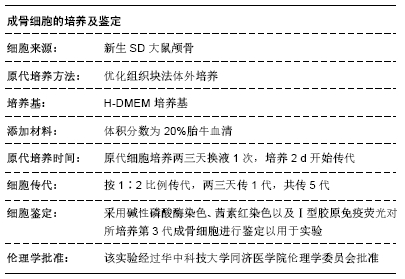
1.3.1 实验动物 新生SD大鼠(24 h内)5只,雌雄不限,由华中科技大学同济医学院动物中心提供,许可证号:SCXK(鄂)2010-0007。实验过程中对动物的处置符合中华人民共和国科学技术部2006年颁布的《关于善待实验动物的指导性意见》标准。
1.3.2 实验药品、试剂 异烟肼(成都锦华制药有限公司);高糖DMEM培养基(Gibco公司);Ⅰ型胶原酶(Sigma公司);胰蛋白酶(Sigma公司);二抗羊抗兔IgG-cy3(Abcam公司);一抗兔抗鼠Ⅰ型胶原抗体(Abcam公司);胎牛血清(Gibco公司);4',6-二脒基-2-苯基吲哚(DAPI,Sigma公司);Cell Counting
Kit-8(CCK-8,上海碧云天公司);碱性磷酸酶染色试剂盒(南京建成公司);碱性磷酸酶(AKP/ALP)活性测试盒(南京建成公司);TritonX-100-PBS (PBST,上海碧云天公司);BSA-PBS(Sigma公司);其他相关试剂均为国产分析纯试剂。
1.3.3 实验仪器 CO2细胞培养箱(Heraeus公司);倒置相差显微镜(Nikon公司);酶标仪(BioTek公司);CX41荧光显微镜(Olympus公司);超净工作台(上海空气净化公司)。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 原代成骨细胞分离培养及传代 将新生SD大鼠浸泡于体积分数为75%乙醇5 min,移入超净台内,取出颅骨,剔除骨膜、血管和结缔组织等放入培养皿中,加入含青霉素、链霉素的0.01 mol/L
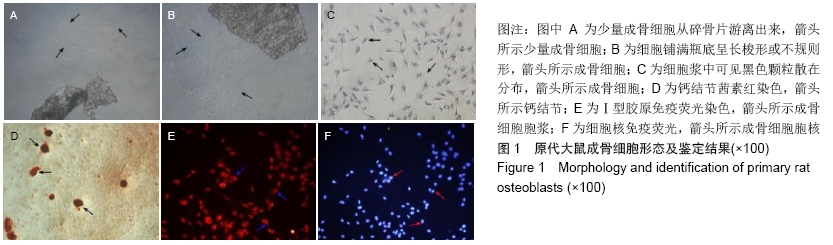
PBS浸泡;然后用PBS冲洗3次,剪碎,修整成约1 mm×1 mm大小的组织块,再用PBS反复浸泡、洗涤。收集碎骨片加入0.25%胰蛋白酶5 mL,37 ℃振荡消化20 min,去除消化液,再次加入0.1%Ⅰ型胶原酶5 mL,37 ℃振荡消化60 min,加入4 mL高糖DMEM培养基终止消化。用筛网过滤消化液,收集碎骨片,均匀接种于培养瓶中,置于37 ℃,体积分数为5%CO2培养箱中倒置培养,2-4 h后翻转培养瓶,加入含体积分数为20%胎牛血清的高糖DMEM培养基进行原代培养。每天大体观察培养基的颜色,是否变浑浊。镜下观察细胞形态和生长状况,是否铺满瓶底。在接种后两三天换液1次,待细胞铺满瓶底90%时可以传代。采用碱性磷酸酶染色、茜素红染色以及Ⅰ型胶原免疫荧光对所培养第3代成骨细胞进行鉴定以用于实验。
1.4.2 成骨细胞鉴定
(1)原代成骨细胞形态学观察:从原代培养开始,每天在倒置显微镜下观察各组细胞生长情况及形态变化,并逐日摄像记录。
(2)碱性磷酸酶染色:取第3代成骨细胞,接种在铺有盖玻片的6孔板上,培养三四天后,用碱性磷酸酶染色试剂盒进行染色,干燥封固,摄像。
(3)钙结节茜素红染色:第3代成骨细胞,胰酶消化后制成DMEM细胞悬液,以1×104个/孔均匀接种于6孔板中培养18 d,期间只换液,不传代,待细胞融合后聚集成灶,形成钙结节,再用体积分数为95%乙醇固定10 min,三蒸水清洗3次,每次1 min,然后用0.1%茜素红溶液染色 30 min,三蒸水冲洗3次,干燥封固并显微镜下观察。
(4)Ⅰ型胶原免疫荧光染色:将培养的第3代细胞接种到盖玻片上,待细胞贴壁后,移去培养基,用40 g/L多聚甲醛固定15 min;PBS晃洗3次,每次5 min;加入适量0.5%TritonX-100-PBS溶液,室温下处理15 min,PBS晃洗3次,每次5 min;加入80 μL 10%NGS-PBS溶液,于37 ℃下封闭30 min;加入8 μL 1∶80稀释的兔抗鼠一抗,4 ℃孵育过夜,PBST晃洗3次,每次10 min;加入80 μL 1∶100羊抗兔二抗IgG-cy3,37 ℃孵育30 min,PBST晃洗3次,每次10 min,晃洗时用锡箔纸盖住;再加入适量 5 mg/L DAPI染色2 min,PBST晃洗3次,每次10 min,最后在荧光显微镜下观察,分别用绿光和蓝光激发,观察、摄像。
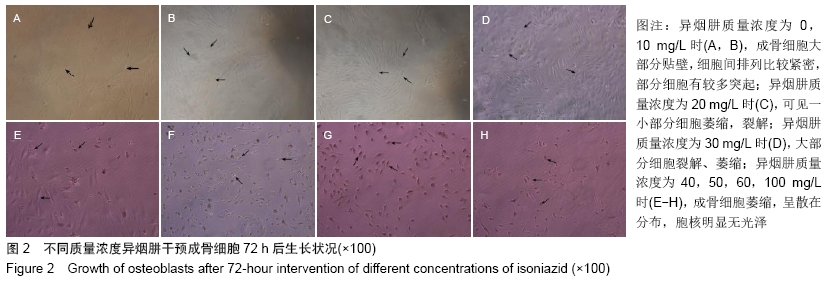
1.4.3 不同质量浓度异烟肼对成骨细胞生长状况的影响 取第3代成骨细胞,用含0.02% EDTA的0.25%胰酶消化,制成DMEM细胞悬液,以1.26×106个/孔接种于6孔板中,随机设对照组和实验组,每组设3个重复孔,培养24 h待细胞贴壁后去除培养液,对照组只加入含体积分数为20%胎牛血清的高糖DMEM培养液100 μL,实验组分别加入不同质量浓度异烟肼(10,20,30,40,50,60,100 mg/L)、体积分数为20%胎牛血清的高糖DMEM培养液100 μL,置于体积分数为5%CO2培养箱中,每天在倒置显微镜下观察各组细胞生长情况及形态变化,并逐日摄像记录。
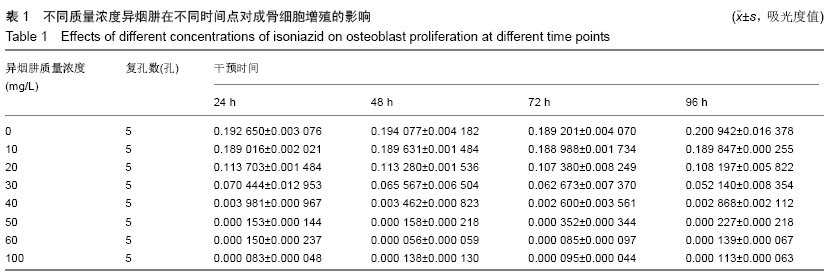
1.4.4 不同质量浓度异烟肼对成骨细胞增殖的影响 取第3代成骨细胞,用含0.02%EDTA的0.25%胰酶消化,制成DMEM细胞悬液,以5 000个/孔接种于96孔板中,每孔100 μL,总共6个板。每个96孔板随机设对照组和实验组,培养24 h待细胞贴壁后去除培养液,对照组只加入含体积分数为20%胎牛血清的高糖DMEM培养液100 μL,实验组分别加入不同质量浓度异烟肼(10,20,30,40,50,60,100 mg/L)、体积分数为20%胎牛血清的高糖DMEM培养液100 μL,置于体积分数为5%CO2培养箱中,培养24,48,72,96 h时取出1个96孔板,每孔加入CCK-8 10 μL继续培养,培养0.5,1,2,4 h后分别用酶标仪在450 nm处测定吸光度值,然后选取吸光度比较适宜的时间点作为后续实验时间点。
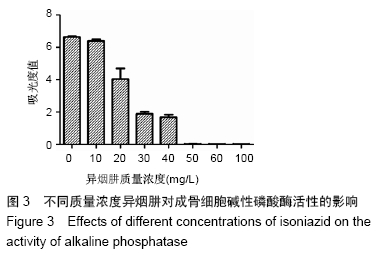
1.4.5 不同质量浓度异烟肼对成骨细胞碱性磷酸酶活性的影响 取第3代成骨细胞,用含0.02%EDTA的0.25%胰酶消化,制成DMEM细胞悬液,以1×104个/孔接种于96孔板中,每孔200 μL,随机设对照组和实验组,总共6个板。每个96孔板随机设对照组和实验组,培养24 h待细胞贴壁后去除培养液,对照组只加入含体积分数为20%胎牛血清的高糖DMEM培养液100 μL,实验组分别加入不同质量浓度异烟肼(10,20,30,40,50,60,100 mg/L)、体积分数为20%胎牛血清的高糖DMEM培养液100 μL,置于体积分数为5%CO2培养箱中,培养3 d后去除培养液, 0.01 mol/L的PBS洗3遍;每孔加入0.05%TritonX-100置4 ℃冰箱内12 h;超声破碎细胞(150 W,5 s,间歇进行);按碱性磷酸酶活性检测试剂盒说明书进行操作,用酶标仪测定405 nm波长处每孔的吸光度值。
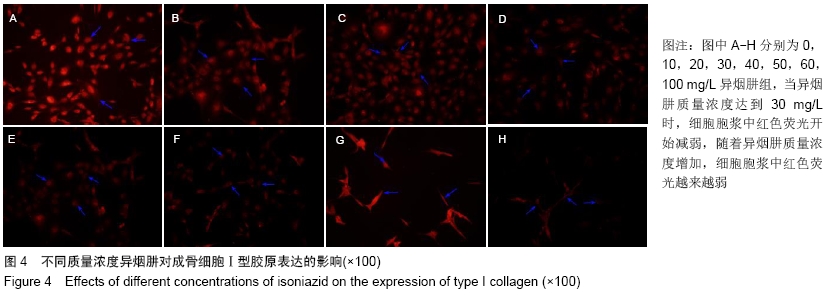
1.4.6 不同质量浓度异烟肼对成骨细胞Ⅰ型胶原表达的影响 取第3代成骨细胞,用含0.02%EDTA的0.25%胰酶消化,制成DMEM细胞悬液,以1×106接种于6孔板中,随机设对照组和实验组,每组设3个重复孔,培养24 h待细胞贴壁后去除培养液,对照组只加入含体积分数为20%胎牛血清的高糖DMEM培养液100 μL,实验组分别加入不同质量浓度异烟肼(10,20,30,40,50,60,100 mg/L)、体积分数为20%胎牛血清的高糖DMEM培养液100 μL,置于体积分数为5%CO2培养箱中,培养3 d后移去各组培养液,用复温到37 ℃的0.01 mol/L PBS快速洗涤3次,40 g/L多聚甲醛溶液固定15 min;PBS晃洗3次,每次5 min;加入适量0.5% TritonX-100-PBS溶液,室温下处理15 min,PBS晃洗3次,每次5 min;加入80 µL 10%BSA-PBS溶液,于37 ℃下封闭30 min;加入0.01 mol/L PBS 1∶80稀释的兔抗鼠Ⅰ型胶原抗体80 µL,4 ℃孵育过夜,PBST晃洗3次,每次10 min;加入0.01 mol/L PBS 1∶100稀释的羊抗兔二抗IgG-cy3 80 µL,37 ℃孵育30 min,PBST晃洗3次,每次10 min(晃洗时用锡箔纸盖住避光);再加入适量5 mg/L DAPI染色2 min,PBST晃洗3次,每次10 min,最后在荧光显微镜下绿光激发观察,拍照并记录。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①原代成骨细胞的形态及鉴定结果;②不同质量浓度异烟肼处理后成骨细胞生长增殖状况、碱性磷酸酶活性、Ⅰ型胶原表达。
1.6 统计学分析 采用SPSS 18.0统计软件进行统计分析,所得数据均以x(_)±s表示,进行方差分析比较,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。