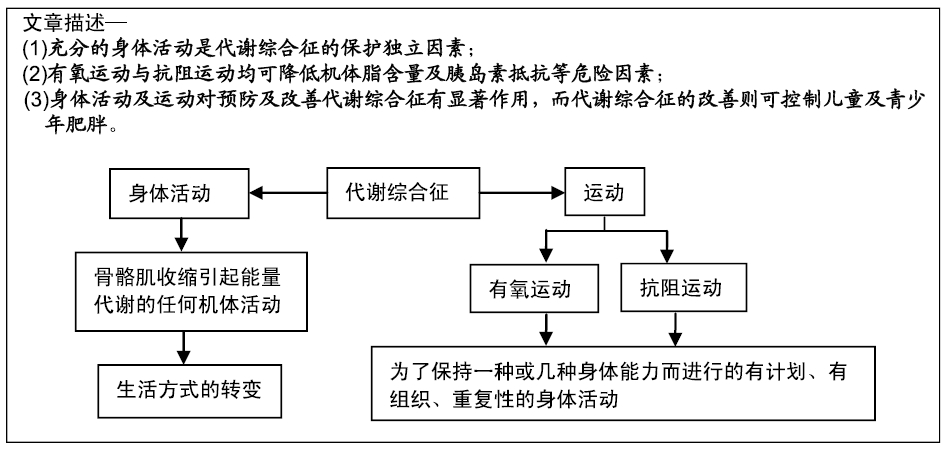
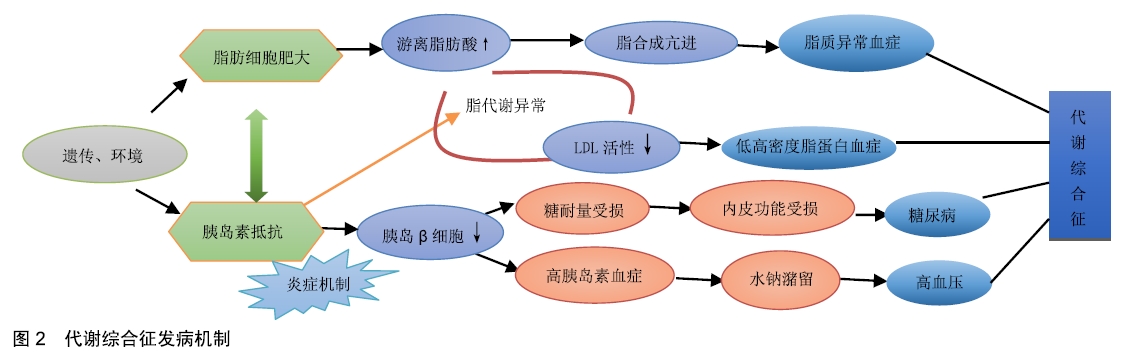
[1] REAVEN GM.Diet and syndrome X. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2000; 2(6):503-507.
[2] REAVEN GM. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988;37(12):1595-1607.
[3] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会代谢综合征研究协作组.中华医学会糖尿病学分会关于代谢综合征的建议[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2004,12(3): 5-10.
[4] LU J, WANG L, LI M, et al. Metabolic Syndrome Among Adults in China: The 2010 China Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(2): 507-515.
[5] 尹士男,江华.代谢综合征的诊治进展[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2018(11):1121-1123.
[6] 李文敏,高凯. 2014—2017年我国居民代谢综合征患病率的meta分析[J].慢性病学杂志,2018,19(11):1476-1480.
[7] 王晓东,谢友红,孙兴国,等.心肺运动试验精准制定个体化强度运动处方对代谢综合征患者心肺功能的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2019,38(01):3-9.
[8] 张蓉.代谢综合征的流行病学研究进展[J].江西医药,2011,46(1): 78-81.
[9] 张春燕,童人杰,李海华,等.综合干预在儿童代谢综合征中的疗效及对患儿生存质量的影响观察[J]. 实用预防医学,2018,25(5): 597-600.
[10] 张晨.12-15岁青少年体力活动水平现状与代谢综合征指标的关联性研究[D].天津:天津体育学院,2013.
[11] OKOSUN IS, BOLTRI JM, LYN R, et al.Continuous Metabolic Syndrome Risk Score, Body Mass Index Percentile, and Leisure Time Physical Activity in American Children. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2010;12(8):636-644.
[12] KAMATH CC,VICKERS KS,EHRLICH A,et al.Behavioral Interventions to Prevent Childhood Obesity: A Systematic Review and Metaanalyses of Randomized Trials. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93(12):4606-4615.
[13] 叶萍. PPARγ基因Pro12Ala和C1431T、ADIPOQ基因-11377C>G多态性及身体活动与儿童代谢综合征的关系[D]. 广州:南方医科大学, 2013.
[14] 王凯风,叶萍,王丹,等. ADIPOQ基因11377C/G位点多态性与身体活动对儿童代谢综合征的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2015,31(23): 3853-3856.
[15] 牛林艳,黄金. 儿童及青少年代谢综合征的干预进展[J]. 医学综述. 2013,19(3):525-527.
[16] MCMURRAY RG, BANGDIWALA SI, HARRELL JS, et al. Adolescents with metabolic syndrome have a history of low aerobic fitness and physical activity levels. Dyn Med. 2008;7:5.
[17] 陈联辉,朱伟芬,梁黎,等.非高密度脂蛋白胆固醇对肥胖儿童非脂性心血管疾病危险因素的预测作用[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2013, 15(5):356-360.
[18] 阳玉晶. 有氧运动对肥胖青少年心外膜脂肪厚度的影响[D]. 南昌:南昌大学, 2016.
[19] 斯坦博格,庄稼英. 关注儿童青少年中的代谢综合征[J]. 糖尿病天地(临床),2010,4(7):296-305.
[20] 吴海英,沈才杰. 饮食及运动干预对代谢综合征儿童左室结构及功能改善的作用[J].浙江中西医结合杂志, 2018,28(8): 667-670.
[21] NETO AS, DE CAMPOS W, SANTOS GD, et al. Metabolic syndrome risk score and time expended in moderate to vigorous physical activity in adolescents. BMC Pediatrics. 2014:42.
[22] 关尚一,朱为模.身体活动与青少年代谢综合征风险的“剂量-效应”关系[J].西安体育学院学报,2013,30(02):211-216.
[23] 李晓南.关注儿童青少年肥胖相关并发症的监测和指导[J].中国儿童保健杂志,2018,26(12):1277-1279.
[24] 张磊,李智慧.运动干预对肥胖代谢综合征青少年脑功能的影响[J]. 河北体育学院学报,2019,33(1):79-86.
[25] RÄIKKÖNEN K, MATTHEWS KA, SALOMON K.Hostility predicts metabolic syndrome risk factors in children and adolescents. Health Psychology. Health Psychol. 2003;22(3):279-86.
[26] GERMAIN CM, VASQUEZ E, BATSIS J A. Physical Activity, Central Adiposity, and Functional Limitations in Community- Dwelling Older Adults. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2016;39(2):71-6.
[27] 麻新远,衣雪洁.论身体活动和运动干预对2型糖尿病的作用[J]. 沈阳体育学院学报,2010,29(3):69-72.
[28] KI-WOL S. Relationship of daily activity and biochemical variables in the elderly with diabetes mellitus. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2011; 41(2):182-190.
[29] 巫丽丽,李必迅,邱晔,等.生活方式干预对代谢综合征患者影响10年随访研究[J].内科, 2018,13(6):823-826.
[30] 谢文娟,卞晓嘉,何志敏,等.身体行为活动与血脂异常、高血压、糖尿病关系的研究[J]. 实用预防医学,2017, 24(3): 319-323.
[31] 马丽.身体活动对城市老年人代谢性疾病患病风险的影响——基于PASE的流行病学调查[J].上海体育学院学报,2018,42(4):100-104.
[32] 安德里亚,谭婷婷. 即便进行运动,久坐行为仍与代谢综合征强相关[J].糖尿病天地(临床),2012,6(7):318-323.
[33] ROZINA A, BIN YB, JUNAID M, et al. Pattern of physical activity among persons with type 2 diabetes with special consideration to daily routine. Pak J Med Sci. 2016;32(1): 234-238.
[34] 于洪军,仇军.身体活动负荷对我国老年人患慢性疾病风险率的影响研究——基于对清华大学老年人群PASE问卷的流行病学调查[J]. 中国体育科技,2013,49(02):139-145.
[35] 王菂.不同运动方式对2型糖尿病康复的影响[J].中国民族民间医药, 2014,23(17):82-83.
[36] YANG Z, SCOTT C A, MAO C, et al. Resistance Exercise Versus Aerobic Exercise for Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2014;44(4):487-499.
[37] 张崇林,王卉,刘绍生,等.有氧运动对代谢综合征大鼠炎症反应的影响及其机制研究[C].无锡:第四届(2016)全国运动生理与生物化学学术会议,2016.
[38] 金萌萌,潘长玉,田慧,等.老年人群代谢综合征与十年心脑血管疾病死亡率关系的研究[J].中华心血管病杂志,2008,36(2): 118-122.
[39] 刘萍,孙静.治疗型生活方式对中老年人代谢综合征的影响[J].中国临床保健杂志,2009,12(4):408-409.
[40] 陈巍,李娟,陈庆合.运动促进骨骼肌功能康复改善代谢综合征的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2012,27(6):577-582.
[41] 董聪敏.力量训练对老年代谢综合征患者空腹和摄糖后自主神经功能调节的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2017,37(20): 5020-5022.
[42] ROBERTS CK, HEVENER AL, BARNARD RJ. Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance:underlying causes and modification by exercise training. Compr Physiol. 2013;3(1):1-58.
[43] 罗曦娟.有氧和抗阻运动对糖尿病前期人群糖调节的影响及其机制探讨[D].北京:北京体育大学, 2015.
[44] 金晓飞. 抗阻力训练对老年人机体健康影响的研究[J]. 运动, 2015(17):155-156.
[45] KIM TN, PARK MS, LIM KI, et al. Skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio is associated with metabolic syndrome and arterial stiffness: The Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study (KSOS). Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;93(2):285-91.
[46] 陈巍,李娟,陈庆合,等.抗阻训练中运动肌血流限制对肥胖者体成分及胰岛素敏感度的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2010,29(6): 646-649.
[47] HUH JY, SIOPI A, MOUGIOS V, et al. Irisin in Response to Exercise in Humans With and Without Metabolic Syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(3):E453-457.
[48] 陈宝宜,李婷,徐鑫亚.抗阻-有氧联合训练对中老年2型糖尿病患者运动干预的影响分析[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2017, 17(54): 46-49.
[49] 石劢.老年2型糖尿病患者运动干预效果的系统评价与实证研究[D]. 北京:北京中医药大学, 2016.
[50] 何江山. 老年人代谢综合征及其组分与抑郁状态的相关性研究[D]. 遵义:遵义医学院, 2018.
[51] 宁秋芬,张晓莉,周刚柱.抗抑郁药联合有氧运动对抑郁症的早期治疗阶段的临床疗效观察[J]. 山西医药杂志12018,47(6): 675-677.
[52] 刘海明.五禽戏对代谢综合征老年人认知功能的影响[J]. 武汉体育学院学报,2012,46(10):56-61.
[53] 张丽,瓮长水.全身振动训练在老年康复领域应用的研究进展[J]. 中国康复理论与实践12015,21(2):163-167.
[54] 张晓涵,张培珍.交叉点的运动训练对女性代谢综合征影响的研究进展[J]. 中国预防医学杂志,2018,19(10):783-786.
|