中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (1): 136-140.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1852
• 干细胞基础实验 basic experiments of stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
红景天干预可改善大强度运动小鼠骨骼肌细胞线粒体自噬及融合-分裂等功能
曹海信1,王小梅2
- 1西安石油大学体育系,陕西省西安市 710065;2延安大学体育学院,陕西省延安市 716000
Rhodiola intervention improves mitochondrial autophagy and fusion-division in skeletal muscle cells of mice with high intensity exercise
Cao Haixin1, Wang Xiaomei2
- 1Department of Physical Education, Xi’an Shiyou University, Xi’an 710065, Shaanxi Province, China; 2School of Physical Education, Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
自噬:指从粗面内质网的无核糖体附着区脱落的双层膜包裹部分胞质和细胞内需降解的细胞器、蛋白质等成分形成自噬体(autophagosome),并与溶酶体融合形成自噬溶酶体,降解其所包裹的内容物,以实现细胞本身的代谢需要和某些细胞器的更新。自噬广泛存在于人体的正常细胞和恶性肿瘤细胞中。
线粒体融合-分裂:线粒体是一种高度动态变化的细胞器,在细胞中不断融合与分裂,形成紧密连接的线粒体网络。这种融合与分裂的变化主要通过在线粒体融合、分裂蛋白的精确控制下,线粒体可在不断变化的生理环境中做出迅速准确的反应,这对于线粒体的遗传以及维持其功能至关重要。
背景:超负荷量的运动会引起体内氧化活性物质大量堆积从而损害骨骼肌细胞,而线粒体在运动过程能量代谢中具有关键作用。研究表明,红景天可以减少肌组织脂质过氧化水平,保护受损内皮细胞。
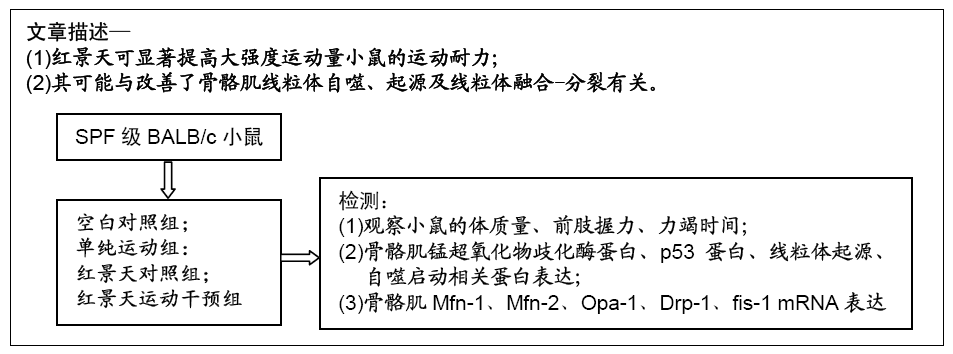
目的:探讨红景天通过调节线粒体功能改善大强度运动小鼠骨骼肌细胞的功能。
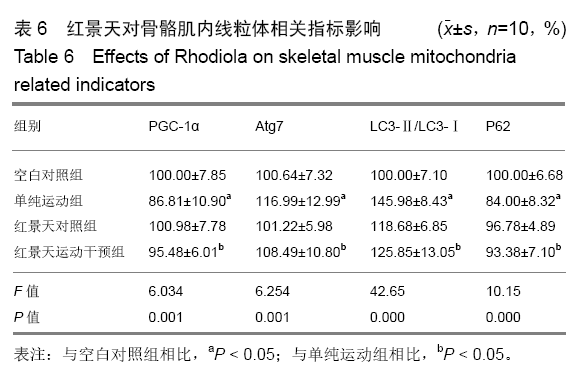
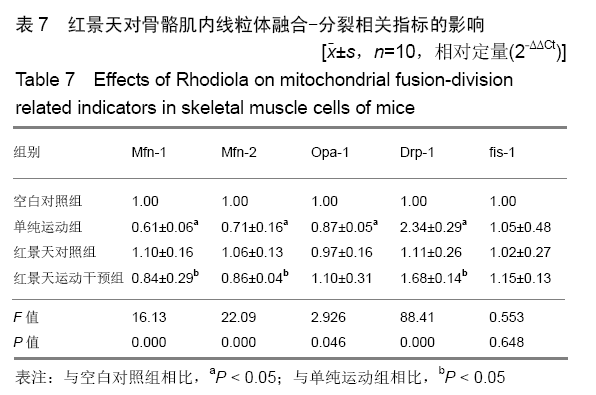
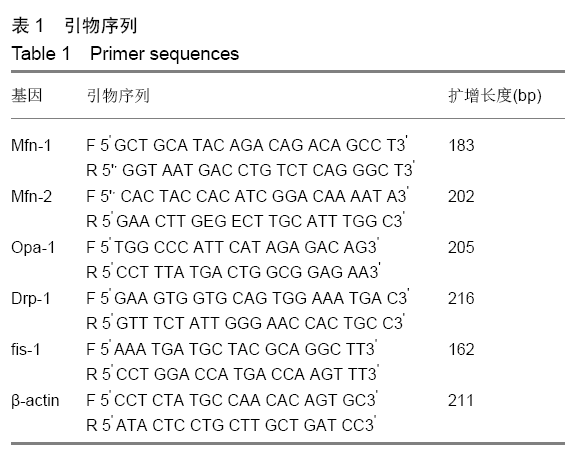
方法:实验方案经西安石油大学伦理委员会批准。选择40只SPF级BALB/c小鼠,根据干预措施的不同,将小鼠分为空白对照组、单纯运动组、红景天对照组、红景天运动干预组。①空白对照组:不进行运动;②单纯运动组:采用生理盐水灌胃后,进行大强度运动;③红景天对照组:将红景天与生理盐水悬浊液灌胃,不运动;④红景天运动干预组:红景天干预措施同红景天对照组,运动方案同单纯运动组。以上各组干预措施均为每天1次,连续28 d。观察小鼠的体质量、前肢握力、力竭时间;Western Blot检测骨骼肌锰超氧化物歧化酶蛋白、p53蛋白、线粒体起源、自噬启动相关蛋白表达;RT-qPCR检测骨骼肌Mfn-1、Mfn-2、Opa-1、Drp-1、fis-1 mRNA表达。
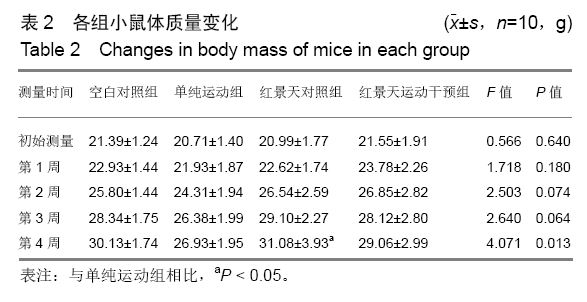
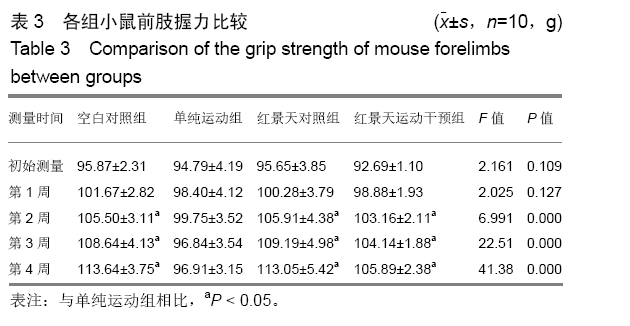
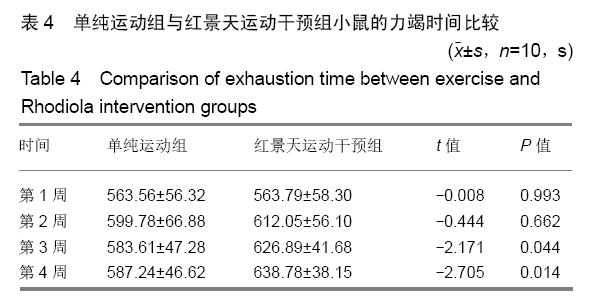
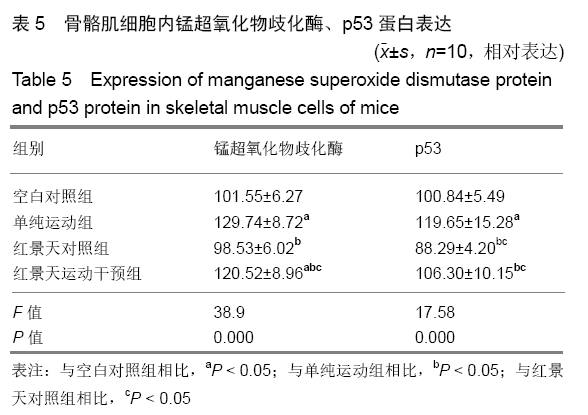
结果与结论:①从第2周开始,单纯运动组小鼠前肢握力显著低于其他3组(P < 0.05),但空白对照组、红景天对照组与红景天运动干预组之间,小鼠前肢握力始终无明显差异(P > 0.05);②第3,4周时,单纯运动组小鼠负重游泳训练力竭时间均显著短于红景天运动干预组(P < 0.05);③单纯运动组小鼠骨骼肌细胞内的锰超氧化物歧化酶、p53蛋白表达显著高于其他组小鼠(P < 0.05),红景天运动干预组小鼠骨骼肌细胞内的锰超氧化物歧化酶、p53蛋白表达显著高于红景天对照组(P < 0.05);④与空白对照组相比,单纯运动组小鼠骨骼肌内PGC-1α、LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ水平明显升高,Atg7、P62水平显著下降(均P < 0.05),与红景天对照组相比,红景天运动干预组PGC-1α、LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ水平明显升高,Atg7、P62水平显著下降(均P < 0.05);⑤与空白对照组相比,单纯运动组的融合基因表达下降,分裂基因Drp-1 mRNA表达上升(P < 0.05);红景天运动干预组的融合基因表达也呈下降趋势,Drp-1 mRNA表达水平呈上升趋势,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);⑥结果说明,红景天可显著提高大强度运动量小鼠的运动耐力,这可能与改善了骨骼肌线粒体自噬、起源及线粒体融合-分裂有关。ORCID: 0000-0002-4143-1195(曹海信)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: