| [1]Singh A,Tetreault L,Kalsiryan S,et al.Global prevalence and incidence of traumatic spinal cord injury. Clin Epidemiol.2014; 6:309-331.[2]Organization WH.International perspectives on spinal cord injury. Weed Res. 2013;11(4): 314-316.[3]Hagg T,Oudega M.Degenerative and spontaneous regenerative processes after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2006;23(3-4):264-280.[4]Gentleman E,Lay AN,Dickerson DA,et al.Mechanical characterization of collagen fibers and scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2003;24(21):3805-3813.[5]Yamane K,Mazaki T,Shiozaki Y,et al.Collagen-Binding Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) alone or with a Gelatin- furfurylamine Hydrogel Enhances Functional Recovery in Mice after Spinal Cord Injury. Sci Rep.2018;8(1):917.[6]Shi Q,Gao W,Han X,et al.Collagen scaffolds modified with collagen-binding bFGF promotes the neural regeneration in a rat hemisected spinal cord injury model.Sci China Life Sci. 2014;57(2):232-240.[7]Chen X,Zhao Y,Li X,et al.Functional Multichannel Poly(Propylene Fumarate)-Collagen Scaffold with Collagen-Binding Neurotrophic Factor 3 Promotes Neural Regeneration After Transected Spinal Cord Injury.Adv Healthc Mater.2018;7(14):e1800315.[8]Iozzo RV.Matrix proteoglycans: from molecular design to cellular function.Annu Rev Biochem.1998.67(1):609-652.[9]Shrestha B,Coykendall K,Li Y,et al.Repair of injured spinal cord using biomaterial scaffolds and stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther.2014;5(4):91.[10]Li G,Che MT,Zhang K,et al.Graft of the NT-3 persistent delivery gelatin sponge scaffold promotes axon regeneration, attenuates inflammation, and induces cell migration in rat and canine with spinal cord injury. Biomaterials.2016;83:233-248.[11]Rao JS,Zhao C,Zhang A,et al.NT3-chitosan enables de novo regeneration and functional recovery in monkeys after spinal cord injury.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(24): E5595-E5604.[12]Li G,Che MT,Zeng X,et al.Neurotrophin-3 released from implant of tissue-engineered fibroin scaffolds inhibits inflammation, enhances nerve fiber regeneration, and improves motor function in canine spinal cord injury.J Biomed Mater Res A.2018;106(8):2158-2170.[13]Yang Z,Zhang A,Duan H,et al.NT3-chitosan elicits robust endogenous neurogenesis to enable functional recovery after spinal cord injury.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(43): 13354-13359.[14]Liu S,Schackel T,Weidner N,et al.Biomaterial-Supported Cell Transplantation Treatments for Spinal Cord Injury: Challenges and Perspectives.Front Cell Neurosci.2017;11:430.[15]Ma YH,Zeng X,Qiu XC,et al.Perineurium-like sheath derived from long-term surviving mesenchymal stem cells confers nerve protection to the injured spinal cord.Biomaterials. 2018; 160:37.[16]Duan H,Li X,Wang C,et al.Functional hyaluronate collagen scaffolds induce NSCs differentiation into functional neurons in repairing the traumatic brain injury.Acta Biomater.2016;45: 182-195.[17]Lai BQ,Feng B,Che MT,et al.A Modular Assembly of Spinal Cord-Like Tissue Allows Targeted Tissue Repair in the Transected Spinal Cord.Adv Sci (Weinh).2018;5(9):1800261.[18]Zhang J,Lu X,Feng G,et al.Chitosan scaffolds induce human dental pulp stem cells to neural differentiation: potential roles for spinal cord injury therapy. Cell Tissue Res. 2016; 366(1): 129-142.[19]Kaneko A,Matsushita A,Sankai Y.A 3D nanofibrous hydrogel and collagen sponge scaffold promotes locomotor functional recovery, spinal repair, and neuronal regeneration after complete transection of the spinal cord in adult rats.Biomed Mater.2015;10(1):015008.[20]Zhang W,Yan Q,Zeng YS,et al.Implantation of adult bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells transfected with the neurotrophin-3 gene and pretreated with retinoic acid in completely transected spinal cord. Brain Res. 2010;1359: 256-2571.[21]Wang JM, Zeng YS, Wu JL,et al.Cograft of neural stem cells and schwann cells overexpressing TrkC and neurotrophin-3 respectively after rat spinal cord transection. Biomaterials. 2011;32(30): 7454-7468.[22]Kelley BJ,Harel NY,Kim CY,et al.Diffusion tensor imaging as a predictor of locomotor function after experimental spinal cord injury and recovery.J Neurotrauma.2014;31(15):1362-1373.[23]Wu GH,Shi HJ,Che MT,et al.Recovery of paralyzed limb motor function in canine with complete spinal cord injury following implantation of MSC-derived neural network tissue. Biomaterials.2018;181:15-34.[24]Parker D.Functional changes after spinal lesions: implications for interventions.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(5):811-812.[25]Wang Q,Zhang H,Xu H,et al.Novel multi-drug delivery hydrogel using scar-homing liposomes improves spinal cord injury repair. Theranostics.2018;8(16):4429-4446.[26]Madigan NN, McMahon S, O'Brien T, et al.Current tissue engineering and novel therapeutic approaches to axonal regeneration following spinal cord injury using polymer scaffolds.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2009;169(2):183-199.[27]Vigani B, Rossi S, Sandri G, et al.Design and criteria of electrospun fibrous scaffolds for the treatment of spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(11):1786-1790.[28]Ricard-Blum S,Beraud M,Raynal N,et al.Structural requirements for heparin/heparan sulfate binding to type V collagen.J Biol Chem. 2006;281(35):25195-25204.[29]Chen Y Scully M,Dawson G,et al.Perturbation of the heparin/heparin-sulfate interactome of human breast cancer cells modulates pro-tumourigenic effects associated with PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK signalling.Thromb Haemost.2013; 109(6):1148-1157.[30]Lu Q,Zhang S,Hu K,et al.Cytocompatibility and blood compatibility of multifunctional fibroin/collagen/heparin scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2007;28(14):2306-2313.[31]甘晓,南吴力.硫酸肝素/胶原蛋白神经组织工程支架修复周围神经损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(25): 3744-3749.[32]张仁坤,涂悦,赵明亮,等.3-D打印胶原蛋白-硫酸肝素仿生脊髓支架的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2015,29(8):1022-1027.[33]曹雄彬,戴军,宫丽,等.胶原蛋白-硫酸肝素生物支架在猪脑内的生物相容性分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(21): 3361-3365.[34]Leong NL,Arshi A,Kabir N,et al.In vitro and in vivo evaluation of heparin mediated growth factor release from tissue- engineered constructs for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.J Orthop Res. 2015;33(2):229-236.[35]Ogle BM,Bursac N,Domian I,et al.Distilling complexity to advance cardiac tissue engineering. Sci Transl Med. 2016; 8(342):342ps13.[36]Jang SH, Lee J, Yeo SS.Central post-stroke pain due to injury of the spinothalamic tract in patients with cerebral infarction: a diffusion tensor tractography imaging study.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(12):2021-2024. |
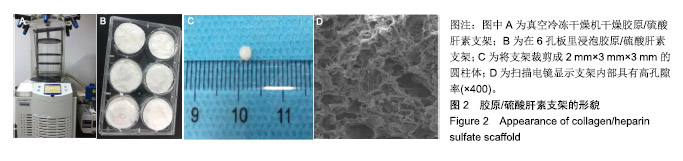
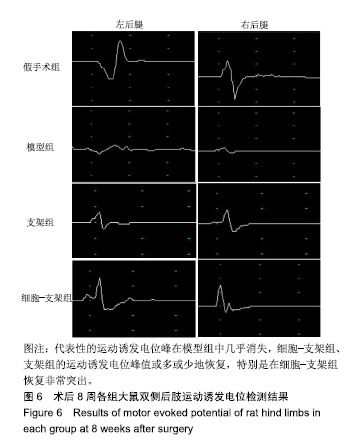
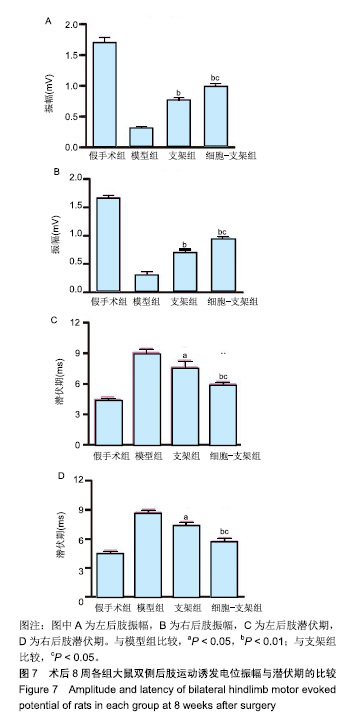
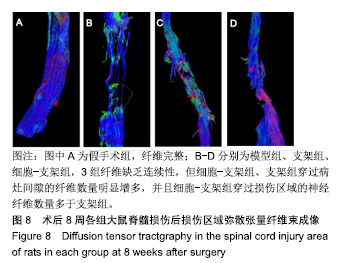
.jpg)
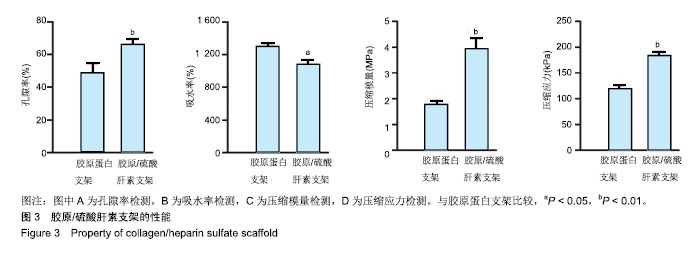
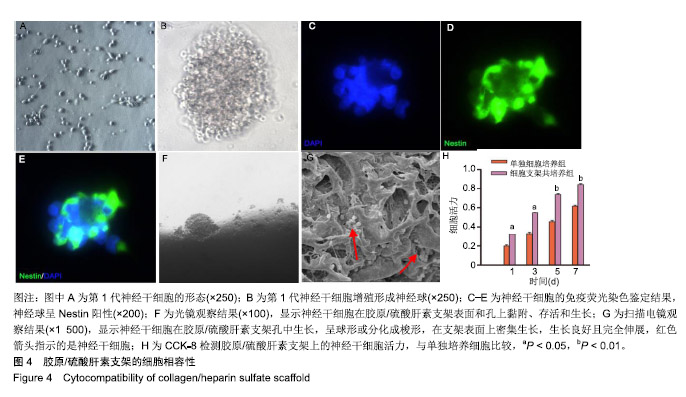
.jpg)
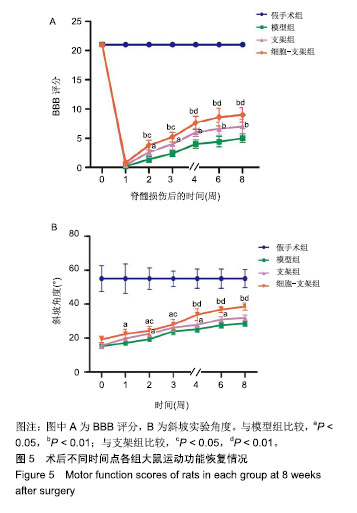
.jpg)