中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (31): 5010-5016.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1488
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
胡椒叶提取物干预可减轻急性脊髓损伤模型大鼠的氧化应激及炎症反应
成建平,李 华,李雄杰
- (海南西部中心医院骨科,海南省儋州市 571700)
Extract of piper auritum can alleviate oxidative stress and inflammation of rat models of acute spinal cord injury
Cheng Jianping, Li Hua, Li Xiongjie
- (Department of Orthopedics, West Central Hospital of Hainan, Danzhou 571700, Hainan Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
氧化应激:是指体内氧化与抗氧化作用失衡,倾向于氧化,导致中性粒细胞炎性浸润,蛋白酶分泌增加,产生大量氧化中间产物。氧化应激是由自由基在体内产生的一种负面作用,并被认为是导致衰老和疾病的一个重要因素。
胡椒叶提取物:胡椒是胡椒科的一种开花藤本植物,具有广谱抑菌性,据报道,胡椒叶的丙酮提取物对薯蓣炭疽菌菌丝生长的抑制率可达83.64%;胡椒提取物对大肠杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、沙门氏菌、酵母菌和黑曲霉均具有抑制作用;胡椒的乙醇提取物对来自口腔中的12种不同属的176个细菌菌株也具有较强的抑制作用。
文题释义:
氧化应激:是指体内氧化与抗氧化作用失衡,倾向于氧化,导致中性粒细胞炎性浸润,蛋白酶分泌增加,产生大量氧化中间产物。氧化应激是由自由基在体内产生的一种负面作用,并被认为是导致衰老和疾病的一个重要因素。
胡椒叶提取物:胡椒是胡椒科的一种开花藤本植物,具有广谱抑菌性,据报道,胡椒叶的丙酮提取物对薯蓣炭疽菌菌丝生长的抑制率可达83.64%;胡椒提取物对大肠杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、沙门氏菌、酵母菌和黑曲霉均具有抑制作用;胡椒的乙醇提取物对来自口腔中的12种不同属的176个细菌菌株也具有较强的抑制作用。
.jpg) 文题释义:
氧化应激:是指体内氧化与抗氧化作用失衡,倾向于氧化,导致中性粒细胞炎性浸润,蛋白酶分泌增加,产生大量氧化中间产物。氧化应激是由自由基在体内产生的一种负面作用,并被认为是导致衰老和疾病的一个重要因素。
胡椒叶提取物:胡椒是胡椒科的一种开花藤本植物,具有广谱抑菌性,据报道,胡椒叶的丙酮提取物对薯蓣炭疽菌菌丝生长的抑制率可达83.64%;胡椒提取物对大肠杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、沙门氏菌、酵母菌和黑曲霉均具有抑制作用;胡椒的乙醇提取物对来自口腔中的12种不同属的176个细菌菌株也具有较强的抑制作用。
文题释义:
氧化应激:是指体内氧化与抗氧化作用失衡,倾向于氧化,导致中性粒细胞炎性浸润,蛋白酶分泌增加,产生大量氧化中间产物。氧化应激是由自由基在体内产生的一种负面作用,并被认为是导致衰老和疾病的一个重要因素。
胡椒叶提取物:胡椒是胡椒科的一种开花藤本植物,具有广谱抑菌性,据报道,胡椒叶的丙酮提取物对薯蓣炭疽菌菌丝生长的抑制率可达83.64%;胡椒提取物对大肠杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、沙门氏菌、酵母菌和黑曲霉均具有抑制作用;胡椒的乙醇提取物对来自口腔中的12种不同属的176个细菌菌株也具有较强的抑制作用。摘要
背景:研究表明胡椒叶提取物对链脲佐菌素诱导糖尿病大鼠有明确的保护作用,作用机制与抗氧化损伤有关,但其是否能通过抗氧化应激减轻急性脊髓损伤还未见报道。
目的:探究胡椒叶提取物对急性脊髓损伤大鼠氧化应激、炎症反应及神经损伤的影响。
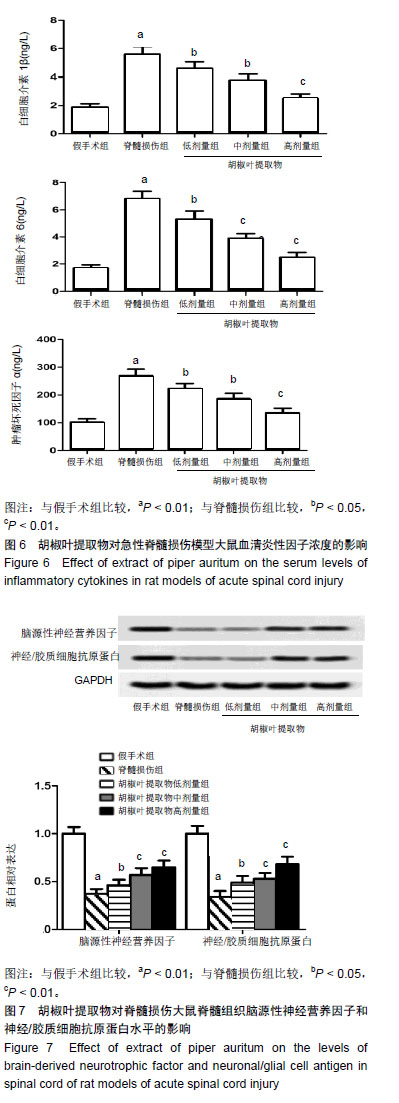
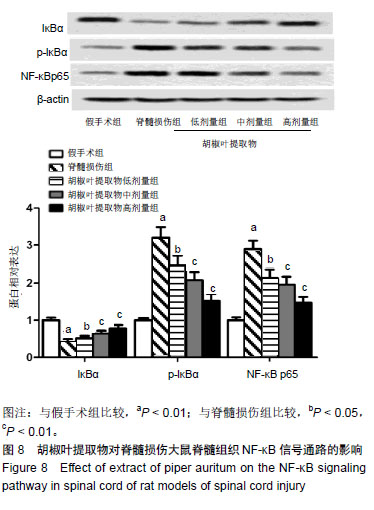
方法:将100只SD大鼠(购自成都达硕实验动物公司)随机分为假手术组、脊髓损伤组及胡椒叶提取物低、中、高剂量组,每组20只。除假手术组外,其余组大鼠采用改良Allen’s法复制大鼠急性脊髓损伤模型,造模后,胡椒叶提取物低、中、高剂量组灌胃给予100,200,400 mg/(kg•d)的胡椒叶提取物,连续给药28 d。给药后3,7,14,28 d后进行BBB评分和斜板实验;给药后28 d,检测血清超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶、丙二醛、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α水平,免疫印迹检测Bcl-2、Bax、Caspase-3、脑源性神经营养因子和神经/胶质细胞抗原、IκBα、p-IκBα和NF-κB p65蛋白表达,同时进行脊髓组织苏木精-伊红染色与TUNEL染色。实验方案经海南大学热带农林学院实验动物伦理委员会批准(NR001803)。
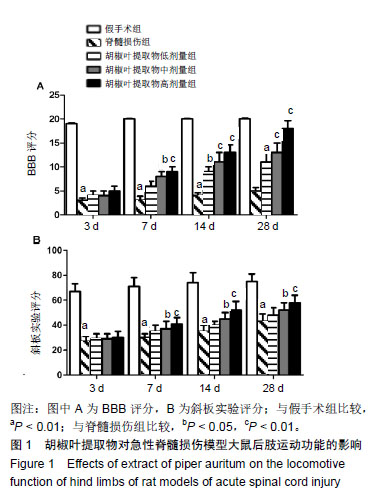
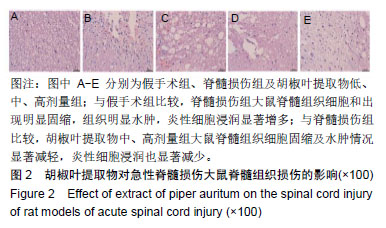
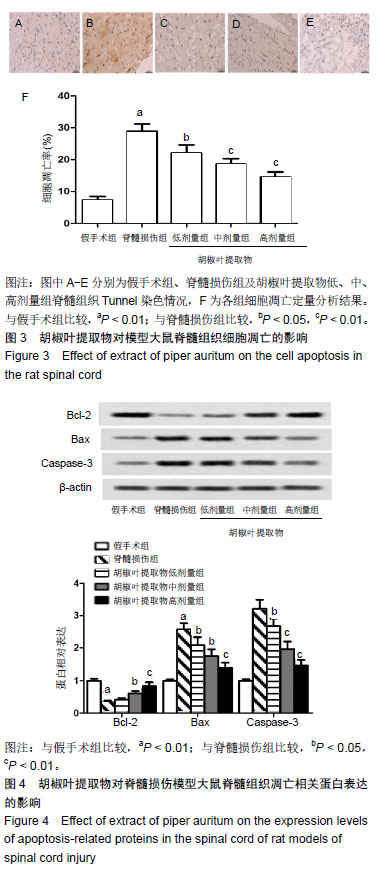
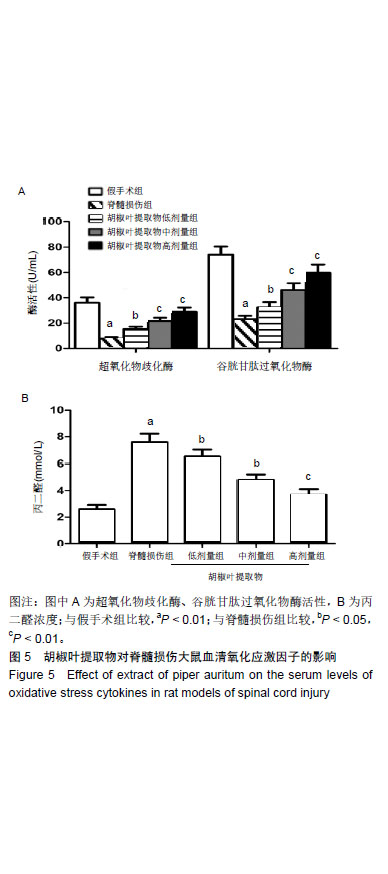
结果与结论:①与假手术组比较,脊髓损伤组给药后不同时间点的BBB评分和斜板实验最大倾斜角度降低(P < 0.01);与脊髓损伤组比较,胡椒叶提取物中、高剂量组给药后7,14,28 d的BBB评分和斜板实验最大倾斜角度升高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);②与假手术组比较,脊髓损伤组脊髓组织损伤严重,细胞凋亡率、Bax、Caspase-3、丙二醛、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、p-IκBα、NF-κB p65、脑源性神经营养因子和神经/胶质细胞抗原表达升高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),Bcl-2、IκBα、超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶表达降低(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);与脊髓损伤组比较,胡椒叶提取物低、中、高剂量组脊髓组织损伤减轻,细胞凋亡率、Bax、Caspase-3、丙二醛、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、p-IκBα、NF-κB p65、脑源性神经营养因子和神经/胶质细胞抗原表达降低(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),Bcl-2、IκBα、超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶表达升高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);③结果表明,胡椒叶提取物可通过抑制急性脊髓损伤大鼠炎症反应及氧化应激减轻脊髓损伤并发挥神经保护作用,作用机制可能与抑制NF-κB信号通路激活有关。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
氧化应激:是指体内氧化与抗氧化作用失衡,倾向于氧化,导致中性粒细胞炎性浸润,蛋白酶分泌增加,产生大量氧化中间产物。氧化应激是由自由基在体内产生的一种负面作用,并被认为是导致衰老和疾病的一个重要因素。
胡椒叶提取物:胡椒是胡椒科的一种开花藤本植物,具有广谱抑菌性,据报道,胡椒叶的丙酮提取物对薯蓣炭疽菌菌丝生长的抑制率可达83.64%;胡椒提取物对大肠杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、沙门氏菌、酵母菌和黑曲霉均具有抑制作用;胡椒的乙醇提取物对来自口腔中的12种不同属的176个细菌菌株也具有较强的抑制作用。
文题释义:
氧化应激:是指体内氧化与抗氧化作用失衡,倾向于氧化,导致中性粒细胞炎性浸润,蛋白酶分泌增加,产生大量氧化中间产物。氧化应激是由自由基在体内产生的一种负面作用,并被认为是导致衰老和疾病的一个重要因素。
胡椒叶提取物:胡椒是胡椒科的一种开花藤本植物,具有广谱抑菌性,据报道,胡椒叶的丙酮提取物对薯蓣炭疽菌菌丝生长的抑制率可达83.64%;胡椒提取物对大肠杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、沙门氏菌、酵母菌和黑曲霉均具有抑制作用;胡椒的乙醇提取物对来自口腔中的12种不同属的176个细菌菌株也具有较强的抑制作用。