中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (31): 4974-4978.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0822
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
复位法矫正发育性髋脱位模型兔:髋臼软骨细胞Caspase-3、Bcl-2的表达水平
熊 飞1,韦宜山2
- (1江西省儿童医院,江西省南昌市 330006;2内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010030)
Reduction for developmental dysplasia of the hip in rabbits: expression levels of Caspase-3 and Bcl-2 in acetabular chondrocytes
Xiong Fei1, Wei Yishan2
- (1Jiangxi Provincial Children’s Hospital, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; 2the Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
发育性髋关节脱位:又称发育性髋关节发育不良及髋发育不全,是较常见的先天性畸形,股骨头在关节囊内丧失其与髋臼的正常关系,以致在出生前及出生后不能正常发育。Hipkocsates早在公元前就描述了该病,之后众多学者对其进行了大量研究,但发育性髋关节脱位的早期诊断和治疗至今仍然是一个尚未完全解决的课题。
Caspase-3:是一种蛋白酶,1994年Fernandez-Alnemri等在BenBank表达序列标记(expression sequence tag,EST)数据库中找到一段与ICE/CED-3活性中心同源的序列,用它合成探针后,筛选人Jurkat T淋巴细胞cDNA文库,从中克隆到一种新基因,因其编码分子质量为32 ku的半胱氨酸蛋白酶而称之为CPP32 (cysteine protease protein)。随后,其他学者独立地将这一蛋白基因克隆出来,并分别命名为prICE、apopain (凋亡素)和Yama(印度传说中的死亡之神)。1996年这种蛋白酶被命名为caspase-3。现在一般认为caspase-3是细胞凋亡过程中最主要的终末剪切酶,也是CTL细胞杀伤机制的重要组成部分。
文题释义:
发育性髋关节脱位:又称发育性髋关节发育不良及髋发育不全,是较常见的先天性畸形,股骨头在关节囊内丧失其与髋臼的正常关系,以致在出生前及出生后不能正常发育。Hipkocsates早在公元前就描述了该病,之后众多学者对其进行了大量研究,但发育性髋关节脱位的早期诊断和治疗至今仍然是一个尚未完全解决的课题。
Caspase-3:是一种蛋白酶,1994年Fernandez-Alnemri等在BenBank表达序列标记(expression sequence tag,EST)数据库中找到一段与ICE/CED-3活性中心同源的序列,用它合成探针后,筛选人Jurkat T淋巴细胞cDNA文库,从中克隆到一种新基因,因其编码分子质量为32 ku的半胱氨酸蛋白酶而称之为CPP32 (cysteine protease protein)。随后,其他学者独立地将这一蛋白基因克隆出来,并分别命名为prICE、apopain (凋亡素)和Yama(印度传说中的死亡之神)。1996年这种蛋白酶被命名为caspase-3。现在一般认为caspase-3是细胞凋亡过程中最主要的终末剪切酶,也是CTL细胞杀伤机制的重要组成部分。
.jpg) 文题释义:
发育性髋关节脱位:又称发育性髋关节发育不良及髋发育不全,是较常见的先天性畸形,股骨头在关节囊内丧失其与髋臼的正常关系,以致在出生前及出生后不能正常发育。Hipkocsates早在公元前就描述了该病,之后众多学者对其进行了大量研究,但发育性髋关节脱位的早期诊断和治疗至今仍然是一个尚未完全解决的课题。
Caspase-3:是一种蛋白酶,1994年Fernandez-Alnemri等在BenBank表达序列标记(expression sequence tag,EST)数据库中找到一段与ICE/CED-3活性中心同源的序列,用它合成探针后,筛选人Jurkat T淋巴细胞cDNA文库,从中克隆到一种新基因,因其编码分子质量为32 ku的半胱氨酸蛋白酶而称之为CPP32 (cysteine protease protein)。随后,其他学者独立地将这一蛋白基因克隆出来,并分别命名为prICE、apopain (凋亡素)和Yama(印度传说中的死亡之神)。1996年这种蛋白酶被命名为caspase-3。现在一般认为caspase-3是细胞凋亡过程中最主要的终末剪切酶,也是CTL细胞杀伤机制的重要组成部分。
文题释义:
发育性髋关节脱位:又称发育性髋关节发育不良及髋发育不全,是较常见的先天性畸形,股骨头在关节囊内丧失其与髋臼的正常关系,以致在出生前及出生后不能正常发育。Hipkocsates早在公元前就描述了该病,之后众多学者对其进行了大量研究,但发育性髋关节脱位的早期诊断和治疗至今仍然是一个尚未完全解决的课题。
Caspase-3:是一种蛋白酶,1994年Fernandez-Alnemri等在BenBank表达序列标记(expression sequence tag,EST)数据库中找到一段与ICE/CED-3活性中心同源的序列,用它合成探针后,筛选人Jurkat T淋巴细胞cDNA文库,从中克隆到一种新基因,因其编码分子质量为32 ku的半胱氨酸蛋白酶而称之为CPP32 (cysteine protease protein)。随后,其他学者独立地将这一蛋白基因克隆出来,并分别命名为prICE、apopain (凋亡素)和Yama(印度传说中的死亡之神)。1996年这种蛋白酶被命名为caspase-3。现在一般认为caspase-3是细胞凋亡过程中最主要的终末剪切酶,也是CTL细胞杀伤机制的重要组成部分。摘要
背景:关节软骨细胞凋亡的异常表达会引起软骨退变,最终发展为骨性关节炎。
目的:观察发育性髋关节脱位模型经过髋关节复位法处理后细胞凋亡相关因子的表达情况。
方法:随机选取28日龄的新西兰大白兔60只,雌雄不限,在兔右后肢屈髋伸膝位时用管型石膏固定8周制作髋关节脱位动物模型,固定的右后肢作为实验组,同只兔的左后肢不做任何处理作为对照组。8周后根据X射线片、髋臼指数、股骨头脱位程度判断造模情况。选取造模成功的48只兔,根据兔右后肢不同的处理方式,将实验组再分为A组(固定8周)、B组(固定10周)、C组(固定8周后解除固定复位2周),每组16只。实验结束后苏木精-伊红染色观察髋臼软骨软骨细胞形态;免疫组织化学法检测软骨细胞中Caspase-3、Bcl-2的表达;TUNEL法检测髋臼软骨中凋亡率的表达水平;并进行相关性分析。
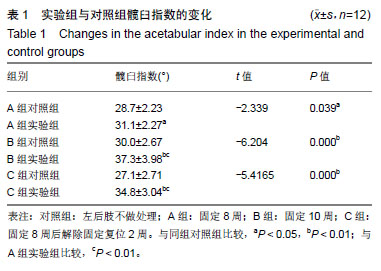
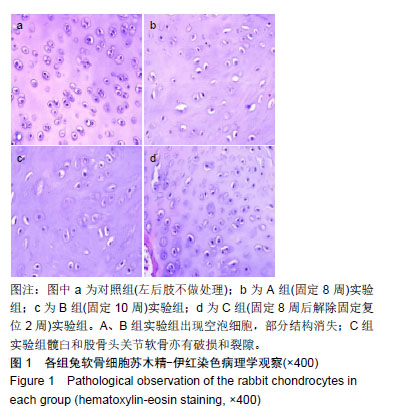
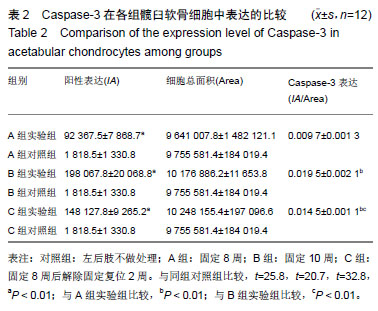
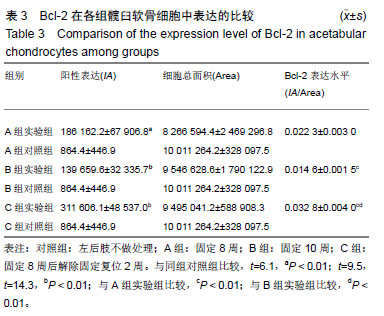
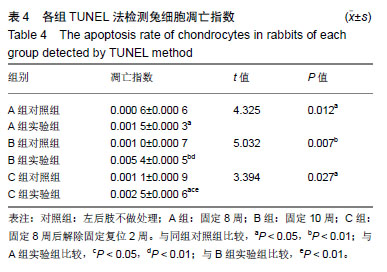
结果与结论:①A、B、C实验组髋臼指数均较其对照组明显增大(P < 0.05);②苏木精-伊红染色后对照组软骨细胞形态规整,A、B实验组出现空泡细胞,部分结构消失,C实验组髋臼和股骨头关节软骨细胞结构较完整,空泡现象较少;③TUNEL结果示C实验组的凋亡率低于B实验组,但高于其对照组(P < 0.05),说明经过复位法处理后凋亡率有所降低;④相关性分析示实验组细胞凋亡率与Caspase-3表达水平呈正相关,与Bcl-2表达水平呈负相关;⑤结果说明,复位组较固定8周、固定10周Bcl-2高表达,凋亡率较固定10周低表达,说明复位处理后软骨细胞凋亡速度放缓,同时凋亡效应蛋白Caspase-3较固定10周低表达,凋亡程度有所降低。复位法可降低髋关节脱位中髋臼软骨细胞凋亡程度的表达水平,延缓软骨进一步退变的进程,从而减缓患者的病情恶化的病程。
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
发育性髋关节脱位:又称发育性髋关节发育不良及髋发育不全,是较常见的先天性畸形,股骨头在关节囊内丧失其与髋臼的正常关系,以致在出生前及出生后不能正常发育。Hipkocsates早在公元前就描述了该病,之后众多学者对其进行了大量研究,但发育性髋关节脱位的早期诊断和治疗至今仍然是一个尚未完全解决的课题。
Caspase-3:是一种蛋白酶,1994年Fernandez-Alnemri等在BenBank表达序列标记(expression sequence tag,EST)数据库中找到一段与ICE/CED-3活性中心同源的序列,用它合成探针后,筛选人Jurkat T淋巴细胞cDNA文库,从中克隆到一种新基因,因其编码分子质量为32 ku的半胱氨酸蛋白酶而称之为CPP32 (cysteine protease protein)。随后,其他学者独立地将这一蛋白基因克隆出来,并分别命名为prICE、apopain (凋亡素)和Yama(印度传说中的死亡之神)。1996年这种蛋白酶被命名为caspase-3。现在一般认为caspase-3是细胞凋亡过程中最主要的终末剪切酶,也是CTL细胞杀伤机制的重要组成部分。
文题释义:
发育性髋关节脱位:又称发育性髋关节发育不良及髋发育不全,是较常见的先天性畸形,股骨头在关节囊内丧失其与髋臼的正常关系,以致在出生前及出生后不能正常发育。Hipkocsates早在公元前就描述了该病,之后众多学者对其进行了大量研究,但发育性髋关节脱位的早期诊断和治疗至今仍然是一个尚未完全解决的课题。
Caspase-3:是一种蛋白酶,1994年Fernandez-Alnemri等在BenBank表达序列标记(expression sequence tag,EST)数据库中找到一段与ICE/CED-3活性中心同源的序列,用它合成探针后,筛选人Jurkat T淋巴细胞cDNA文库,从中克隆到一种新基因,因其编码分子质量为32 ku的半胱氨酸蛋白酶而称之为CPP32 (cysteine protease protein)。随后,其他学者独立地将这一蛋白基因克隆出来,并分别命名为prICE、apopain (凋亡素)和Yama(印度传说中的死亡之神)。1996年这种蛋白酶被命名为caspase-3。现在一般认为caspase-3是细胞凋亡过程中最主要的终末剪切酶,也是CTL细胞杀伤机制的重要组成部分。