中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (28): 4541-4545.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1335
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
仿真分析不同步态下腰椎受力的生物力学变化
邓健全1,陈进军2,梁洪生2,陈小宇2
- 1肇庆医学高等专科学校基础医学部,广东省肇庆市 526020;2肇庆市中医院影像科,广东省肇庆市 526020
Biomechanical changes of lower lumbar spine stress under different gaits by simulation analysis
Deng Jianquan1, Chen Jinjun2, Liang Hongsheng2, Chen Xiaoyu2
- 1Department of Basic Medicine, Zhaoqing Medical College, Zhaoqing 526020, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Imaging, Zhaoqing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhaoqing 526020, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义:有限元分析:其本质是数学求解,它是将复杂区域的形状划分为众多定义明确的元素来求解微分方程。元素与元素累积成方程组,这个方程组可以用迭代法进行数值求解。有限元分析法的优势是能够进行参数化分析和个性化虚拟试验,对比实验研究,计算机仿真有限元分析能够减少经济和社会成本,同时也可以进行真实情况下无法开展试验的模拟研究。
倒退行走:是流行的一种用于治疗腰椎间盘突出症的康复锻炼方法,近年来已经有不少学者研究关于倒退行走的力学特征。虽然研究者们通过临床治疗发现倒退行走锻炼确实对腰椎间盘突出症的治疗有作用,但是并没有对倒退行走治疗腰椎间盘突出症的原理进行探究。
摘要
背景:临床保守治疗易导致腰椎间盘突出症复发,倒退行走是流行的一种用于治疗腰椎间盘突出症的康复锻炼方法。临床指导治疗后患者倒退行走并进行跟踪统计,肯定了倒退行走是一种有效的康复锻炼疗法。
目的:以生物力学为出发点,用有限元的分析法探究倒退行走对腰椎康复治疗的意义。
方法:基于CT图像建立腰椎三维模型,然后模拟腰椎在不同运动状态下的力学环境,并对其进行有限元分析,从生物力学角度探究倒退行走在腰椎间盘突出症治疗中发挥的作用。
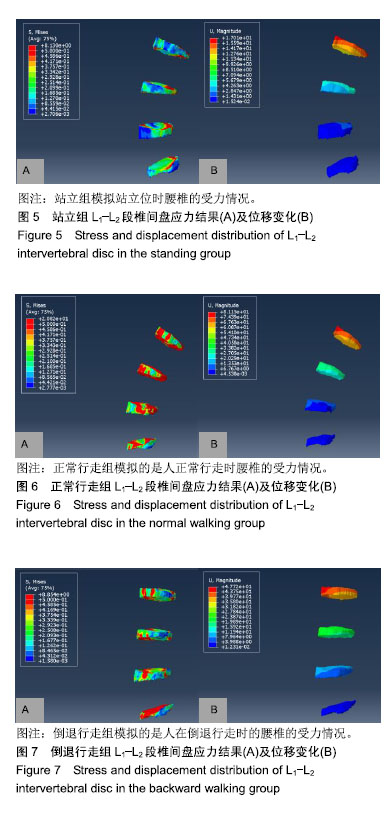
结果与结论:①倒退行走时,L1-L2段椎间盘的位移变化只有步态前进时的1/2,而且椎间盘应力也明显减小;②步态前进时L1-L2段腰椎椎间盘的应力是倒退行走时的2.35倍;③因此腰椎和椎间盘的应力和位移变化都相对于正常步态前进时变小,从而减轻了对髓核的压迫,有助于腰椎间盘突出症患者的恢复。
ORCID: 0000-0001-5931-781X(邓健全)
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: